Institution and characterization of Dtx and Cbz resistant PCa cells
Dtx and Cbz resistant cell traces (DtxR and CbzR, respectively) had been generated from CR-PCa cell traces, Du145 and 22Rv1. The parental cells had been allowed to develop for twenty-four h earlier than being handled (72 h) with dose escalation (Sup. Determine 1A). Cell development assays had been carried out to evaluate the acquired resistance, revealing a big variety of viable cells within the resistant compartments following taxane publicity (Sup. Determine 1B, C). The IC50 values of resistant cells had been considerably greater than these of parental cells, exhibiting ~40–560 fold enhance for DtxR and ~14–170 fold for CbzR (Desk 1). We confirmed that these viability variations noticed in cells had been certainly related to cell demise, as evident by the numerous will increase in annexin-v and caspase 3/7 optimistic cells in parental cells (Sup. Fig. 1D). Even at greater doses, resistant cells didn’t show these apoptosis markers, thus reflecting the non-responder state in accordance with the viability assays. Subsequent, we assessed the goal engagement (TE) for tubulin, the first goal of taxanes, utilizing Mobile Thermal Shift Assay (CETSA), which measures TE in intact cells by heating them and figuring out if taxanes stabilize the tubulin in opposition to thermal denaturation. As proven in Sup. Fig. 1E, the next stage of goal engagement was noticed in parental cells, indicating their skill to retain the drug in comparison with resistant cells. These findings recommend a possible inadequacy of taxane uptake in resistant cells, resulting in a consequent lack of goal engagement. Consistent with our findings, a examine involving each delicate and resistant cells, CETSA TE measurements correlated with taxane sensitivity and effectively revealed the presence of acquired drug resistance [31].
Apparently, whereas the cells had been cross-resistant in opposition to different chemotherapeutics equivalent to paclitaxel and doxorubicin (Sup. Fig. 2A), they grew to become extra prone to platinum group medicine (Sup. Fig. 2B), suggesting {that a} widespread mechanism acted to detoxify medicine which can be substrates of drug efflux pumps, on the expense of changing into extra susceptible in the direction of different medicine. All these knowledge have introduced us to a degree the place we are able to elucidate the mechanism underlying taxane resistance in our well-characterized PCa cell fashions.
Transcriptome profiles of taxane-sensitive and -resistant PCa cells
We carried out an entire transcriptome evaluation between taxane-sensitive and -resistant Du145 cells to unravel potential molecular mechanisms of resistance. Among the many differentially expressed genes (DEGs), the highest 10 upregulated and downregulated genes in Du145-DtxR and Du145-CbzR cells are listed in Sup. Tables 2 and 3, respectively. The transcriptomic profile was additional analyzed utilizing gene set enrichment evaluation (GSEA). The ranked gene units had been examined on the hallmark gene units, which signify well-defined biologic states and processes (MSigDB, Broad Institute). The relative normalized enrichment scores (NES) demonstrated that MYC signaling, unfolded protein response (UPR), E2F and NF-κB signaling had been essentially the most considerably enriched gene units in Du145-DtxR cells (Fig. 1A). The genes demonstrating core enrichment inside these gene units are listed in Sup. Desk 4.
A Gene set enrichment (GSEA) evaluation utilizing hallmark gene units from the MSigDB revealed the upregulation of genes concerned in MYC signaling, unfolded protein response (UPR), NF-κB and E2F signaling (FDR < 0.05, and Log2FC ≥ 0.5 or ≤ −0.5). GSEA was carried out utilizing the h.all.v2023.1.Hs.symbols.gmt dataset within the MsigDB database. B DEGs (FDR < 0.05, and Log2FC ≥ 1 or ≤−1) from resistant cells had been additional distributed primarily based on their expression modifications in the identical path (up or down). The pink and purple scatters point out up- and downregulated DEGs, respectively, in resistant Du145 cells. C Expression ranges of ABCB1 mRNA had been decided by qRt-PCR. Information is the imply ± SEM. D ABCB1 protein expression ranges in parental and taxane resistant PCa cells had been decided by western blotting. E Comparability of affected person survival primarily based on ABCB1 expression ranges utilizing a Kaplan-Meier plot (Metastatic Prostate Adenocarcinoma, MCTP). F ABCB1 mRNA ranges in medical specimens (TCGA-PRAD) had been investigated by utilizing cBioPortal and its relationship with the prevalence of native recurrence and metastasis (Pan-cancer Evaluation of Superior and Metastatic Tumors, BCGSC); (G) and gleason rating (Metastatic Prostate Adenocarcinoma, SU2C/PCF Dream Group) had been proven as scatter plots. Uncropped western blot photographs equivalent to Fig. 1D had been proven in Supplemental Materials.
The enrichments of “MYC Targets_V1” and “E2F Targets” had been additionally noticed in Du145-CbzR cells, much like Dtx-resistant cells. This implies a possible involvement of MYC and E2F signaling pathways in mediating resistance mechanisms throughout completely different taxanes (Sup. Fig. 3). Nevertheless, there’s additionally some extent of variation within the underlying mechanisms inside every cell. Subsequently, we utilized a Venn diagram to establish the widespread gene pool particular to taxane resistance in each cells, categorizing the DEGs primarily based on their expression modifications (up or down) (Fig. 1B). Our evaluation revealed that 107 genes had been generally upregulated and 336 had been downregulated in taxane resistant cells. Notably, ABCB1 emerged because the gene with the best transcriptional change in each resistant cells (Fig. 1B).
ABCB1 overexpression in taxane-resistant PCa cells
The highest transcriptional change passed off for the ABCB1 gene, with a ten.3 and 12.9-fold (log2 scale) upregulation in Du145-DtxR and Du145-CbzR, respectively, in comparison with parental cells. After validating the transcript expression of ABCB1 (Fig. 1C), we confirmed the corresponding protein upregulation in all taxane-resistant cells (Fig. 1D). The affected person knowledge evaluation highlighted the medical significance of ABCB1 expression, with ABCB1-high sufferers exhibiting unfavorable outcomes by way of general survival (Fig. 1E). Moreover, the evaluation of superior and metastatic tumors revealed a big relationship between greater ABCB1 mRNA ranges and an elevated incidence of metastasis in comparison with sufferers with native recurrence (Fig. 1F). In one other dataset of sufferers with metastatic illness, an affiliation was noticed between greater Gleason scores and elevated ABCB1 mRNA expression (Fig. 1G). Taken collectively, these findings present proof supporting a possible relationship between ABCB1 expression and illness development.
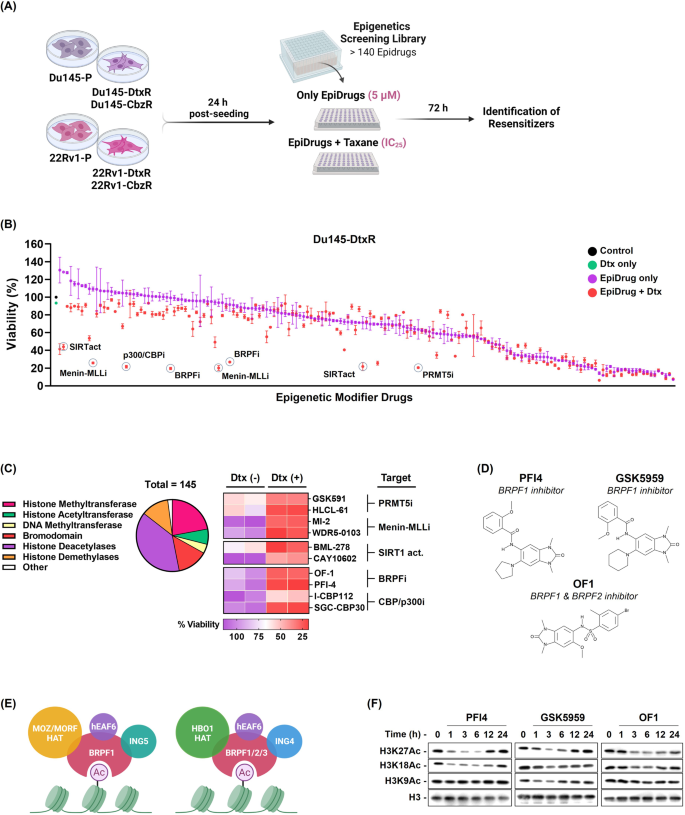
One of many potential causes for the elevated expression of ABCB1 is gene amplification. Subsequently, we examined ABCB1 gene copy numbers in all PCa cell traces. ABCB1 amplification was evident solely in Du145-CbzR cells (Sup. Determine 4). The explanation for such upregulation of ABCB1 is also by way of promoter activation, indicating doable epigenetic laws. The absence of amplification in 3 out of 4 cells has led us to contemplate the opportunity of epigenetic regulation, which additionally drove us to display screen these cells with an epidrug library to disclose their vulnerabilities (Fig. 2).
A Schematic view of the epidrug library screening. The determine was generated utilizing BioRender software program. B Screening of 145 focused medicine to establish epigenetic modulators able to overcoming taxane resistance was carried out utilizing the SRB assay and the end result obtained in Du145-DtxR cells is proven representatively. Purple dots present the cell viabilities upon the standalone use of every epidrugs, whereas the pink dots point out the cell-killing impact of their mixture with Dtx. Re-sensitizers ranked within the high 5 teams are highlighted in circles. C Pie Chart illustrates the epigenetic proteins focused by the small molecules (epidrugs) within the library. Epidrugs had been screened for resistance reverter exercise which resulted within the identification of 5 courses of epigenetic targets (PRMT5, Menin-MLL, SIRT1, BRPF, and CBP/p300) that induced essentially the most pronounced resensitization when utilized to resistant cells. D Molecular construction of BRPF inhibitors. E Cartoon illustration of the BRPF household and (F) demonstration of the efficacy of BRPF inhibition on histone acetylation by western blotting. Uncropped western blot photographs equivalent to F had been proven in Supplemental Materials.
To evaluate the significance of ABCB1 expression in taxane resistance, we used siRNA to focus on ABCB1 in resistant Du145 cells (Sup. Fig. 5A, B). Nevertheless, we encountered difficulties in reaching efficient knockdown of ABCB1 utilizing the identical siRNA in resistant 22Rv1 cells. Subsequently, we proceeded to knock out ABCB1 expression in these cells (Sup. Fig. 5C, D). The inhibition of ABCB1 expression in all resistant cells resulted in decreased survival on the doses of taxanes that confirmed minimal cytotoxicity within the earlier outcomes, highlighting the importance of ABCB1 expression in mediating taxane resistance (Sup. Fig. 5E–H). Moreover, the cells had been handled with epothilone B (Epo B), a tubulin focusing on drug which isn’t an ABCB1 substrate. Resistant cells exhibited comparable viability curves to parental cells upon Epo B publicity, offering additional proof that the noticed distinction between the resistant and parental cells was predominantly depending on ABCB1 (Sup. Fig. 5I, J).
Episensitization of taxane-resistant PCa cells
Focusing on epigenetic modulators in PCa holds promise with quite a few pre-clinical research supporting its potential. As an example, Asangani et al. demonstrated that the mixture of BET inhibitors with AR antagonists can overcome resistance mechanisms in metastatic CR-PCa fashions [32]. Xu et al. noticed that chemotherapy-resistant PCa cells displayed elevated ranges of acyl-CoA and acetylated proteins, making them extra delicate to HDAC inhibition (TSA/SAHA) in comparison with their parental counterparts [33]. Gupta et al. confirmed that LSD1 inhibition with HCI-2509 enhanced the response of Dtx-resistant PCa cells to the remedy, resulting in a discount in c-MYC ranges [34]. Not surprisingly, with all these research and collected data, the FDA has accredited eight small molecules focusing on DNA methylation, histone methylation, and histone deacetylation for most cancers remedy primarily based on their effectiveness in varied stable and hematologic malignancies [35]. Leveraging this development and the established effectiveness of epidrugs, we carried out an epigenetic drug library display screen to uncover potential targets and vulnerabilities in taxane-resistant PCa cells (Fig. 2A). The epigenetic drug library has 145 compounds together with a majority of at present accessible agonists and antagonists of epigenetic regulatory enzymes. The highest 5 courses of epigenetic targets that induced essentially the most pronounced resensitization when utilized to resistant cells had been recognized as CBP/p300, BRPF, Menin-MLL, PRMT5, and SIRT1 (Fig. 2B, C). The efficacy of the epigenetic medicine was additional validated utilizing cell viability assays at completely different concentrations, revealing a restoration in taxane susceptibility with growing doses of epidrugs (Sup. Fig. 6). Nevertheless, subsequent investigation confirmed that expressing SIRT1 didn’t have a big influence on resensitization of taxane-resistant cells. (Sup. Fig. 7A, B). Moreover, silencing CBP, a well known transcriptional coactivator with histone acetyltransferase exercise, resulted in a whole lack of colony-forming skill of cells, indicating their essentiality for PCa cell survival (Sup. Fig. 7C). Alternatively, our laboratory has ongoing research on Menin-MLL and PRMT5, that are being investigated intimately and will likely be reported individually. Subsequently, the findings from our epigenetic drug library display screen led us to prioritize BRPF proteins as a possible goal for overcoming taxane resistance in PCa. We additionally recognized a data hole relating to the capabilities of BRPF epiregulators and the efficacy of BRPF inhibitors (Fig. 2D) in most cancers drug resistance, which drove us to focus on these proteins as promising and novel targetable epiregulators on this context.
Focusing on BRPF epiregulators in taxane-resistant PCa cells
The BRPF epigenetic reader household (BRPF1, BRPF2, and BRPF3) acts as scaffolds for assembling HAT complexes of MOZ/MORF and HBO1 households with ING5 and Eaf6, carrying these to chromatin by way of its bromodomain [36] (Fig. 2E). Each BRPF2 and BRPF3, regardless of their excessive sequence similarity to BRPF1, have a choice for forming complexes with HBO1 as a substitute of MOZ and MORF, suggesting a definite practical conduct of BRPF1. Furthermore, BRPF1 directs histone acetylation in the direction of H3 as a substitute of H4, indicating its pivotal position in controlling the substrate specificity of HBO1 [37]. In truth, we noticed that remedies with BRPF inhibitors altered the worldwide H3K18, H3K27, and, to some extent, H3K9 acetylation ranges, offering proof of the intracellular actions of those compounds (Fig. 2F). BRPF1 is thought to be indispensable for embryonic improvement [38, 39]; nevertheless, its involvement in most cancers, aside from restricted research, stays poorly characterised.
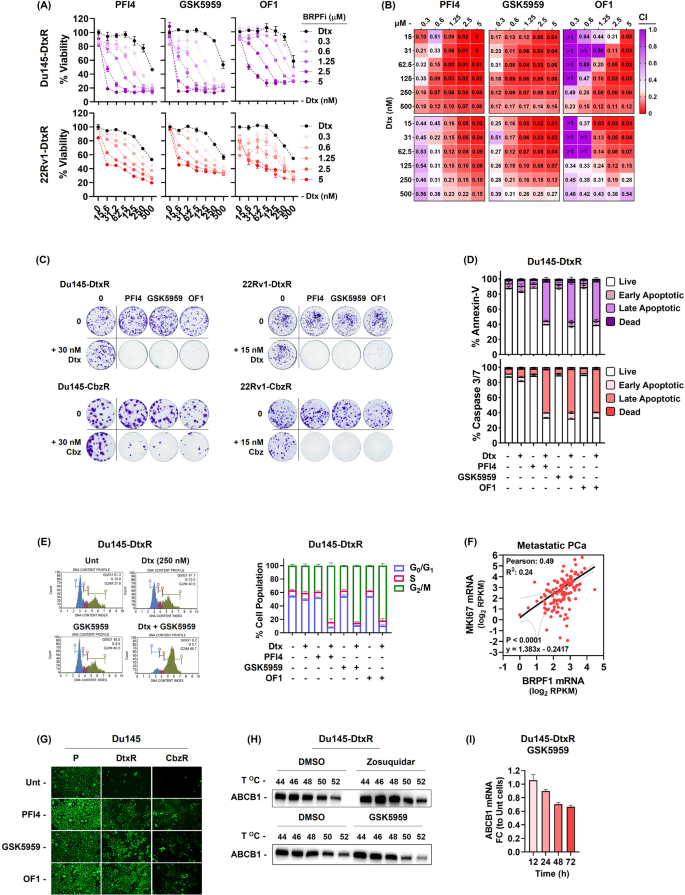
We validated these hits by screening every BRPF inhibitor in a wider dose vary and confirmed the resensitizing impact as resistant cells grew to become extra attentive to taxanes with growing doses of those inhibitors (Fig. 3A and Sup. Fig. 8A). Moreover, the noticed impact was discovered to be synergistic, as evident by mixture index (CI) values (Fig. 3B). These findings had been additional supported by colony formation assays, the place particular person use of both of the medicine had minimal to negligible influence. Nevertheless, when the 2 medicine had been mixed, they successfully eradicated a lot of the cells (Fig. 3C). Apparently, parental cells didn’t present any elevated sensitivity to epidrug remedies indicating that BRPF inhibitors have the potential to selectively goal resistant cells (Sup. Fig. 8B). To substantiate whether or not the expansion inhibition noticed in response to the drug combos was on account of cell demise, we assessed apoptotic markers. Combining taxanes and epidrugs resulted in elevated annexin-v staining and caspase 3/7 activation in comparison with utilizing both drug alone (Fig. 3D). Moreover, the G2/M arrest of resistant PCa cells by BRPF inhibitors gives additional assist for the restoration of taxane sensitivity (Fig. 3E and Sup. Fig. 8C). Lastly, elevated BRPF1 expression was discovered to be related to elevated expression of the cell development indicator, mKI67, in sufferers with metastatic PCa, offering proof for its position in selling mobile proliferation pathways (Fig. 3F).
A Validation dose-response curves of BRPF inhibitors (PFI4, GSK5959 and OF1) on Dtx-resistant cells. Cells had been co-treated with indicated medicine (Dtx; 1–250 nM and BRPF inhibitors; 1.25–5 µM) and the outcomes had been obtained by SRB viability assay (72 h). The information is expressed as imply ± SEM. B Warmth map illustration of the Mixture Index (CI) values, with pink shade indicating a synergistic impact. CI was calculated utilizing the CalcuSyn software program. C Clonogenic photographs had been obtained by treating cells with indicated medicine for 72 h and the colony formation skill was analyzed 10–15 days after drug publicity. D Circulation cytometry evaluation of cell demise (48 h) and (E) cell cycle distribution (24 h) in resensitized Du145-DtxR cells. F The expression of BRPF1 confirmed a optimistic correlation with MKi67 expression in metastatic PCa. G Calcein retention assay was carried out within the absence or presence of BRPF inhibitors (5 µM, 24 h). H CETSA for in-cell ABCB1 engagement. Western blots exhibiting thermostable ABCB1 following indicated warmth shocks (44 °C, 46 °C, 48 °C, 50 °C and 52 °C) within the presence of Zosuquidar (5 µM) and GSK5959 (5 µM) in Du145-DtxR cells. I The expression of ABCB1 was evaluated by qRt-PCR on the indicated time factors following remedy with GSK5959 (5 µM). P parental, R resistant. Uncropped western blot photographs equivalent to H had been proven in Supplemental Materials.
Primarily based on the obvious position of ABCB1 in taxane response (Sup. Determine 5), it’s affordable to invest that these inhibitors may intrude with its perform. To check this, we carried out calcein efflux assay with BRPF inhibitors. Regardless of lowered calcein accumulation in resistant cells on account of excessive ABCB1 expression, inexperienced fluorescence considerably elevated with all BRPF inhibitors, supporting their potential position in inhibiting ABCB1 perform (Fig. 3G, Sup. Determine 8D). It may very well be assumed that these epidrugs could be efficient by binding to ABCB1. To analyze the potential binding of BRPF inhibitors with ABCB1, we carried out CETSA in opposition to ABCB1. Zosuquidar, a identified inhibitor of ABCB1, was used as a optimistic management and never surprisingly, it confirmed an ABCB1-binding in comparison with DMSO (Fig. 3H). Alternatively, BRPF inhibitors didn’t trigger any thermal shift, subsequently we concluded as they don’t interact with ABCB1 bodily (Fig. 3H, Sup. Determine 8E). The restoration of taxane sensitivity in resistant cells may be attributed to downstream mechanisms relatively than direct binding to ABCB1. Certainly, a time-dependent lower within the expression of ABCB1 was noticed upon remedy with GSK5959 (Fig. 3I). Moreover, the dearth of cytotoxic results noticed in RPE-1 cells upon remedy with BRPF inhibitors gives promising proof for his or her potential therapeutic software (Sup. Determine 8F). The differential response to epidrug remedies between delicate and resistant cells could be attributed to the expression of ABCB1. Certainly, knocking out ABCB1 within the resistant cells abolished the effectiveness of BRPF inhibitors, suggesting that the impact of BRPF inhibitors relies on the presence of ABCB1 (Sup. Fig. 9).
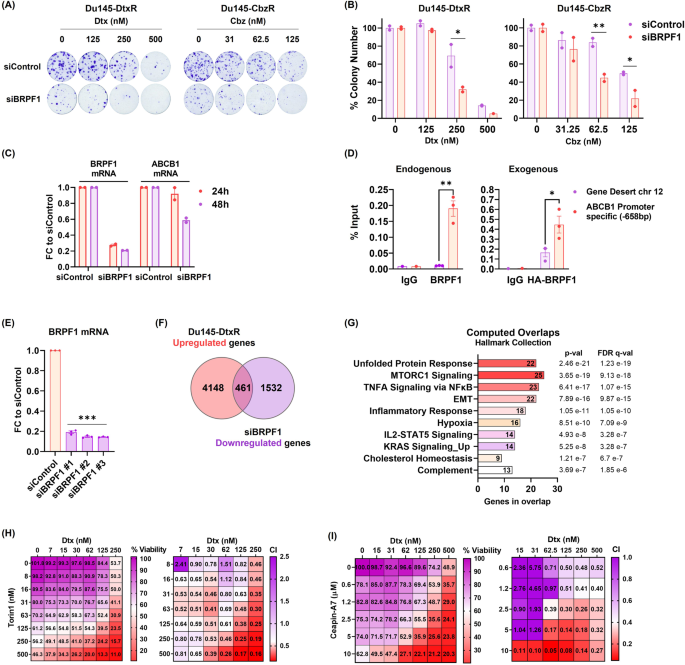
So as to examine whether or not the impact of BRPFi could be recapitulated utilizing gene focusing on, we employed each CRISPR-guided knockout and siRNA-mediated silencing methods. A number of makes an attempt to generate BRPF knock out cells failed, as resistant cells didn’t survive following introduction of focused gRNAs indicating that the exercise of BRPF1 gene grew to become important for the resistance phenotype. Alternatively, short-term depletion, as within the case of RNA interference, was relevant. The colony formation assay confirmed that knockdown of BRPF1 suppressed the power to kind colonies (Sup. Determine 10A). Nevertheless, this impact was noticed to be extra intense in resistant cells, as soon as once more exhibiting the essentiality of BRPF1 in resistant cells. Certainly, secure and particular knock-down of BRPF1 led to the next variety of apoptotic cells in Dtx-resistant cells (Sup. Fig. 10B, C).
Whereas not as pronounced because the impact seen with pharmacological inhibition, knockdown of BRPF1 additionally led to the resensitization of cells to taxanes (Fig. 4A, B). We additionally famous a lower in ABCB1 expression upon BRPF1 knockdown (Fig. 4C). The noticed lower in ABCB1 expression with each pharmacological and genomic suppression implies a possible position of BRPF1 in transcriptional regulation. So as to check whether or not BRPF1 instantly regulates ABCB1 expression, we analyzed the enrichment of BRPF1 on the promoter of ABCB1 in Du145-DtxR cells utilizing ChIP assay. We discovered that, compared with IgG and gene desert area controls, BRPF1 was certainly enriched on the promoter area of ABCB1 (Fig. 4D). To get rid of potential off-target results of the endogenous BRPF1 antibody, HA-ChIP was carried out utilizing exogenous expression of BRPF1, as soon as once more exhibiting enrichment on the ABCB1 promoter, additional supporting BRPF1-mediated regulation of the ABCB1 gene.
A Taxane response of siBRPF1 handled resistant cells evaluated by colony formation assay. Consultant photographs and (B) quantifications are proven. C The expression of ABCB1 was evaluated by qRt-PCR on the indicated time factors following remedy with siBRPF1 in Du145-DtxR cells. D ChIP-qPCR exhibiting BRPF1 enrichment on the ABCB1 promoter in Du145-DtxR cells expressing endogenous BRPF1 (left panel) and exogenous HA-tagged BRPF1 (proper panel). BRPF1 enrichment at a management area (Chr12 gene desert) can also be proven. Information are proven as share of ChIP enter; dots signify particular person organic replicates; bars signify imply replicates. E BRPF1 mRNA ranges of RNA-seq samples from siControl and siBRPF1 in Du145-DtxR cells. F Venn diagram exhibiting the variety of genes (intersection, 461) whose expression decreased after silencing of BRPF1 amongst genes with elevated expression in Du145-DtxR cells (vs Du145-P). G Computed overlaps of the 461 genes within the Hallmark Assortment of GSEA (MSigDB) database. H The efficacy of Torin1 (mTORC1/2 inhibitor, 8–500 nM) on Du145-DtxR cells was decided by CTG assay and represented as a warmth map. I The efficacy of Ceapin-A7 (ATF6α inhibitor, 0.6–10 µM) on Du145-DtxR cells was decided by SRB assay and represented as a warmth map. The Mixture Index (CI) was calculated utilizing the CalcuSyn program. Statistical significance denoted as *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.0001.
To know the molecular mechanisms behind BRPF1-mediated reversion of drug resistance, we wished to look at the transcriptome of siBRPF1 handled Dtx-resistant cells (Fig. 4E). We restricted the gene pool of curiosity by filtering the upregulated genes whose expression was beforehand decided in resistant cells (relative to parental cells) however confirmed an wrong way of regulation after siBRPF1 remedy (Fig. 4F and Sup. Fig. 11). Among the many pathways/sign transductions during which a complete of 461 genes overlaps within the GSEA (MSigDB) database (Hallmark Assortment), mTORC1 and Unfolded Protein Response (UPR) have emerged as essentially the most important overlaps (Fig. 4G and Sup. Desk 5). Torin1 (an inhibitor of mTORC1/2) and Ceapin-A7 (an inhibitor of ATF6α, which is certainly one of three foremost UPR sensors) had been used to evaluate the essentiality of those pathways in reversing resistance. Administration of the inhibitors restored the sensitivity of resistant cells to Dtx, whereas having no impact on the response of delicate cells, mimicking the impact noticed with BRPF inhibitors (Fig. 4H, I and Sup. Fig. 12). These observations recommend that BRPF1 might exert a regulatory position in modulating ABCB1 expression via its interplay with the UPR and mTORC1 signaling pathways. Certainly, the mixture of ABCB1 silencing and mTOR inhibition enhances the sensitization of cells to taxanes, suggesting a mechanism involving a number of downstream pathways regulated by BRPF1 (Sup. Fig. 13). These outcomes point out the involvement of various mechanisms in overcoming taxane resistance. The mixed focusing on of ABCB1 and mTOR pathways might act via complementary mechanisms, equivalent to inhibiting drug efflux and modulating intracellular signaling cascades, in the end resulting in the restoration of drug sensitivity.
Upon inspecting the practical clusters of upregulated genes with siBRPF1 remedy, it was affordable to look at the emergence of gene units associated to PCa, equivalent to “androgen response” or “mitotic spindle” and “G2M checkpoint”, given the mechanism of motion of taxanes (Sup. Fig. 11). Complete research are wanted to research the importance of those genes in taxane resistance (Sup. Desk 6).
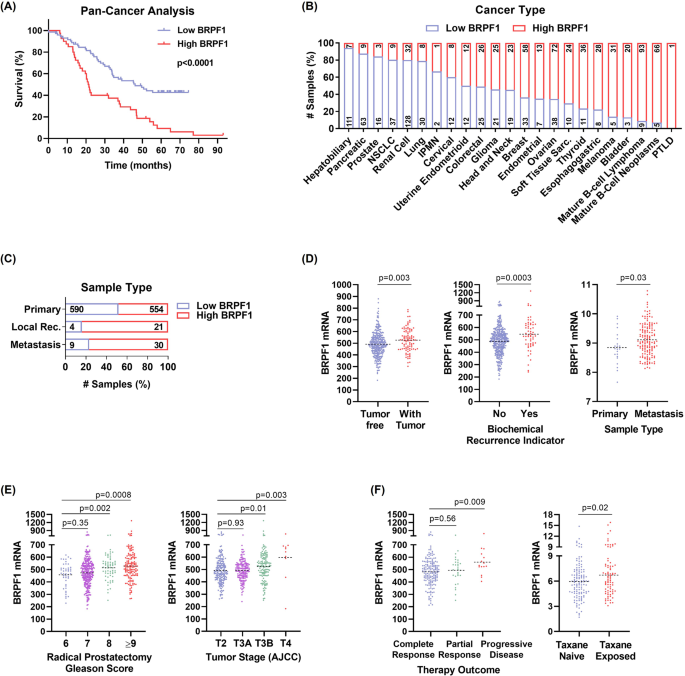
We analyzed publicly accessible medical knowledge and initially carried out a pan-cancer evaluation. We divided the sufferers into high and low BRPF1 expression teams utilizing the median values decided by the cBioPortal (Fig. 5). Our findings demonstrated a big lower within the general survival of sufferers exhibiting excessive ranges of BRPF1 expression (Fig. 5A). Additional evaluation of the precise most cancers sorts revealed greater BRPF1 expression in lymphoma, whereas decrease expression ranges had been noticed in hepatobiliary, pancreatic, and prostate cancers (Fig. 5B). Within the evaluation of pattern sorts, we noticed the next expression of BRPF1 in native recurrence and metastasis (Fig. 5C). This discovering was additional supported by the elevated BRPF1 ranges noticed in sufferers with tumors in comparison with these with out tumors (Fig. 5D). Furthermore, BRPF1 expression may be a possible recurrence indicator, as greater expression was noticed in sufferers upon recurrence (Fig. 5D). Supportingly, its expression was discovered to be elevated in metastatic samples (Fig. 5D). These findings recommend that regardless of being categorized within the low BRPF1 group, the expression of BRPF1 in PCa could also be implicated in illness development. Certainly, we discovered a big affiliation between BRPF1 expression ranges and PCa development, with greater expression ranges being correlated with growing Gleason rating and tumor stage (Fig. 5E). BRPF1 expression additionally appears to mirror remedy consequence, as sufferers with greater expression ranges are inclined to have a poorer response to remedy and extra progressive illness (Fig. 5F). Moreover, it’s noteworthy that a rise in BRPF1 expression was noticed in sufferers who had been uncovered to taxane (Fig. 5F), additional emphasizing its potential relevance in remedy consequence and illness development. General, these knowledge spotlight the medical significance of BRPF1 expression as a possible biomarker for PCa development.
A BRPF1 mRNA ranges had been analyzed within the Pan-Most cancers Evaluation dataset (ICGC/TCGA, Nature 2020) from cBioPortal. Kaplan-Meier plot exhibiting the comparability of affected person survival primarily based on BRPF1 expression ranges. The sufferers had been categorised into Low BRPF1 and Excessive BRPF1 teams primarily based on the expression median. The distribution of BRPF1 expression (B) throughout completely different cancers and (C) pattern sorts. The numbers inside the column bars correspond to the pattern measurement. D BRPF1 mRNA ranges in medical PCa specimens had been examined for his or her correlation with neoplasm standing (Prostate Adenocarcinoma, TCGA, PanCancer Atlas), recurrence (Prostate Adenocarcinoma, TCGA, Firehose Legacy), pattern kind (Prostate Adenocarcinoma, Fred Hutchinson CRC, Nat Med 2016) (E) Gleason rating (Prostate Adenocarcinoma, TCGA, Firehose Legacy), tumor stage (Prostate Adenocarcinoma, TCGA, Firehose Legacy), (F) remedy consequence (Prostate Adenocarcinoma, TCGA, Firehose Legacy), and taxane publicity standing (Metastatic Prostate Adenocarcinoma, SU2C/PCF Dream Group, PNAS 2019). The outcomes had been introduced as scatter plots.
The evaluation of BRPF gene expression in our isogenic cells indicated minimal modifications general, with variations noticed amongst PCa cells and taxanes (Sup. Fig. 14A). The dearth of noticed enhance in BRPF1 expression in our cells, in contrast to in affected person tissues, may doubtlessly be attributed to the developed drug resistance that has change into power in cells. However, there may very well be variations in BRPF actions between resistant and parental cells, which warrants additional investigation. If this was certainly related to a power state, our speculation was that PCa parental cells might acutely enhance BRPF expression following taxane publicity, as supported by the commentary of BRPF1 upregulation in PCa sufferers (Fig. 5F). Certainly, the remedy with Dtx resulted in a big enhance within the expression of BRPF1 (Sup. Fig. 14B). As well as, we additionally noticed an upregulation of ABCB1 expression following Dtx remedy (Sup. Fig. 14B).
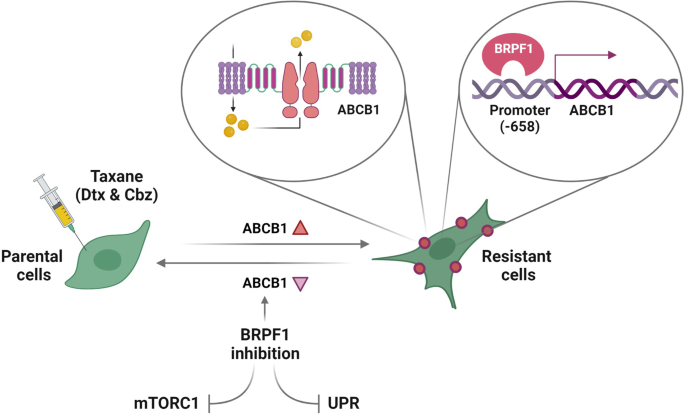
Our findings present the primary proof for (i) the potential of BRPF inhibitors to beat taxane resistance and (ii) the regulatory position of BRPF1 via direct modulation of ABCB1 expression on the promoter stage. Moreover, we confirmed that BRPF1 might not directly regulate ABCB1 expression by interfering with UPR and mTORC1 signaling pathways. The graphical summary summarizing the examine is depicted in Fig. 6.