Medical traits
The baseline traits of the 2 teams stratified by mCXI are offered in Desk 1. General, 215 sufferers recognized with colorectal most cancers have been concerned on this analysis, comprising 124 (57.7%) males and 91 (42.3%) females. The contributors’ imply age was 58.4 years (±12.8 years). Using time-dependent ROC curves, sufferers with mCXI <161.4 have been categorized into the low mCXI group, whereas these with mCXI ≥161.4 have been categorized into the excessive mCXI group. In contrast with sufferers who exhibit excessive mCXI, sufferers within the low mCXI group had decrease ranges of BMI (low mCXI vs excessive mCXI: 22.1 ± 3.5 kg/m2 vs 23.2 ± 3.1 kg/m2, p = 0.02), SMI (low mCXI vs excessive mCXI: 40.6 ± 4.7 cm2/m2 vs 44.1 ± 3.7 cm2/m2, p < 0.01), hemoglobin (low mCXI vs excessive mCXI: 117.0 ± 24.3 g/L vs 124.9 ± 24.4 g/L, p < 0.01), lymphocytes (low mCXI vs excessive mCXI: 1.2 ± 0.6 × 109/L vs 1.7 ± 0.6 × 109/L, p < 0.01), extra elevated neutrophils (low mCXI vs excessive mCXI: 4.6 ± 2.5 × 109/L vs 3.4 ± 1.3 × 109/L, p < 0.01), Albumin(g/L) (low mCXI vs excessive mCXI: 39.8 ± 5.4 vs 41.9 ± 3.7, p < 0.01), Creatinine(low mCXI vs excessive mCXI: 59.9 ± 18.9 umol/L vs 67.7 ± 17.1 umol/L, p < 0.01), Blood urea nitrogen(low mCXI vs excessive mCXI: 5.7 ± 2.2 mmol/L vs 5.0 ± 1.2 mmol/L, p < 0.01) (Desk 1). There was no vital distinction in age, gender, white blood cell depend, platelets, CRP, CEA, CA199, tumor location, postoperative pathological stage, presence of underlying ailments, and postoperative problems between the 2 teams.
mCXI and survival
With a median follow-up interval of 45 months (vary 8–85 months), the 3-year OS (76.6% vs 96.7%, p < 0.01) and 3-year RFS (68.3% vs 94.1%, p < 0.01) within the mCXI low group have been significantly decrease than these within the mCXI excessive group (Fig. 1). We additional subgroup analyzed the impact of mCXI on OS and RFS in sufferers with completely different levels. Notably, sufferers with CRC levels 1–2 and three within the low mCXI group had considerably poorer OS and RFS than these within the excessive mCXI group (Fig. 1).
Cox regression evaluation
To look at the impression of varied medical components on sufferers’ OS and RFS, we carried out univariate Cox regression evaluation. We found that BMI ≥ 24 (HR = 0.199, 95% CI: 0.046–0.860, P = 0.031) and hemoglobin ≥90 (HR = 0.354, 95% CI: 0.127–0.982, P = 0.046) have been extra helpful for 3-year OS, whereas CRC stage III (HR = 4.100, 95% CI: 1.477–11.385, P = 0.007) and mCXI Low (HR = 8.179, 95% CI: 2.945–22.719 P < 0.01) exerted extra danger on 3-year OS (Desk 2). Excessive BMI (HR = 0.365, 95% CI: 0.139–0.959, P = 0.041), excessive CEA degree (HR = 2.279, 95% CI: 1.031–5.039, P = 0.042), CRC III of tumor severity (HR = 3.845, 95% CI: 1.690–8.747, P < 0.01), and low mCXI (HR = 6.399, 95% CI: 2.893–14.154, P < 0.01) have been considerably related to 3-year RFS (Desk 3). After adjusting statistically vital variables within the multivariate evaluation, preoperative hemoglobin (HR = 0.300, 95% CI: 0.104–0.869, P = 0.027), affected person’s CRC stage (HR = 4.402, 95% CI: 1.544–12.557, P = 0.006) and mCXI (HR = 8.951, 95% CI: 3.105–25.807, P = < 0.01) have been extremely correlated with OS (Desk 2). Preoperative CEA degree (HR = 2.382, 95% CI: 1.071–5.300, P = 0.033), affected person tumor stage (HR = 4.001, 95% CI: 1.721–9.302, P < 0.01), and mCXI (HR = 6.767, 95% CI: 3.017–15.176, P < 0.01) have been considerably correlated with the 3-RFS have been correlated significantly (Desk 3).
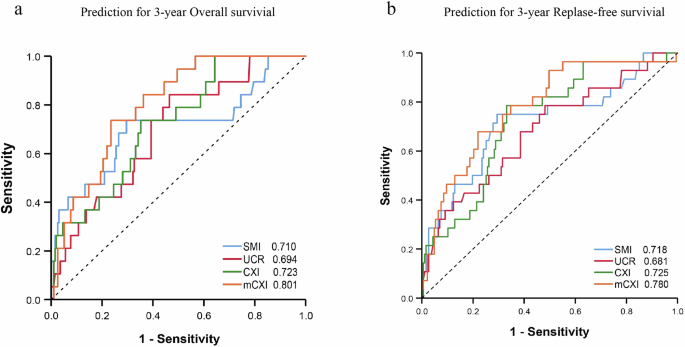
Prediction accuracy comparability between mCXI and CXI
Utilizing time-dependent ROCs to foretell 3-year OS in sufferers as an entire. The areas underneath the curves (AUC) for SMI, 1/UCR, CXI and mCXI have been 0.710 (95% CI 0.566–0.855, P < 0.01), 0.694 (95% CI 0.579–0.809, P < 0.01), 0.723 (95% CI 0.614–0.831, P < 0.01) and 0.801 (95% CI 0.717–0.885, P < 0.01) respectively (Fig. 2). Moreover, when predicting the 3-year RFS, the AUC was 0.718 (95% CI 0.605–0.831, P < 0.01), 0.681 (95% CI 0.571–0.792, P < 0.01), 0.725 (95% CI 0.631–0.820, P < 0.01), 0.780 (95% CI 0.689–0.871, P < 0.01) (Fig. 2). After Delong check, we discovered that the AUC distinction between mCXI and CXI was statistically vital in predicting three-year OS (P = 0.01) and three-year RFS (P = 0.048). Due to this fact, on this examine, mCXI was the most effective predictor of survival and recurrence in CRC sufferers.