Affected person traits
Throughout the 20-year examine interval, we analyzed 328 episodes of bacterial BSIs in 228 sufferers with hematological malignancies. Of them, 67 (29.4%) sufferers skilled a number of episodes of bacteremia, starting from 2 to six occurrences through the examine interval. Of 328 BSIs, 81 (24.7%) had been attributable to MRDOs. The prevalence of MDROs steadily elevated from 10.3% throughout 2003–2007 to 39.7% throughout 2018–2022 (P < 0.001). Particularly, the prevalence of Gram-positive MDROs elevated from 14.7% to 32.0% (P = 0.21) and the prevalence of Gram-negative MDROs elevated from 7.0 to 44.4% (P < 0.001) (Fig. 1). Among the many 328 episodes of bacterial BSIs, Gram-positive micro organism had been recognized because the causative brokers in 141 circumstances (43.0%), GNB in 166 (50.6%), anaerobes in 3 (0.9%), and polymicrobial micro organism in 18 episodes (5.5%) (Desk 1). Desk 1 exhibits the main points of bacterial pathogens in sufferers with bacterial BSIs, distinguishing between these with and with out neutropenia.
Twenty-year developments within the charges of multidrug resistance (MDR) in bacterial bloodstream infections (BSIs) in sufferers with hematological most cancers. MDR charges through the intervals of 2007–2010, 2011–2014, 2015–2018, and 2019–2022 had been in contrast with these through the interval of 2003–2006. The statistical significance was displayed utilizing the next notation: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.
Baseline threat components for MDROs
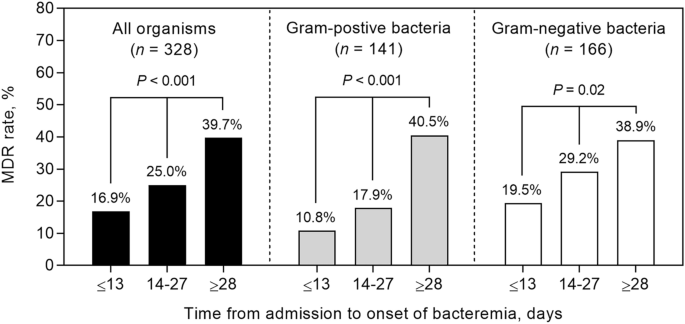
Desk 2 exhibits the baseline traits and outcomes of 328 sufferers with hematologic most cancers and bacterial BSIs attributable to MDROs and non-MDROs. Sufferers contaminated with MDROs had been extra prone to have a extra prolonged hospital keep earlier than bacteremia onset (median 22 vs. 13 days; P = 0.001), decrease platelet counts (median 28 vs. 44 × 103/µL; P < 0.001), and better C-reactive protein ranges (median 16 vs. 10 mg/dL; P = 0.001) than these contaminated with non-MDROs. Sufferers contaminated with MDROs had been extra prone to obtain inappropriate preliminary antibiotic remedy (42.0 vs. 13.8%, P < 0.001) (Desk 2). There was a big pattern in direction of rising MDR charge in accordance with the size of hospital keep: 16.9% (≤ 13 days), 25.0% (14–27 days), and 39.7% (≥ 28 days) (linear-by-linear affiliation take a look at; P < 0.001) (Fig. 2). This pattern was additionally evident amongst sufferers contaminated with Gram-positive cocci (10.8%, 17.9%, and 40.5%; P < 0.001) and Gram-negative bacilli (19.5%, 29.2%, and 38.9%; P = 0.02) (Fig. 2). Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) was related to a better charge of MDROs and these sufferers exhibited the longest period of hospitalization (median, 19 days) in contrast with these with acute lymphoid leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma (median, 18, 11, and 4 days, respectively).
Impression of illness standing and MDROs on affected person end result
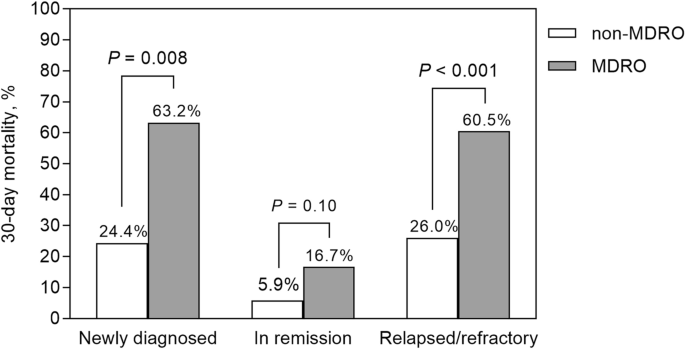
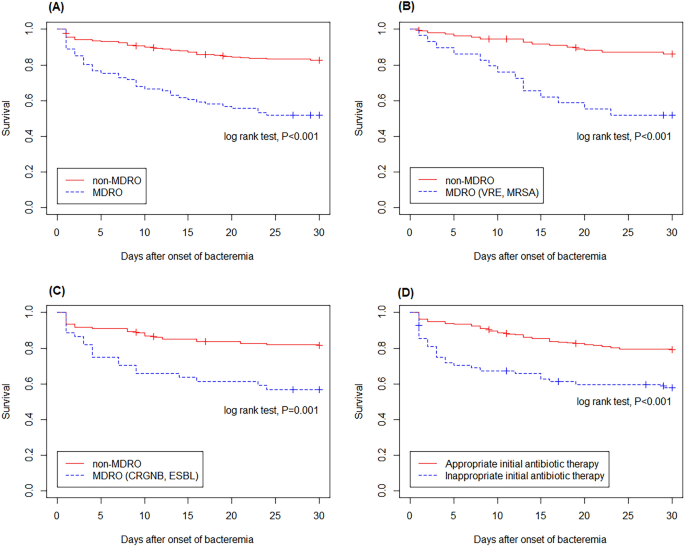
Of the 328 sufferers with bacterial BSI, 82 (25.0%) died inside 30 days of BSI onset (Desk 2). The 30-day mortality charge differed in accordance with illness standing: 35.9% (23/64) for newly identified most cancers, 7.9% (10/126) for full remission, and 35.5% (49/138) for relapsed/refractory illness most cancers (P < 0.001) (Desk 3). The mortality charge was increased in sufferers contaminated with MDROs than in these contaminated with non-MDROs (48.1 vs. 17.4%; P < 0.001). This discovering was evident in sufferers who had been first identified with malignancy (63.2 vs. 24.4%; P = 0.008) and relapsed/refractory illness (60.5 vs. 26.0%; P < 0.001) however not in those that had been in full remission (16.7 vs. 5.9%; P = 0.10) (Fig. 3). Kaplan–Meier evaluation confirmed that the mortality charge of sufferers contaminated with MDROs was increased than that of sufferers contaminated with non-MDROs (log-rank take a look at, P < 0.001; Fig. 4A). Related findings had been noticed in sufferers contaminated with Gram-positive and Gram-negative MDROs (Fig. 4B,C).
Comparability of 30-day mortality between sufferers contaminated with multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs) and people contaminated with non-MDROs in accordance with illness standing. Amongst sufferers newly identified with malignancy or experiencing relapsed/refractory illness, the mortality charge was increased within the MDROs group in comparison with the non-MDROs group. Nonetheless, this distinction was not noticed in sufferers who had been in full remission.
Kaplan–Meier evaluation demonstrated a better mortality charge amongst sufferers contaminated with multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs) in comparison with these contaminated with non-MDROs (A). Related developments had been noticed in sufferers contaminated with Gram-positive MDROs (B) and Gram-negative MDROs (C). Sufferers who acquired inappropriate empirical remedy exhibited a better mortality charge in comparison with those that acquired applicable empirical remedy (D).
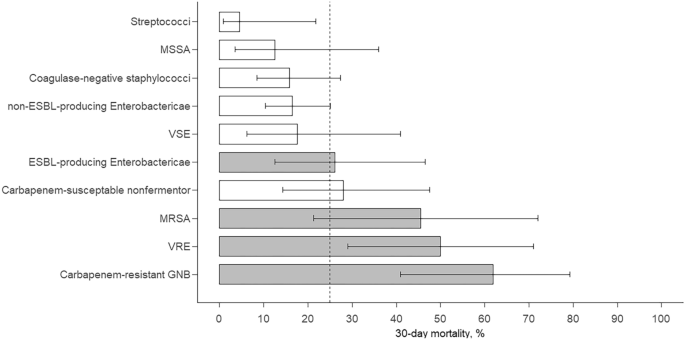
Among the many MDROs, carbapenem-resistant GNB exhibited the best 30-day mortality charge (61.9%), adopted by VRE (50.0%), MRSA (45.5%), and ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae (26.1%) (Fig. 5). The mortality for every pathogen, aside from ESBL-producing Enterobactericae, didn’t differ between sufferers with and with out neutropenia (Supplementary Desk S1). The affiliation between MDROs and 30-day mortality was evident for carbapenem-resistant GNB (odds ratio [OR], 5.61; P < 0.001) and VRE (OR, 3.25; P = 0.02) however was much less evident for MRSA (OR, 2.60; P = 0.12) and never evident for ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae (OR, 1.06; P = 0.90).
Bar chart displaying 30-day mortality and 95% confidence intervals for BSIs attributable to totally different pathogens. ESBL, extended-spectrum β-lactamase; GNB, Gram-negative micro organism; GPB, Gram-positive micro organism; MRSA, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; MSSA, methicillin-susceptible S. aureus; VRE, vancomycin-resistant enterococci; VSE, vancomycin-susceptible enterococci.
Desk 3 presents the outcomes of univariate and multivariate analyses for 30-day mortality amongst hematological sufferers with bacterial BSIs. Univariate evaluation indicated that age ≥ 65 years (P = 0.002), newly identified illness (P < 0.001), relapsed/refractory illness (P < 0.001), absence of central venous catheters (P = 0.02), white blood cell ≥ 15,000/µL (P = 0.01), C-reactive protein stage ≥ 20 mg/L (P < 0.001), infections attributable to MDROs (P < 0.001), and inappropriate preliminary antibiotic remedy (P < 0.001) had been the unbiased threat components for 30-day mortality. Kaplan–Meier evaluation confirmed that the mortality charge of sufferers who acquired inappropriate empirical remedy was increased than that of sufferers who acquired applicable empirical remedy (log-rank take a look at, P < 0.001; Fig. 4D). Multivariate evaluation indicated that the unbiased threat components for 30-day mortality had been age ≥ 65 years (OR, 2.15; 95% CI 1.12–4.23), newly identified illness (in contrast with full remission, OR, 5.80; 95% CI 2.25–16.20), relapsed/refractory illness (in contrast with full remission, OR, 6.89; 95% CI 2.98–17.88), C-reactive protein stage ≥ 20 mg/L (OR, 3.35; 95% CI 1.68–6.77), polymicrobial an infection (OR, 3.68; 95% CI 1.07–13.31), infections attributable to MDROs (OR, 3.02; 95% CI 1.52–6.04), and inappropriate preliminary antibiotic remedy (OR, 2.38; 95% CI 1.11–5.13).