Identification of noncoding regulatory variants impacting the pharmacogenomics of ALL therapy
Single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) impacting numerous pharmacological traits in ALL have been recognized for useful interrogation. We selected SNVs related to relapse or persistence of MRD after induction chemotherapy in childhood ALL sufferers to research the function of inherited noncoding regulatory variants impacting medical phenotypes (i.e., therapy consequence). These SNVs have been recognized from revealed GWAS of ALL sufferers enrolled in St. Jude Youngsters’s Analysis Hospital and the Youngsters’s Oncology Group medical protocols3,4,5 (see Strategies for variant choice standards). Variant choice additionally included prioritization for therapy consequence SNVs related to drug resistance phenotypes in major ALL cells to counterpoint for variation impacting ALL cell biology (see Strategies for variant choice standards). These therapy outcome-associated variants, in addition to all variants in excessive LD (r2 > 0.8) with the sentinel GWAS variants, have been additional evaluated (Fig. 1a, b).
a SNVs of curiosity from GWAS have been pursued primarily based on affiliation with ex vivo chemotherapeutic drug resistance in major ALL cells from sufferers and/or therapy consequence. Dex dexamethasone, Pred prednisolone, VCR vincristine, 6MP 6-mercaptopurine, 6TG 6-thioguanine, LASP L-asparaginase. b GWAS SNVs have been mixed with ALL illness susceptibly management GWAS SNVs and SNVs in excessive LD (R2 > 0.8) and c mapped to accessible chromatin websites in ALL cell strains, ALL PDXs, and first ALL cells from sufferers. Of the 1696 SNVs mapped to accessible chromatin websites, 35 are management SNVs. Supply knowledge are supplied within the Supply Knowledge file.
We additionally recognized variants straight related to ex vivo chemotherapeutic drug resistance in major ALL cells from sufferers by performing GWAS analyses utilizing SNV genotype info and ex vivo drug resistance assay outcomes for six antileukemic brokers (prednisolone, dexamethasone, vincristine, L-asparaginase, 6-mercaptopurine [6MP] and 6-thioguanine [6TG]) in major ALL cells from 312–344 sufferers (not all sufferers have been examined for all medicine) enrolled within the Complete Remedy XVI medical protocol at St. Jude Youngsters’s Analysis Hospital (see Strategies). We additional prioritized useful ex vivo drug resistance SNVs by figuring out in the event that they have been eQTLs in major ALL cells or associated cell varieties (i.e., entire blood and EBV-transformed lymphocytes) from the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) consortium37 (see Strategies for variant choice standards). Ex vivo drug resistance variants that have been additionally recognized as eQTLs, in addition to variants in excessive LD (r2 > 0.8) with these sentinel GWAS variants, have been additional evaluated (Fig. 1a, b).
GWAS have additionally been carried out for childhood ALL illness susceptibility and recognized a number of GWAS loci harboring variants with genome-wide significance44,45,46,47,48,49,50. A number of follow-up research of those GWAS loci have recognized candidate causal noncoding variants and mechanisms involving gene regulatory disruptions51,52,53. In consequence, we used ALL illness susceptibility variants (n = 11), in addition to variants in excessive LD (r2 > 0.8) with them, for additional evaluation as constructive controls in our examine (Fig. 1a, b).
As a result of most of those variants map to noncoding parts of the human genome, these knowledge level to disruptions in gene regulation because the underlying mechanism of how these variants affect ALL cell biology. We due to this fact utilized assay for transposase-accessible chromatin with high-throughput sequencing (ATAC-seq)54 chromatin accessibility knowledge in 161 ALL cell fashions, comprised of major ALL cells (cryopreserved, n = 2455; contemporary, n = 12056), ALL cell strains (n = 14) and ALL patient-derived xenografts (PDXs, n = 3), to uncover which variants map to putative CREs in ALL cells57 (i.e., regulatory variants; Fig. 1c). Though we detected variation in ATAC-seq TSS enrichment scores and peak counts that’s to be anticipated from such a big, blended cohort of ALL cell fashions, the peaks known as have been largely reproducible (present in >3 samples) inside every group (Supplementary Fig. 1a–c). ATAC-seq knowledge from major ALL cells, ALL cell strains, and PDXs have been mixed and recognized 1696 regulatory variants at accessible chromatin websites in ALL cells for useful investigation (Fig. 1c and Supplementary Knowledge 1).
Assessing the affect of regulatory variation on transcriptional output utilizing MPRA
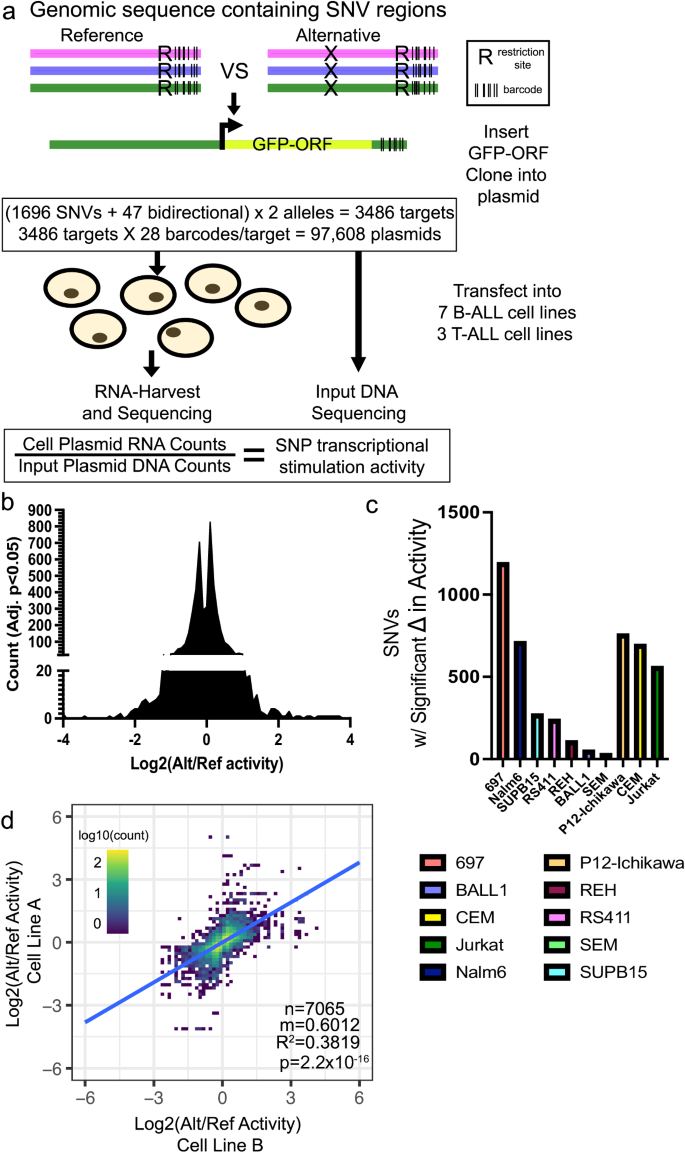
To look at the useful results of those 1696 regulatory variants on transcriptional output in a high-throughput method we utilized a barcode-based MPRA platform29,32 to measure variations in allele-specific transcriptional output (Fig. 2a). Oligonucleotides containing 175-bp of genomic sequence centered on every reference (ref) or various (alt) variant allele, a restriction website, and a singular 10-bp barcode sequence have been cloned into plasmids. An open studying body containing a minimal promoter driving GFP was then inserted on the restriction website between the alleles of curiosity and their distinctive barcodes (Fig. 2a). We utilized 28 distinctive 3′UTR DNA barcodes per variant allele (56 barcodes per regulatory variant), and variants close to bidirectional promoters (47 whole variants) have been examined utilizing each sequence orientations. In whole, 97,608 variant-harboring oligonucleotides have been evaluated for allele-specific variations in gene regulatory exercise (Fig. 2a).
a Diagram describing design of MPRA (additionally see Strategies). b–d Vital MPRA hits have been recognized by Benjamini–Hochberg FDR corrected two-tailed College students T assessments. b Distribution of serious modifications in allele-specific transcriptional exercise throughout all SNVs. c Variety of MPRA SNVs displaying vital (Adj. p < 0.05) modifications in allele-specific transcriptional exercise in every ALL cell line. d Pairwise linear correlation between modifications in allele-specific transcriptional exercise for all vital (Adj. p < 0.05) modifications throughout all cell strains. R2 correlation and p worth are supplied. All supply knowledge and statistical parameters are supplied within the Supply Knowledge file.
Following transfection into 7 totally different B-cell precursor ALL (B-ALL; 697, BALL1, Nalm6, REH, RS411, SEM, SUPB15) and three T-cell ALL (T-ALL; CEM, Jurkat, P12-Ichikawa) human cell strains (n = 4 transfections per cell line; 40 whole), the transcriptional exercise of every allele variant was measured by high-throughput sequencing to find out the barcode illustration in reporter mRNA and in comparison with DNA counts obtained from high-throughput sequencing of the MPRA plasmid pool (Fig. 2a). Within the 10 cell strains MPRA detected 4633 cases of serious differential exercise between alleles throughout 91% (1538/1696) of regulatory variants examined (Fig. 2b, c, Supplementary Knowledge 2). The ten ALL cell strains confirmed substantial variations within the whole variety of regulatory variants harboring vital allele-specific exercise, which we suspect largely stems from variations in transfection effectivity (Fig. 2c). Importantly, when evaluating modifications in allele-specific MPRA exercise for every regulatory variant we discovered that vital modifications in exercise (adj. p < 0.05) have been extremely correlated between ALL cell strains, with 87% concordance in allelic-specific exercise, suggesting that vital MPRA hits have been prone to be strong and reproducible between cell strains (Fig. second). Allele-specific MPRA actions have been additionally correlated utilizing all pairwise cell line comparisons for every regulatory variant, no matter significance (Supplementary Fig. 2a). Importantly, 31 of the 35 constructive management variants (i.e., ALL illness susceptibility-associated variants and variants in excessive LD) confirmed vital allelic results in a minimum of 1 cell line, and 10 confirmed vital and concordant allelic results in a minimum of three ALL cell strains, together with two variants (rs3824662 at GATA3 locus and rs75777619 at 8q24.21) straight related to ALL susceptibility44,49,52 (Supplementary Knowledge 2). The chance A allele at rs3824662 was related to larger GATA3 expression and chromatin accessibility and demonstrated considerably larger allele-specific exercise in our MPRA44,52, thereby demonstrating that the MPRA might detect allelic results beforehand recognized by others.
To additional validate MPRA hits in an ex vivo mannequin, we carried out MPRA utilizing two B-ALL PDX samples that have been freshly harvested from mice. These samples detected 26 and 67 vital gene regulatory variants, respectively, and confirmed vital correlation with the cell line MPRA knowledge (Supplementary Fig. 2b, c, Supplementary Knowledge 3). We attribute the detection of comparatively decrease numbers of variants in PDXs to technical results stemming from poor transfection effectivity and restricted cell survival ex vivo. General, our knowledge counsel that the cohort of SNVs examined contained useful regulatory variants with the potential to affect gene regulation.
Identification of useful regulatory variants displaying reproducible and concordant modifications in allele-specific gene expression
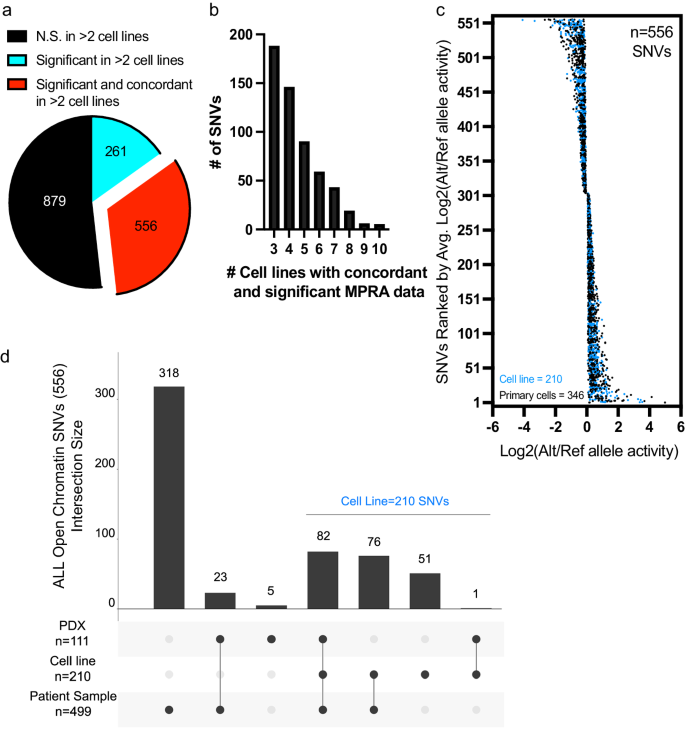
To additional concentrate on regulatory variants almost certainly to broadly affect gene regulation in ALL cells, we prioritized 556 variants with vital (adj. p < 0.05) and concordant allele-specific actions in a minimum of three ALL cell strains (i.e., useful regulatory variants; Fig. 3a–d, Supplementary Knowledge 4). Most of those useful regulatory variants (318/556) mapped to accessible chromatin discovered solely in major ALL cell samples, underscoring the significance of incorporating chromatin structure from major ALL cells, and 54 useful regulatory variants mapped to transcription issue footprints in major ALL cells (Supplementary Fig. 3). Moreover, we used Genomic Areas Enrichment of Annotations Software (GREAT) to affiliate these SNVs with their close by genes and seek for enrichment in gene ontology organic processes pathways58. Though GREAT recognized gene associations for almost all SNVs, we discovered no vital pathway associations (Supplementary Knowledge 4 and 5). As a result of additional useful investigation of variants in major ALL cells or PDXs ex vivo is basically intractable, we centered on 210 useful regulatory variants that have been detected in open chromatin in one of many 14 ALL cell strains that we had generated ATAC-seq knowledge (Fig. 3d). Most of those variants (159/210; 76%) have been additionally present in accessible chromatin in PDXs and/or in major ALL cells from sufferers (Fig. 3d).
a 556 of the 1696 SNVs assayed are useful regulatory variants with reproducible (FDR < 0.05 in >2 cell strains) and concordant (similar directionality in >2 cell strains) modifications in allele-specific exercise. b Frequency distribution plot displaying the variety of cell samples displaying concordant and vital MPRA exercise of variants. c Plot displaying the distribution of log2-adjusted exercise between various (Alt) and reference (Ref) alleles throughout 556 useful regulatory variants. 210 SNVs (in blue) mapped to accessible chromatin websites in ALL cell strains and 346 SNVs (in black) mapped solely to accessible chromatin websites recognized in major ALL cells and/or PDXs. d Upset plot reveals what number of useful regulatory variants map to open chromatin in numerous ALL cell fashions. 210 of the 556 useful regulatory variants are present in accessible chromatin websites that have been recognized in an ALL cell line. Supply knowledge are supplied within the Supply Knowledge file.
For added validation utilizing conventional luciferase reporter assays, we prioritized these 210 useful regulatory variants primarily based on allele-specific impact measurement and chosen high-ranking SNVs. Twin-luciferase reporter assays confirmed related allele-specific modifications in exercise to that which was detected by MPRA for 7 SNVs examined (Supplementary Fig. 4a–ok). The truth is, a big constructive correlation (p = 0.0017) was noticed between the allelic results detected by MPRA and luciferase reporter assays (Supplementary Fig. 4l). Collectively, these analyses assessed the robustness of our MPRA display of useful regulatory variants and recognized 556 SNVs with reproducible and concordant allele-specific results on gene regulation. Importantly, 210 of the 556 vital hits that have been concordant in a minimum of three cell strains have been present in open chromatin websites in ALL cell strains and, due to this fact, warranted additional exploration.
Affiliation of useful regulatory variants with putative gene targets
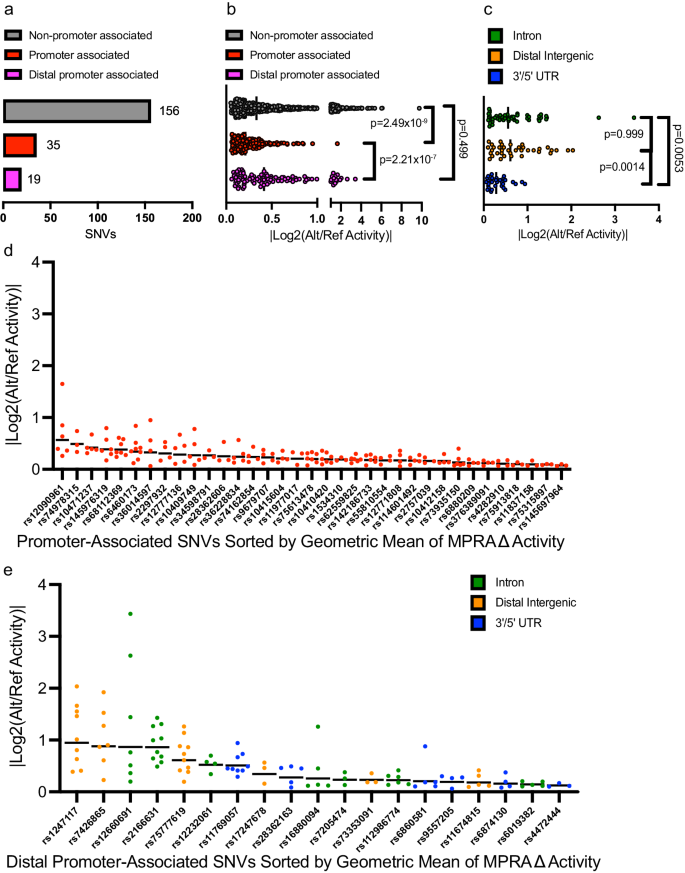
To higher perceive how these variants affect mobile phenotypes, we first decided if the 210 useful regulatory variants present in accessible chromatin websites in ALL cell strains may very well be straight related to a goal gene. Whereas 35 useful regulatory variants have been localized shut (±2.5 kb) to close by promoters (Fig. 4a, Supplementary Knowledge 4 and 6), 175 variants have been promoter-distal (>2.5 kb), and due to this fact prone to map to CREs with unclear gene targets (Fig. 4a). Whereas CREs are sometimes related to the closest genes, 3D chromatin looping strategies are a extra dependable technique to affiliate a CRE with its goal gene promoter. In pursuit of evidence-based affiliation of promoters and particular CREs, we carried out two associated chromatin looping strategies, H3K27Ac HiChIP59 and promoter seize HiC (CHiC)39, in 8 of 10 ALL cell strains utilized in MPRA and decided that 19 of the 175 non-promoter useful regulatory variants confirmed connectivity to distal promoters in the identical cell line the place allele-specific MPRA exercise and chromatin accessibility have been detected (Fig. 4a, Supplementary Knowledge 6). Curiously, H3K27Ac HiChIP and promoter CHiC known as related numbers of loops throughout all 8 cell strains (690,579 versus 660,313, respectively), however promoter CHiC loop calling was extra constant per cell line (Supplementary Fig. 5, Supplementary Knowledge 7). HiChIP detected no looping at any of the 556 reproducible and concordant SNVs from the MPRA, and the 19 SNVs displaying connectivity to a promoter have been solely detected by promoter CHiC, additional highlighting the utility of this technique in GWAS-oriented research41,60,61,62,63.
a Knowledge present the variety of useful regulatory variants mapping to open chromatin in cell strains that affiliate straight with promoters (inside 2.5 kb) or which might be distally promoter-connected by way of promoter CHiC. b MPRA knowledge present distal regulatory variants in accessible chromatin (some promoter-connected by promoter CHiC knowledge) exhibit stronger results on allele-specific exercise than promoter-associated useful regulatory variants. ANOVA with Kruskal–Wallis take a look at was carried out with Dunn’s correction for a number of comparisons. c Amongst distally promoter-connected useful regulatory, variants that map to intronic and distal intergenic sequences confirmed higher exercise than these in UTRs. ANOVA with Kruskal–Wallis take a look at was carried out with Dunn’s correction for a number of comparisons. d, e Knowledge present the ranked allele-specific exercise distribution of MPRA knowledge for d promoter-associated useful regulatory variants and e distally promoter-connected useful regulatory variants. All supply knowledge and statistical parameters are supplied within the Supply Knowledge file.
In prioritizing useful regulatory variants, we have been within the gene regulatory affect of variants at TSS-proximal promoter-associated versus TSS-distal promoter-connected CREs as measured by MPRA. Curiously, we discovered that SNVs discovered at TSS-distal open chromatin websites, promoter-associated or not, confirmed larger allele-specific modifications in MPRA exercise than these at promoters (Fig. 4b). Whereas we acknowledge that lots of the 156 variants for which we didn’t detect a relationship with a promoter are prone to have significant gene targets, we centered on CREs containing variants with recognized gene targets in ALL cells for useful validation. Amongst the TSS-distal promoter-connected useful regulatory variants, we discovered that distal intergenic and intronic SNVs confirmed considerably larger allele-specific exercise than these in UTRs (Fig. 4c). These knowledge counsel that essentially the most strong allelic results attributable to those regulatory variants are prone to happen at distal intergenic and intronic websites >2.5 kb from the TSS of the goal gene.
Subsequent, we ranked TSS-proximal promoter-associated and TSS-distal promoter-connected useful regulatory variants by the geometric imply of their vital MPRA knowledge to account for the magnitude of allele-specific exercise and the reproducibility of a big change throughout ALL cell strains (Fig. 4d, e). This evaluation recognized rs1247117 as essentially the most strong useful regulatory variants, which we then pursued for mechanistic understanding (Fig. 4e).
rs1247117 determines genomic accessibility, PU.1 binding, and EIF3A expression
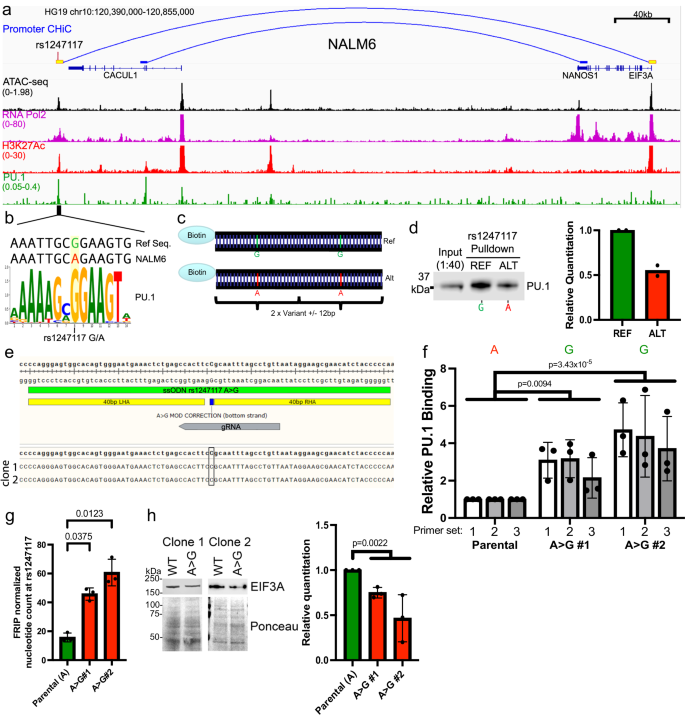
We pursued useful validation of rs1247117 primarily based on its highest-ranking geometric imply of MPRA allelic impact. rs1247117 is in excessive LD with two GWAS sentinel variants (rs1312895, r2 = 0.99; rs1247118, r2 = 1) which might be related to persistence of MRD after induction chemotherapy3. This useful regulatory variant maps to a distal intergenic area harboring chromatin accessibility downstream of the CACUL1 gene, for which it’s an eQTL in EBV-transformed lymphocytes37. Nevertheless, we discovered that rs1247117 loops to the EIF3A promoter in Nalm6 B-ALL cells (Fig. 5a). We, due to this fact, explored how this accessible chromatin website may recruit transcriptional regulators that might rely on the allele current at rs1247117. For this, we first carried out ChIP-seq for RNA pol II and H3K27Ac, which confirmed RNA Pol II occupancy and H3K27Ac enrichment in Nalm6 cells, indicating that rs1247117 is related to an energetic CRE (Fig. 5a). By an examination of the underlying DNA sequence spanning rs1247117, we discovered that the reference guanine (G) danger allele at rs1247117 resides in a PU.1 transcription issue binding motif that’s disrupted by the choice adenine (A) allele (Fig. 5b). Though the danger G allele is the reference allele, the choice A allele is extra frequent in human populations. Supporting PU.1 binding at this location, accessible chromatin profiling in major ALL cells recognized an accessible chromatin website and PU.1 footprint spanning rs1247117 in numerous ALL samples (Supplementary Fig. 6a, b). Considerably higher chromatin accessibility at rs1247117 was additionally noticed in heterozygous (GA) affected person samples in comparison with affected person samples homozygous for the choice A allele (Supplementary Fig. 6c), and the G allele at rs1247117 harbored considerably higher ATAC-seq learn rely in comparison with the A allele (Supplementary Fig. 6d). Importantly, we decided that PU.1 was sure at this website in Nalm6 cells utilizing CUT and RUN64 (Fig. 5a).
a IGV genome browser picture in Nalm6 cells displaying the genomic context, chromatin accessibility, and EIF3A promoter connectivity utilizing promoter CHiC of the highest useful regulatory variant, rs1247117, with the very best allele-specific MPRA exercise. Genomic binding profiles are additionally proven for RNA polymerase II (RNA Pol2), histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27Ac), and PU.1. b rs1247117 lies in a PU.1 binding motif. The human genome reference sequence, Nalm6 genome sequence, location of rs1247117, and PU.1 place weight matrix are proven. c Design of biotinylated DNA probes for in vitro rs1247117 pulldown. d Biotinylated DNA pulldown reveals rs1247117 allele-dependent enrichment of PU.1 binding. Blot proven is consultant of two unbiased experiments. Densitometric quantification of two blots is proven. e CRISPR/Cas9 was used to alter the allele at rs1247117 from A > G in Nalm6 cells. Knowledge present the situation of gRNA and ssODN, in addition to NGS reads obtained from clone 1 and a pair of at rs1247117. f PU.1 ChIP-PCR reveals elevated PU.1 binding on the rs1247117 locus utilizing two A > G modified clones and three primer units. Knowledge proven are imply ± SD of three unbiased experiments for every primer set. Two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s a number of comparisons correction, n = 3. g ATAC-seq knowledge normalized for frequency of reads in peaks (FRIP) present a considerably larger rely of G nucleotides in two clones of A > G modified Nalm6 cells in comparison with the rely of A nucleotides detected in parental Nalm6 cells. Knowledge proven are the imply ± SD. Bonferroni corrected, two-tailed Pupil’s T assessments, n = 3. h Western blots and quantification displaying decreased EIF3A expression in A > G modified Nalm6 cells. Blots proven are consultant of three unbiased experiments. Quantification knowledge proven are the imply ± SD. Two-tailed Pupil’s T assessments evaluate parental Nalm6 to mixed knowledge from A > G clones, n = 3. All supply knowledge and statistical parameters are supplied within the Supply Knowledge file.
Nalm6 cells include the choice A allele that disrupts the PU.1 motif at rs1247117, but our knowledge means that this website nonetheless binds PU.1 (Fig. 5a, b). This led us to hypothesize that PU.1 binding affinity for the PU.1 motif surrounding rs1247117 can be strengthened by the danger G allele. Due to this fact, we designed biotinylated DNA probes containing two tandem 25-bp areas centered on reference G or various A allele-containing rs1247117 to check this speculation (Fig. 5c). Utilizing biotinylated probes, we carried out an in vitro DNA-affinity pulldown from Nalm6 nuclear lysate and located that whereas PU.1 was certainly sure to the choice A allele, PU.1 was extra robustly sure to the reference G allele at rs1247117 (Fig. 5d). To additional assess the affect of the rs1247117 allele on PU.1 binding, we modified the Nalm6 allele from A to G utilizing CRISPR/Cas9 (Fig. 5e; AA = parental genotype, GG = mutated genotype). We used ChIP-PCR to find out that PU.1 binding was elevated with the G allele relative to the A allele on the CRE containing rs1247117 in two A > G Nalm6 clones throughout 3 distinctive primer units throughout the PU.1 peak at rs1247117 that was detected in Nalm6 cells (Fig. 5f). We then requested if transposase accessibility was additionally elevated on the CRE containing rs1247117 when the G allele was current. Utilizing ATAC-seq, we discovered that accessibility was certainly elevated at rs1247117 in mutated Nalm6 cells with the G allele when in comparison with the parental Nalm6 cells containing the A allele (Fig. 5g). These knowledge counsel that the danger G allele will increase genomic accessibility and the affinity of PU.1 binding at rs1247117 relative to the choice A allele.
We have been subsequent curious about how allele-specific PU.1 binding at rs1247117 was associated to the expression of the protein encoded by the related gene, EIF3A. We discovered that the G allele, which elevated recruitment of PU.1, resulted in decreased expression of EIF3A when in comparison with Nalm6 cells with the A allele (Fig. 5h). These knowledge counsel that PU.1 recruitment to the CRE containing rs1247117 leads to a net-repressive impact on EIF3A protein ranges, and that much less PU.1 recruitment with the A allele leads to higher EIF3A expression.
Deletion of CREs containing high MPRA SNVs demonstrates their affect on drug sensitivity
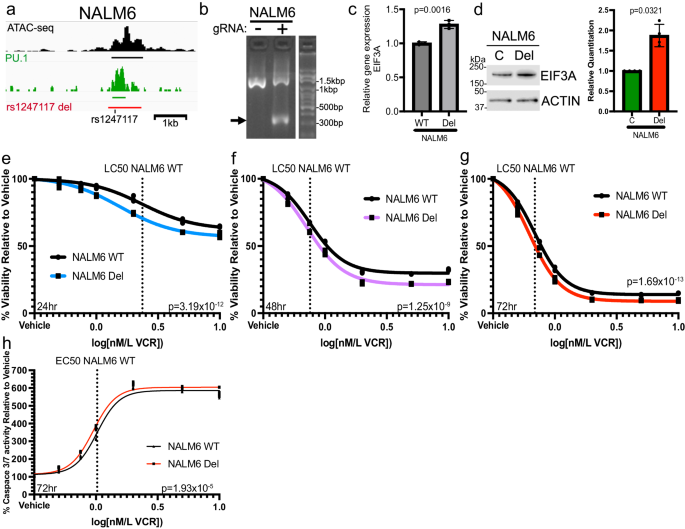
Clonal choice can result in the buildup of random SNVs and even bigger structural variations65 that may confound useful interpretation of extra complicated trans phenotypic results. Due to this fact, to look at the connection between rs1247117 and the persistence of MRD after induction chemotherapy, we determined to make use of CRISPR/Cas9 to delete the CRE containing rs1247117 in heterogeneous cell swimming pools of Nalm6 and SUPB15 cells (rs1247117 del) to keep away from clonal choice (Fig. 6a, b, Supplementary Fig. 7a). Provided that lack of the CRE containing rs1247117 would abolish PU.1 recruitment at this area, we hypothesized that rs1247117 del would end in elevated EIF3A expression. Accordingly, we discovered that EIF3A expression was elevated in rs1247117 del cells relative to parental Nalm6 and SUPB15 cells, respectively (Fig. 6c, d, Supplementary Fig. 7b), additional supporting an inverse relationship between PU.1 binding at rs1247117 and EIF3A expression.
a Diagram on the left displaying the genomic context of the rs1247117 CRE deletion in Nalm6 cells in relation to chromatin accessibility, PU.1 binding and rs1247117. Black bar represents ATAC-seq peak, inexperienced par represents PU.1 peak, and purple bar represents area deleted utilizing CRISPR/Cas9 genome enhancing. b Gel reveals validation of deletion utilizing primers flanking deleted area. Arrow factors to PCR fragment with deletion in heterogeneous Nalm6 cell swimming pools harboring deletion in comparison with wild-type parental Nalm6 cells. c EIF3A gene expression is upregulated upon deletion of the CRE containing rs1247117. RT-qPCR knowledge present the imply ± SD of three unbiased experiments. Two-tailed Pupil’s T take a look at. d Western blots and quantification displaying elevated EIF3A expression in rs1247117 del Nalm6 cells. Blots proven are consultant of 4 unbiased experiments. Quantification knowledge present the imply ± SD. Two-tailed Pupil’s T assessments, n = 4. e–g Drug sensitivity knowledge evaluating viability relative to automobile therapy of wild-type parental Nalm6 cells and Nalm6 cells with rs1247117 CRE deletion after vincristine (VCR) therapy for twenty-four (n = 3), 48 (n = 3) and 72 (n = 3) hours on the indicated concentrations. Non-linear regression and F take a look at evaluation point out that these dose-response curves are considerably totally different. h Caspase 3/7 exercise assays evaluating Caspase exercise relative to automobile therapy of wild-type parental Nalm6 cells and Nalm6 cells with rs1247117 CRE deletion after vincristine (VCR) therapy for 72 hours on the indicated concentrations (n = 3). Dose-response curves of non-linear regression point out that these curves are considerably totally different. Non-linear regression and F take a look at evaluation point out that these dose-response curves are considerably totally different. All supply knowledge are supplied within the Supply Knowledge file.
As a result of the danger G allele at rs1247117 was additionally related to vincristine resistance in major ALL cells from sufferers, we moreover sought to find out the affect of the CRE deletion containing rs1247117 on mobile response to vincristine therapy. We hypothesized that as a result of the danger G allele is related to enhanced PU.1 binding and resistance to vincristine, full disruption of PU.1 binding in Nalm6 cells harboring the CRE deletion would present elevated sensitivity to vincristine relative to parental Nalm6 cells. As predicted, Nalm6 cells with the CRE deletion exhibited considerably elevated sensitivity to vincristine throughout a spread of concentrations after 24, 48, and 72 hours of therapy (Fig. 6e–g), and we discovered constant results on cell viability in SUPB15 cells (Supplementary Fig. 7c). Per enhanced sensitivity to vincristine, we additionally discovered elevated caspase 3/7 exercise in rs1247117 del Nalm6 cells relative to parental Nalm6 cells after 72hrs and throughout a spread of vincristine concentrations (Fig. 6h). These knowledge counsel {that a} useful regulatory variant alters the binding affinity of a key transcription issue, PU.1, and disruption of this locus impacts EIF3A expression and vincristine sensitivity in ALL cells. To additional validate our methodology using CRISPR/Cas9 to delete CREs, we deleted CREs spanning two further high variants, rs7426865 and rs12660691 (see Fig. 4e), that was related to the ex vivo resistance to 6-mercaptopurine and dexamethasone, respectively, in major ALL cells. Deletion of those CREs additionally impacted protein expression and sensitivity to the related chemotherapeutic agent, thereby supporting our useful strategy (Supplementary Figs. 8 and 9).
We subsequent wished to attach EIF3A on to vincristine resistance. Provided that EIF3A is an important gene per the Broad Institute’s DepMap, we opted to check the speculation EIF3A overexpression alone was enough to affect the Nalm6 cell response to vincristine. We, due to this fact, used lentiviral transduction to overexpress EIF3A in Nalm6 cells and in contrast EIF3A overexpression (EIF3A OE) cells to regulate contaminated cells (Nalm6 WT, Supplementary Fig. 10a). Utilizing two unbiased infections of EIF3A OE, we discovered that at 48 hr and 72 hr, EIF3A OE cells have been extra delicate to vincristine than Nalm6 WT cells (Supplementary Fig. 10b). These knowledge counsel that EIF3A expression impacts the ALL cell response to vincristine, with larger expression sensitizing cells to the drug, and additional establishes this gene because the doubtless goal of the affiliation.