On this part, you’ll study:
- Screening for most cancers means searching for most cancers or irregular cells which will turn out to be most cancers in individuals who wouldn’t have any indicators of the illness.
- In the US, impartial panels of specialists, convened by the federal government or by skilled organizations, fastidiously consider the advantages and harms of most cancers screening exams earlier than issuing screening suggestions.
- Intensive analysis has proven that routine most cancers screening saves lives.
- Advances in medical analysis are underscoring the potential for synthetic intelligence and minimally invasive screening exams as new frontiers in early detection of most cancers.
- Further analysis is required for early detection of sure most cancers sorts, akin to cancers of the ovary, pancreas, and liver, which have excessive mortality charges however no population-level screening exams.
- Proof-based interventions can improve adherence to really helpful screening pointers however disparities within the uptake of most cancers screening persist.
Most cancers screening means checking for most cancers, or for irregular cells which will turn out to be cancerous, in individuals who don’t have any indicators or signs of the illness. Screening for most cancers in keeping with evidence-based pointers can assist discover aberrations on the earliest attainable detectable part throughout most cancers improvement and development. Well being care suppliers use the data gleaned from a most cancers screening take a look at to make an knowledgeable choice on whether or not to observe or deal with, or surgically take away, precancerous lesions or early-stage most cancers earlier than they progress to a extra superior stage (see Determine 10).
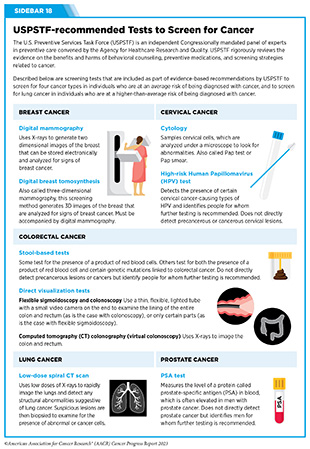
There are completely different sorts of most cancers screening exams that embrace laboratory exams to find out the modifications in most cancers biomarkers in biospecimen samples, and imaging or endoscopic procedures to search for particular abnormalities. In the US, the U.S. Preventive Providers Activity Power (USPSTF), an impartial Congressionally-mandated panel of specialists in preventive care, rigorously critiques the proof on the advantages and harms of behavioral counseling, preventive medicines, and screening methods associated to most cancers (see Sidebar 18).
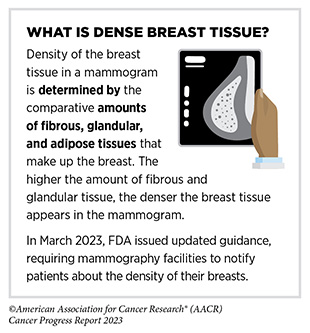
There are different exams past these really helpful by the USPSTF which might be additionally utilized by clinicians for detecting most cancers. As one instance, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is just not a USPSTF-recommended take a look at, and isn’t sometimes used to display screen for breast most cancers. Nevertheless, a breast MRI could also be carried out to additional consider irregular findings on mammograms for individuals with dense breast tissue, which makes it arduous to see irregular areas on mammography (272). Researchers additionally frequently consider the protection and accuracy of latest and improved strategies.
Significance of Most cancers Screening
The overarching aim of most cancers screening is to scale back the burden of most cancers within the common inhabitants. Tips and suggestions have been created to assist people and their well being care suppliers determine collectively whether or not a person ought to be screened for most cancers, at what age the screening ought to begin, how ceaselessly the screening ought to be executed and by which technique, and if and at what age the screening ought to cease.
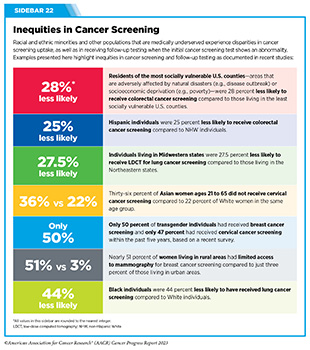
Routine screening goals to catch precancerous lesions or most cancers at an early stage when they are often handled extra successfully, thus decreasing cancer-related deaths (see Determine 10) (274). Accruing proof means that really helpful most cancers screening lowers most cancers mortality. In a current examine, researchers analyzed the speed of lung cancer-related mortality from eight medical trials comprising greater than 90,000 contributors who obtained lung most cancers screening utilizing both the low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) or chest radiography, or who didn’t obtain lung most cancers screening (275). Findings confirmed a 21 % discount in lung cancer-related deaths in contributors who have been screened for lung most cancers utilizing LDCT, in comparison with the opposite two teams. Regardless of the proof of the advantages, uptake of the really helpful lung most cancers screening stays suboptimal amongst eligible people (see Sidebar 22).
It’s equally very important to obtain follow-up testing if the screening take a look at is irregular, which can point out the presence of precancerous lesions or most cancers. There may be sturdy proof that many individuals don’t obtain follow-up testing after a optimistic screening take a look at (see Sidebar 22).
One examine examined information from greater than 32,000 average-risk people who had obtained a optimistic consequence from stool-based screening for colorectal most cancers between 2017 and 2020. Researchers discovered that solely 53.4 % obtained follow-up colonoscopy inside one yr of receiving the optimistic consequence from the preliminary screening take a look at (276). That is unlucky contemplating current information, which present that not receiving the follow-up colonoscopy after a optimistic stool-based take a look at doubles the danger of dying from colorectal most cancers (277). A modeling examine estimated a 16 to 23 % discount in colorectal cancer-related deaths amongst people who adopted up with colonoscopy after a optimistic stool-based take a look at (278). These findings spotlight the significance of receiving follow-up testing after an irregular screening take a look at.
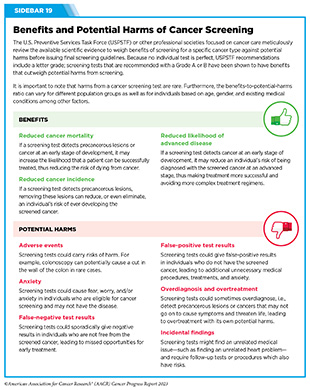
Though dangers and advantages of most cancers screening exams are fastidiously thought of throughout the improvement of screening suggestions, you will need to be aware that screening exams are medical procedures and carry potential harms. It’s thus regarding {that a} current examine discovered that not all most cancers screening suggestions and pointers included potential harms related to screening exams. Researchers reviewed 33 generally used screening pointers from numerous professional panels and located that some harms weren’t talked about in any respect, whereas others have been talked about solely briefly (279). It’s vital that the details about advantages and potential harms of most cancers screening is clearly and simply out there so that individuals could make an knowledgeable and shared choice in session with their well being care suppliers (see Sidebar 19).
Tips for Most cancers Screening
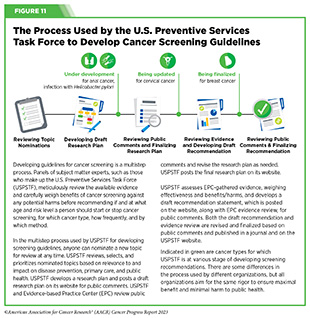
In the US, pointers for most cancers screening are fastidiously developed by teams of material specialists {and professional} societies. For instance, an impartial group of specialists convened by the Company for Healthcare Analysis and High quality of the U.S. Division of Well being and Human Providers fastidiously evaluates information relating to the advantages and potential harms of various approaches to illness prevention, together with most cancers screening exams, genetic testing, and preventive therapeutics, to make evidence-based suggestions about the usage of these in major care settings. These volunteer specialists kind the U.S. Preventive Providers Activity Power (USPSTF). In the course of the improvement of most cancers screening suggestions, USPSTF is supported by researchers from the Proof-based Apply Heart (EPC) program, a U.S. Company for Healthcare Analysis and High quality initiative (see Determine 11).
When growing most cancers screening pointers, material specialists akin to those that make up USPSTF contemplate gender and age, in addition to further traits which might be particular to people or inhabitants teams for whom the screening pointers are being developed. These issues embrace whether or not or not an individual has a specific organ (e.g., for cervical most cancers screening, whether or not a person by no means had a cervix or had a hysterectomy with cervix elimination); has a smoking historical past (e.g., for lung most cancers screening); has an all-negative prior screening historical past (e.g., for cervical most cancers screening); has different health-related points which will cut back life expectancy (e.g., for prostate most cancers screening); and/or has a household historical past of most cancers (e.g., for colorectal and breast most cancers screening).
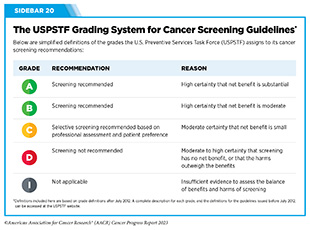
For the finalized pointers, USPSTF assigns a grade to its suggestions (see Sidebar 20). The grade of proof additionally informs which companies are coated with out out-of-pocket prices underneath the Reasonably priced Care Act. The USPSTF can assign completely different grades to completely different inhabitants teams throughout the identical most cancers sort. For instance, a Grade A suggestion is assigned for adults ages 50 to 75 and a Grade B for adults ages 45 to 49 to display screen for colorectal most cancers.
USPSTF steerage for most cancers screening contains recommending for screening sure people at sure intervals (see Sidebar 21); recommending in opposition to screening that has been proven to be dangerous; and deciding that there’s inadequate proof to make a suggestion. For instance, USPSTF not too long ago concluded that there’s inadequate present proof to help visible pores and skin examination as a foundation to display screen average-risk adolescents and adults for pores and skin most cancers (281).
Eligibility for Most cancers Screening
Most cancers screening pointers are developed for people who’re at a median threat of being identified with most cancers, in addition to for many who are at a higher-than-average threat of being identified with most cancers.
Key issues that decide who ought to obtain most cancers screening and for which most cancers embrace gender and age. Further elements thought of for most cancers screening embrace genetic, environmental, behavioral, and social influences. As a result of a few of these elements are completely different for every particular person and should change all through life, the eligibility of a person for most cancers screening may additionally change over time. The choice of whether or not somebody ought to obtain most cancers screening is completely different for every particular person.
Researchers are additionally frequently evaluating accruing proof to advocate modifications to current eligibility standards to display screen for various kinds of most cancers. For instance, research have discovered that even when all those that are eligible for lung most cancers screening underneath the present USPSTF-recommended pointers have been to endure screening, a big proportion of lung cancers will nonetheless be missed (282). One examine of almost 2000 sufferers with lung most cancers discovered that solely 54 % of sufferers would have been deemed eligible for screening underneath the present USPSTF suggestions (283). As extra proof accumulates indicating that current suggestions must be revised, USPSTF and different cancer-focused organizations reevaluate current screening suggestions and make evidence-based changes.
It’s important that individuals empower themselves with probably the most up-to-date info on most cancers screening eligibility by having an ongoing dialogue with their well being care suppliers and develop a customized most cancers screening plan that considers their particular dangers and tolerance of potential harms from screening exams.
These at an Common Threat of Being Recognized with Most cancers
People at common threat of being identified with most cancers are those that wouldn’t have a household historical past of most cancers or private historical past of most cancers, and wouldn’t have an inherited genetic situation that locations them at the next threat of growing most cancers. Two key issues for recommending screening in average-risk people are gender and age. USPSTF recommends that average-risk people ought to obtain routine screening for breast, cervical, and colorectal most cancers once they attain the eligible age (Grades A and/or B suggestions). For prostate most cancers screening, USPSTF recommends that average-risk people ought to have an ongoing dialogue with their well being care supplier to make an knowledgeable and shared choice, once they attain the eligible age (Grade C) (see Sidebar 21).
The chance of growing most cancers will increase with superior age. In keeping with the latest estimates, 88 % of individuals identified with most cancers within the U.S. are 50 or older (28). Subsequently, researchers frequently consider, amongst different elements, the optimum age for beginning or stopping most cancers screening, and professional panels, akin to USPSTF, periodically replace pointers primarily based on the brand new proof.
As one instance, in Could 2023, USPSTF proposed decreasing the really helpful beginning age of screening from 50 to 40 for girls who’re at a median threat of growing breast most cancers. Researchers estimate that the brand new steerage may save 19 % extra lives from breast most cancers (284). Folks ought to talk about most cancers screening throughout routine consultations with their well being care suppliers, and consider their most cancers screening plans in keeping with probably the most up-to-date info.
These at a Larger-Than-Common Threat of Being Recognized with Most cancers
People at a higher-than-average threat of being identified with most cancers are those that have a powerful household historical past of most cancers, a private historical past of most cancers, sure tissue make-up, an inherited genetic situation, or are uncovered to a number of most cancers threat elements, all of which place them at the next threat of growing most cancers. One instance is people who eat tobacco merchandise. In keeping with CDC, individuals who smoke cigarettes are 15 to 30 instances extra prone to develop lung most cancers or die from it than individuals who don’t smoke.
Girls with extraordinarily dense breast tissue are thought of at higher-than-average threat of growing breast most cancers in comparison with ladies with much less dense breast tissue. Due to gaps within the present data, USPSTF doesn’t advocate further screening exams for girls with extraordinarily dense breasts within the not too long ago launched draft assertion of the revised suggestions for breast most cancers screening (284). Nevertheless, different cancer-focused organizations do advocate further screening exams for girls with dense breast tissue (285). Moreover, 38 U.S. states at present require some degree of breast density-related notification after a mammogram, and lots of present expanded insurance coverage protection for extra screening for many who have dense breast tissue (286).
You will need to be aware that extraordinarily dense breast tissue is just one of many threat elements for breast most cancers. Extra analysis is important to find out why ladies with dense breast tissue are at a higher-than-average threat of being identified with breast most cancers and whether or not this information can be utilized to enhance threat prediction fashions for breast most cancers.
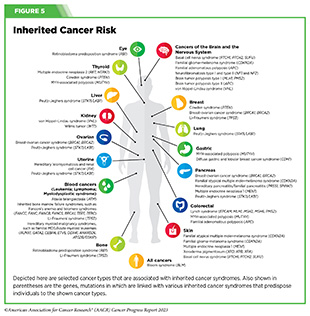
One other group of people at higher-than-average threat of being identified with most cancers is individuals with inherited most cancers susceptibility syndromes (or hereditary most cancers syndromes), that are attributable to genetic mutations that may be handed on from one technology to the subsequent and may predispose a person to develop sure kinds of most cancers (see Determine 5). For instance, people who’ve Lynch syndrome, which is attributable to mutations in genes essential for repairing broken DNA, have an elevated threat of growing colorectal most cancers, endometrial most cancers, ovarian most cancers, and lots of different kinds of most cancers. USPSTF recommends that people with a private or household historical past of Lynch syndrome ought to communicate with their well being care suppliers about acceptable screening choices (288).
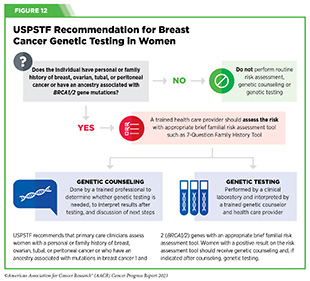
People who contemplate themselves at a excessive threat for an inherited cancer-predisposing genetic mutation ought to, in session with their well being care suppliers, additionally contemplate genetic counseling and testing. Knowledgeable panels typically difficulty pointers for genetic counseling and testing. For instance, in 2019, USPSTF issued suggestions for breast most cancers threat evaluation, genetic counseling and genetic testing for girls with a private or household historical past of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal most cancers or an ancestry related to BRCA1/2 gene mutation (see Determine 12) (289).
Genetic testing might support people and their well being care groups in deciding whether or not, elevated frequency of breast most cancers screening with MRI, preventive surgical procedure (see Supplemental Desk 1), or chemoprevention (e.g., use of selective estrogen receptor modulators) would assist cut back the danger of growing most cancers in a while in life. It’s regarding that solely 6.8 % of greater than 1.3 million individuals had undergone genetic testing, in keeping with a current examine inspecting the extent of germline mutations amongst individuals identified with most cancers (290). It’s crucial that people who’re at a excessive threat for being identified with most cancers due to inherited mutations seek the advice of with their care group for whether or not or when they need to endure genetic testing.
Suboptimal Uptake of Most cancers Screening
Proof reveals that adherence to really helpful most cancers screening saves lives (see Significance of Most cancers Screening). In a current examine, researchers discovered that 80 % of the examine contributors who obtained a prognosis of lung most cancers at an early stage by way of routine lung most cancers screening have been dwelling 20 years after the preliminary prognosis (291). Regardless of the good thing about lung most cancers screening, sadly, solely six % of U.S. people eligible for lung most cancers screening have been updated with the really helpful screening in 2022 (236).
It’s equally essential to know when a person ought to cease screening for most cancers. USPSTF suggestions embrace the age previous which the potential harms from screening exams are prone to outweigh advantages (see Sidebar 20). For instance, USPSTF pointers advocate in opposition to screening for prostate most cancers in males older than 69. Nevertheless, a current examine discovered that 55.3 % of males ages 70 to 74, 52.1 % of males ages 75 to 79, and 39.4 % of males age 80 and older have been screened for prostate most cancers in 2020 (292).
Suboptimal adherence to really helpful most cancers screening pointers is obvious throughout most cancers sorts, and researchers are frequently working to develop evidence-based approaches to extend adherence to most cancers screening pointers (see Progress Towards Rising Adherence to Most cancers Screening Tips). The COVID-19 pandemic has additional adversely impacted most cancers screening charges (293). A current examine evaluating the influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on most cancers screening discovered that, in the US between 2019 and 2021, screening inside a previous yr decreased from 60 % to 57 % for breast most cancers, from 45 % to 39 % for cervical most cancers, and from 39.5 % to 36 % for prostate most cancers (259).
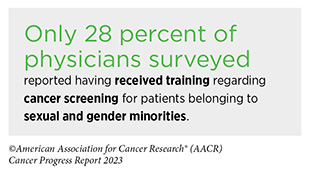
One other space of main concern is the inequities in most cancers screening and follow-up testing amongst sure U.S. inhabitants teams (see Sidebar 2). For instance, in comparison with the general U.S. inhabitants, most cancers screening charges are decrease amongst sure racial and ethnic in addition to sexual and gender minorities (see Sidebar 22) (293). A large number of limitations contribute to low screening charges, together with social and structural limitations; bias and discrimination in opposition to minorities within the well being care system; distrust of well being care professionals amongst minorities; lack of entry to high quality medical health insurance and protection; low well being literacy; and miscommunication between sufferers and suppliers (13).
You will need to absolutely perceive why people belonging to sure inhabitants teams are at the next threat of being identified with sure kinds of most cancers, and whether or not suboptimal uptake of screening contributes to this larger threat. Moreover, there may be an pressing want to gather disaggregated information associated to all points of most cancers burden and medical care from people belonging to racial and ethnic minorities, sexual and gender minorities, and others who’re socially and economically deprived, together with individuals who belong to multiple of those populations, as detailed within the AACR Most cancers Disparities Progress Report 2022 (13). Proof gathered from such information will assist with growing most cancers care pointers and interventions to enhance care supply that’s tailor-made to particular populations, which can result in well being fairness for all.
Progress Towards Rising Adherence to Most cancers Screening Tips
Multilevel and multipronged approaches are required to get rid of most cancers well being inequities throughout the continuum of care, together with uptake and follow-up of really helpful evidence-based most cancers screening amongst all eligible people (see Sidebar 23). Stakeholders throughout the most cancers care continuum (see Sidebar 1) are working collectively to realize these targets.
In the US, the Neighborhood Preventive Providers Activity Power (CPSTF), established by the U.S. Division of Well being and Human Providers in 1996 at CDC, develops steerage on community-based well being promotion and illness prevention. Based mostly on the out there scientific proof, CPSTF periodically points suggestions and findings on public well being interventions designed to enhance well being and security. As one instance, CPSTF not too long ago reviewed 34 research evaluating the effectiveness of affected person navigation in rising most cancers screening uptake amongst racial and ethnic minority populations and other people with decrease incomes (303). Based mostly on the findings, CPSTF really helpful within the 2022 Annual Report back to Congress that affected person navigation companies ought to be supplied to medically underserved communities to extend breast, cervical, and colorectal most cancers screening (304). The Activity Power concluded that affected person navigation companies advance well being fairness. Affected person navigation additionally improves well timed and acceptable follow-up care and remedy, and should enhance well being and cut back cancer-related disparities for the racial and ethnic populations and other people with decrease incomes who’re medically underserved.
Recognizing the vital significance of standard most cancers screening in saving lives, the Nationwide Most cancers Plan, launched by NCI in April 2023, prioritizes early most cancers detection and most cancers prevention (309). The plan calls for brand spanking new applied sciences and strategies to detect cancers early, particularly cancers for which no screening exams exist at present (akin to cancers of the liver and pancreas), and to get rid of precancerous lesions earlier than they turn out to be cancerous whereas minimizing unwanted side effects.
New Frontiers in Most cancers Screening
Researchers are engaged on novel strategies and methods which will enhance detection of early cancers and/or precancerous lesions to scale back the demise fee from most cancers, whereas minimizing any potential hurt from the process. Two areas of analysis with thrilling new developments are the usage of synthetic intelligence and blood-based exams to detect most cancers early.
Realizing the Potential of Synthetic Intelligence for Early Detection of Cancers
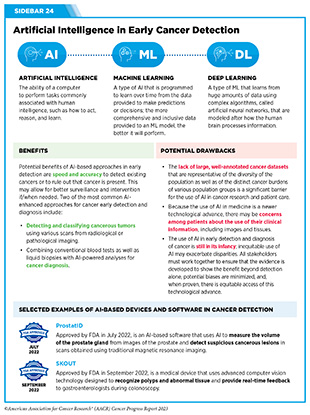
There have been unprecedented advances lately in the usage of synthetic intelligence (AI) and machine studying (ML) in medication, together with for most cancers detection. One of many a number of methods researchers are utilizing AI and ML for most cancers detection is in analyzing giant quantities of imaging information collected for the needs of most cancers screening to acknowledge patterns which might be in any other case time-consuming and tough to discern by eye even by skilled well being care professionals (see Sidebar 24).
A current examine discovered that AI-assisted colonoscopy detected 21 % extra polyps (clumps of normally benign cells that construct up on the liner of the colon and may be precursors to colon most cancers) in comparison with a traditional expert-directed colonoscopy (310). One other examine described the event of a deep studying mannequin that may predict future threat of growing lung most cancers throughout the subsequent one to 6 years following a single LDCT scan (311). You will need to be aware that making use of AI in medication is an space of energetic analysis and never all research have discovered AI-assisted enhancements in most cancers detection (312). Further analysis is required to know the good thing about AI-driven purposes in most cancers medication and whether or not AI mitigates or worsens well being disparities.
A number of the AI-driven medical units and software program have confirmed to be extremely correct in medical trials when in comparison with present normal practices. In recent times, the variety of FDA-approved AI-enhanced software program techniques to be used in medication, together with early detection, has elevated considerably (315). Right here, we’re utilizing two current examples—ProstatID and SKOUT—to focus on the progress on this thrilling space of most cancers analysis.
In July 2022, FDA accepted ProstatID, which makes use of AI to measure the amount of the prostate gland from scans obtained utilizing conventional MRI and detect suspicious cancerous lesions. ProstatID is accepted to be used in a well being care facility or hospital to help skilled radiologists within the detection and characterization of probably cancerous lesions utilizing MRI information. The approval was, partially, primarily based on two medical research exhibiting improved detection of prostate most cancers and fewer false positives when radiologists used ProstatID.
In September 2022, FDA accepted SKOUT, a medical system that makes use of superior pc imaginative and prescient expertise designed to acknowledge polyps and suspicious tissue and supply real-time suggestions to clinicians throughout colonoscopy. The approval was primarily based on outcomes from a big medical examine exhibiting that detection of polyps and suspicious lesions was considerably improved when colonoscopy was aided with SKOUT in comparison with normal colonoscopy with out the help of SKOUT (719 versus 562 detections, respectively). The improved detection was much more pronounced for smaller polyps (44 % improve when utilizing SKOUT versus 29 % improve when utilizing normal colonoscopy) (313).
Examples of current FDA approvals mentioned right here underscore the potential purposes of AI within the clinic to help early detection and diagnostic functions. Makes use of of AI in different points of most cancers care—genomic characterization of tumors, drug discovery, and improved most cancers surveillance—are additionally energetic areas of analysis (see Synthetic Intelligence) (316).
Shifting Towards Minimally Invasive Most cancers Screening
Most most cancers screening exams in present use are designed to detect just one sort of most cancers. A number of the exams are invasive medical procedures, with potential well being dangers (see Sidebar 19). Researchers are actively working to develop methods to detect most cancers utilizing exams which might be much less invasive and safer. Liquid biopsy is one such means wherein a pattern of blood, urine, or different physique fluid is used to search for indicators of most cancers.
Because of analysis, the data that precancerous lesions and tumors shed a wide range of supplies (akin to most cancers cells and small items of DNA, RNA, or proteins) has led to the event of exams that may detect these supplies in blood, urine, or different physique fluids. Liquid biopsy approaches are already in routine use for making remedy selections and/or monitoring if most cancers has returned in sufferers who’ve already obtained most cancers remedy, and may be particularly helpful for pediatric sufferers with most cancers (317)(318).
Liquid biopsy procedures can detect irregular cells and/or different supplies from tumors which might be circulating within the blood. It’s vital that liquid biopsy exams are extremely particular in detecting cancer-derived modifications which might be absent in wholesome cells earlier than these exams may be really helpful for most cancers screening within the common inhabitants (319). Ongoing efforts are targeted on growing methods to make sure that liquid biopsy exams are particular in detecting most cancers(s) with out compromising sensitivity of the take a look at (320).
An thrilling facet of liquid biopsy exams is the opportunity of screening for a lot of most cancers sorts concurrently and probably with excessive specificity. If these procedures, referred to as multicancer detection (MCDs) assays or multicancer early detection exams, are discovered to be efficient, they could make receiving most cancers screening simpler for people. These exams may additionally lower potential bodily hurt(s) from a number of the typical most cancers screening exams, akin to colonoscopy. Moreover, a minimally invasive take a look at that can be utilized to display screen for a number of most cancers sorts may rework early detection of cancers; probably improve participation in most cancers screening; and should lower some present limitations to most cancers screening.
An ongoing examine is evaluating the specificity and accuracy of an MCD take a look at for greater than 50 kinds of most cancers. Findings up to now present that the take a look at appropriately recognized two out of each three cancers in additional than 5,000 individuals who had visited their well being care suppliers with suspected signs. The take a look at additionally appropriately recognized the location from which most cancers originated in 85 % of these circumstances (321). A current modeling examine utilizing the most cancers mortality information from England estimated that utilizing MCDs would lead to 17 % fewer deaths from most cancers per yr (322).
You will need to be aware that the analysis evaluating the protection and efficacy of MCD exams for routine most cancers screening is at an early stage. Whereas the preliminary research are encouraging, at present there are restricted information from potential medical research (319)(320). Key points that stay unresolved embrace whether or not MCD exams can detect early levels of a number of most cancers sorts precisely; what would be the fee of false optimistic outcomes; whether or not utilizing an MCD take a look at will present advantages that outweigh potential harms; and the way a lot these exams will value. Massive ongoing research, akin to NCI’s Vanguard Trial, will reply a few of these critically essential questions.
Subsequent Part: Advancing the Frontiers of Most cancers Science and Medication