Baseline knowledge
The investigation included 750 sufferers with a imply age of 62 years (7.6 years). The longest follow-up interval was 66 months (median: 36 months), and 169 PD occasions occurred on the conclusion of the follow-up interval. The examine cohort was divided by a 7:3 ratio into 527 instances within the coaching set and 223 instances within the validation set, with 126 PDs occurring within the coaching set and 43 PDs noticed within the validation set, as detailed in Appendix 1. There have been statistically vital variations (P < 0.05) in earnings, TNM, marital standing, household, training, SAS, SDS, and AIS within the cohorts with and with out PD occasions, together with the total cohort, coaching set, and validation set, and there have been no vital variations between the three cohorts, as detailed in Desk 1.
SAS, SDS, AIS, and prognosis
In response to the outcomes of the examine, SAS, SDS, and AIS could also be used to distinguish the prognosis of sufferers. There have been statistically vital variations within the SAS, SDS, and AIS scores between sufferers with and with out PD occasions. The AUC have been: 0.8049 (0.7685–0.8613), 0.768 (0.727–0.809), and 0.7661 (0.724–0.808), with cut-off values of 43.5, 48.5, and 4.5 respectively. Kaplan-Meier evaluation by grouping SAS, SDS, and AIS by cut-off values confirmed statistically vital variations between the 2 teams, logrank check P < 0.001, hazard ratio (HR) values of 5.6 (3.98–7.88), 3.87 (2.73–5.5), and three.88 (2.86–5.26) (Fig. 1).
SAS, SDS, AIS rating, and postoperative illness development and survival evaluation. SAS, SDS, and AIS scores have been statistically completely different between sufferers whose illness progressed and people whose illness didn’t progress (A, D, and G), ROC curve evaluation revealed that SAS, SDS, and AIS all had a excessive skill to distinguish prognosis (B, E, and H). Kaplan-Meier survival evaluation signifies that the prognosis of the excessive SAS, SDS, and AIS rating group is considerably worse than the low group. (C, F, I)
Screening of observational indices
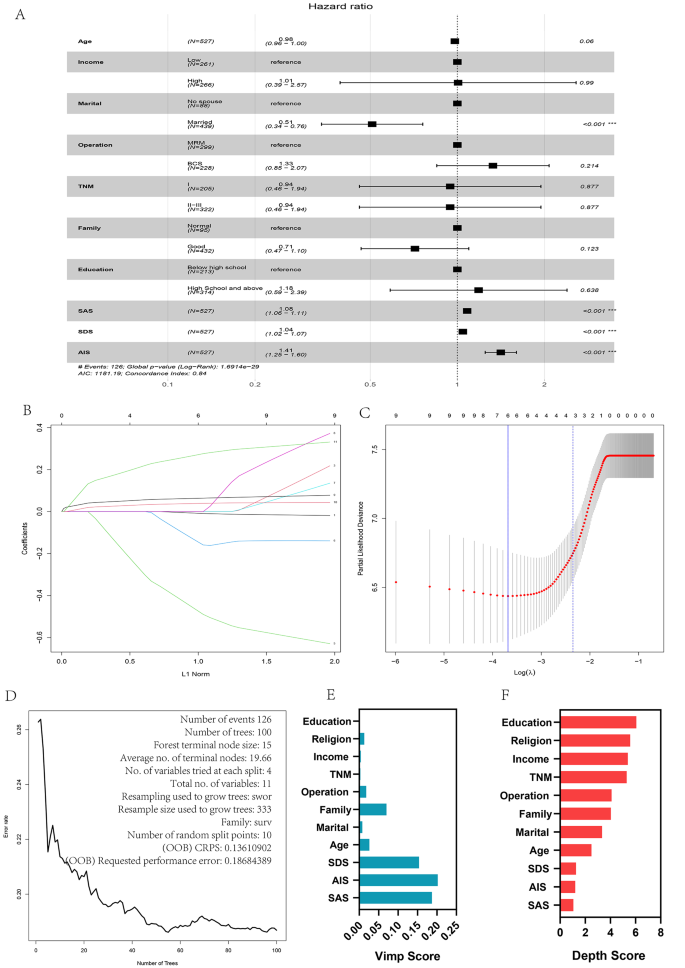
On this examine, we meant to develop a prediction mannequin based mostly on the related knowledge obtainable on the preliminary therapy stage and examine the strategies that would information the correct implementation of a multidisciplinary steady care mannequin. These variables included age (years), earnings, surgical methodology, marital standing, household help, academic background, faith, SAS, SDS, AIS, and prognostic indices. Variance inflation components (VIF) have been calculated for every issue within the multivariate evaluation, and it was found that the VIFs of age, earnings, household help, and SAS have been all better than 5 factors, which can be attributed to collinearity amongst associated variables. A lasso evaluation was carried out to scale back high-dimensional knowledge, with correlation components evaluated because the optimum predictive options [13, 14] and a lasso regression mannequin was used to get rid of options with non-zero coefficients [15]. Vital variables have been recognized utilizing single-factor evaluation and multi-factor evaluation to create mannequin 1, lasso regression and cross-lasso regression evaluation to create mannequin 2, random forest calculation methodology to create mannequin 3, stepwise regression methodology (backward methodology) to create mannequin 4, and together with all variables for Cox regression to incorporate vital variables to create mannequin 5 (Desk 2; Fig. 2).
Variable filtering. Forest plots incorporating Cox regression evaluation of all variables confirmed that marital standing, SAS, SDS, and AIS scores have been vital variables (P < 0.05) (A). Lasso regression evaluation and cross-lasso regression. Lasso regression evaluation yields an optimum mannequin incorporating SAS, SDS, AIS scores (B, C). Random forest mannequin screening variables (D, E, F)
Mannequin validation, comparability, and screening
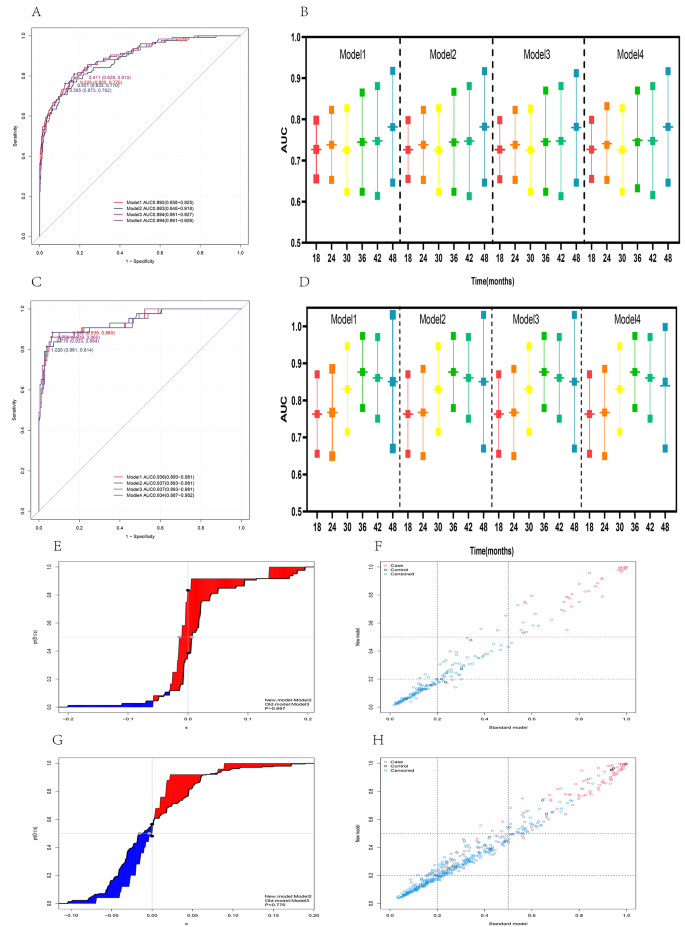
5 fashions have been developed by screening vital variables into the mannequin utilizing completely different strategies, the place mannequin 1 and mannequin 5 have been similar, indicating that the variables with P < 0.05 have been included within the multi-factor evaluation by first conducting a one-way evaluation, which was according to the impact of together with all variables straight into the multi-factor evaluation on this examine; mannequin 5 just isn’t mentioned right here. The ROC was plotted within the coaching and validation units, to research the AUC values of various fashions. This yielded 0.892 (0.858–0.925) for mannequin 1, 0.883 (0.848–0.918) for mannequin 2, 0.894 (0.861–0.927) for mannequin 3, and 0.894 (0.861–0.926) for mannequin 4 within the coaching set, and 0.936 (0.890–0.98) for the validation set, respectively. 0.981), 0.937 (0.893–0.981), 0.937 (0.893–0.981), and 0.934 (0.887–0.982), respectively. The fashions reveal improved prediction efficiency in each the coaching and validation units, nevertheless, the AUC is larger within the validation set than within the coaching set, in all probability as a result of larger distribution of emergent occasions within the validation set than within the coaching set. The prediction efficiency of various fashions at completely different time factors was additional analyzed utilizing time-dependent ROC curves, and it was discovered that mannequin 2 had the least variety of unbiased variables, whereas mannequin 3 had the very best prediction efficiency, The 2 fashions have been analyzed utilizing NRI and IDI, and there was no statistically vital distinction between them in both the coaching set or the validation set. Due to this fact, mannequin 2, which integrated fewer variables, was chosen as the topic of a follow-up examine to research its potential use as a medical prediction mannequin (Fig. 3).
Mannequin comparability, validation, and choice. Comparability of ROC curves of a number of fashions within the coaching dataset (A); comparability of the world underneath the time-dependent ROC curve of a number of fashions within the coaching dataset (B); comparability of ROC curves of a number of fashions within the validation dataset (C); comparability of the world underneath the time-dependent ROC curve of a number of fashions within the validation dataset (D); IDI evaluation of mannequin 2 and mannequin 3 confirmed no statistically vital distinction between the 2 in each the coaching and validation datasets (E, G); NRI evaluation of mannequin 2 and mannequin 3 revealed no statistically vital distinction between the 2 in each the coaching and validation datasets (F, H)
Mannequin testing and visualization
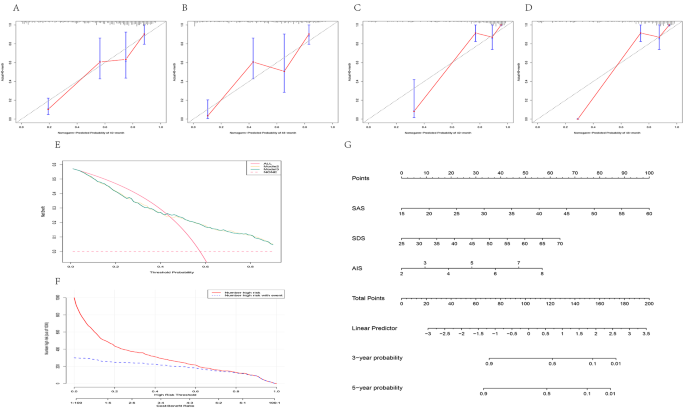
The calibration curves have been plotted for mannequin 2 at two time factors of 40 and 48 months, respectively, and for the coaching and validation units of even knowledge units. It was found that though mannequin 2 didn’t overlap the usual line, fluctuating above and under it, the general predictive stability was honest, with DCA and CIC curves, indicating that intervention in sufferers at larger danger could lead to medical profit, whereas intervention in sufferers at decrease danger interventions is prone to improve medical consumption. This means the necessity for selective medical interventions, together with interventions in multidisciplinary fashions of care. Determine 4 depicts a nomogram, which is a visible illustration of the mixing of a number of predictors based mostly on the multivariate regression evaluation, by which a price was assigned, and a scaled line section was drawn for every index to make it handy for medical use [16, 17]. Nomogram was used to foretell linear survival possibilities at each 36 and 60 months. The CIC map evaluation revealed a convergence of the 2 curves when the danger worth reached 0.6. Particularly, at this threshold, the mannequin’s effectiveness at 36 months exhibited the next metrics: Sensitivity: 0.8047, Specificity: 0.8124, Constructive Predictive Worth: 0.5551, Unfavourable Predictive Worth: 0.9347, Prevalence: 0.2253, Detection Price: 0.1813, Detection Prevalence: 0.3267, Balanced Accuracy: 0.8086, Precision: 0.5551, Specificity: 0.8124, F1 Rating: 0.6570, and Recall: 0.8047. Equally, at a danger worth of 0.6 and 60 months, the mannequin’s efficiency was as follows: Sensitivity: 0.8402, Specificity: 0.7556, Constructive Predictive Worth: 0.5000, Unfavourable Predictive Worth: 0.9421, Prevalence: 0.2253, Detection Price: 0.1893, Detection Prevalence: 0.3787, Balanced Accuracy: 0.7979, Precision: 0.5000, Specificity: 0.7556, F1 Rating: 0.8402, and Recall: 0.8402.
Mannequin testing and visualization. Calibration curves of mannequin 2 within the coaching dataset for months 40 and 48 (A, B); calibration curves of mannequin 2 within the validation dataset for months 40 and 48 (C, D). DCA curves and CIC curves of mannequin 2 within the full knowledge set (E, F). Nomogram for mannequin 2 (G)
Convert mannequin 2 to a scoring system and validate
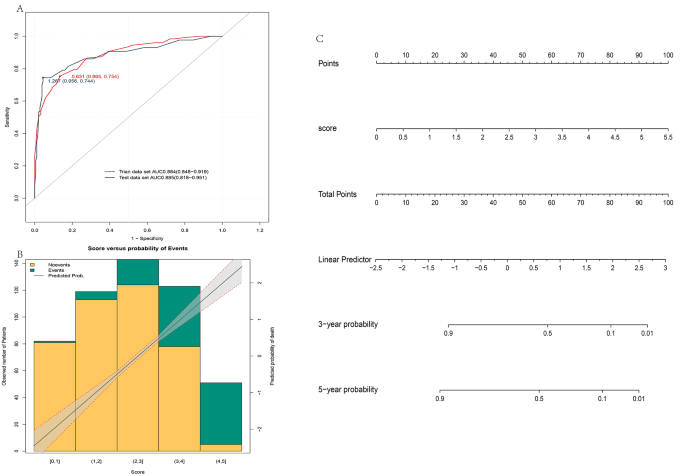
Whereas the predictive efficacy and stability of Mannequin 2 developed with the continual scores of SAS, SDS, and AIS are larger, the continual scores are inconvenient for medical use. We analyzed the connection between the noticed variables and the result variables (see Appendix 2 for particulars), excised the continual variables into a number of intervals based mostly on the change pattern, and assigned values to every interval utilizing Cox regression evaluation (see Desk 3 for particulars). We then aggregated the continual variables to acquire the full rating, carried out Cox regression evaluation on the full rating, and analyzed the connection between the full rating and the result. We found that in each the coaching and validation units, the full rating had higher predictive efficacy, with AUC values of 0.884 (0.848–0.919) and 0.885 (0.818–0.951), respectively. Because the rating will increase, sufferers have an elevated danger of illness development. We additionally plotted the column line graphs to visualise our outcomes (Fig. 5).
Validation and visualization after mannequin 2 transformation scoring. ROC curves for remodeled mannequin 2 scores within the coaching and validation datasets; (A). Evaluation of the chance and correlation of illness development in several rating areas (B). Nomogram of mannequin 2 after remodeling the rating (C)