Phenotypic adjustments in breast most cancers cell strains throughout CDK4/6 inhibition
The organic adjustments that happen throughout CDK4/6 inhibition have been assessed in T47D (HR+/HER2-/HER2-enriched), MCF7 (HR+/HER2-/Luminal B), and BT474 (HR+/HER2+ /HER2-enriched) breast most cancers cell strains. Regardless of being HER2+ , the inclusion of the BT474 cell line to our examine might be of relevance because it belongs to the HER2-enriched subtype by PAM50, and palbociclib has been proven to be much less environment friendly in HR+/HER2+/HER2-enriched breast most cancers19. Furthermore, it has been proven that, aside from the amplification and RNA/protein overexpression of ERBB2 in HER2+ tumors, very minor organic variations exist at DNA, RNA, and protein ranges between HER2+/HER2-enriched and HER2-/HER2-enriched tumors32.
First, we analyzed the proliferation inhibitory impact of palbociclib and ribociclib +/− fulvestrant in opposition to all three cell strains and located that each CDK4/6 inhibitors had very comparable results (Fig. 1A, Supplementary Fig. 1A). In T47D and MCF7 cells, the mix of CDK4/6 inhibitors plus fulvestrant was superior than palbociclib or ribociclib alone, whereas in BT474 no important variations have been noticed between the mix of CDK4/6 inhibitors with fulvestrant and palbociclib or ribociclib alone (Supplementary Fig. 2A).
Organic adjustments throughout CDK4/6 inhibition in vitro. (A) T47D and MCF7 cells have been handled with growing doses of palbociclib or ribociclib +/− fulvestrant (1 nM) for 72 h. Proven are consultant graphs of cell viability redouts decided by Hoechst 33342. Information was normalised to untreated cells and three impartial experiments have been carried out. Imply values ± SEM are proven. (B) T47D and MCF7 cells have been handled with palbociclib or ribociclib (100 or 500 nM) for twenty-four, 72 or 144 h and expression of p-RB1 and Lamin-B1 was assessed by western blot. Actin was used as a loading management. (C) T47D and MCF7 cells have been handled with palbociclib or ribociclib (100 or 500 nM) for twenty-four, 72 or 144 h and SA-β-gal exercise was decided by move cytometry. Information was normalised to untreated cells and three impartial experiments have been carried out. Imply values ± SEM are proven.
RB1-competent T47D and MCF7 cell strains have been handled with two totally different doses of palbociclib or ribociclib (i.e., 100 or 500 nM) for various intervals of time (i.e., 24, 72, or 144 h) in an effort to assess adjustments within the phosphorylation of RB1 (p-RB1). In T47D and MCF7 cells therapy with 100 nM CDK4/6 inhibitors partially lowered p-RB1 with an additional lower in cells handled with 500 nM palbociclib or ribociclib no matter therapy length (Fig. 1B). Whole RB1 mRNA expression didn’t change after CDK4/6 inhibition (Supplementary Fig. 3). The cytotoxic impact of palbociclib and ribociclib was additionally assessed within the RB1-mutated MDA-MB-468 cell line to make sure that no off-target results got with the chosen doses (i.e., 100 or 500 nM) (Supplementary Fig. 2B).
Subsequent, the impact on mobile senescence was assessed upon therapy with CDK4/6 inhibitors by figuring out protein expression ranges of Lamin-B1, a structural part of the nucleus whose loss has been related to senescence33,34. In T47D and MCF7 cells, CDK4/6 inhibitors decreased the expression of Lamin-B1 in a time and dose-dependent method, with the bottom expression ranges akin to these handled with 500 nM palbociclib or ribociclib for 144 h (Fig. 1B). Moreover, we assessed the senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-β-gal) exercise. Each palbociclib and ribociclib (100 or 500 nM) elevated β-galactosidase staining in T47D and MCF7 cell strains after 72 or 144 h therapies in comparison with non-treated controls indicating induction of senescence35 (Fig. 1C). Though no important variations have been noticed between therapy situations, a dose- and time-related tendency was noticeable, with the very best β-galactosidase staining ranges akin to cells handled with 500 nM CDK4/6 inhibitors for 144 h. Related adjustments have been noticed in cells handled with palbociclib or ribociclib for all therapy situations (Fig. 1C).
As for the RB1-competent BT474 cell line, a discount of p-RB1 was additionally noticed upon 24 or 72 h therapies with CDK4/6 inhibitors (100 or 500 nM), though p-RB1 ranges have been reestablished 144 h from therapy (Supplementary Fig. 1B). Decrease ranges of β-galactosidase exercise have been detected usually and the very best exercise was detected after 72 h therapies with both CDK4/6 inhibitor, adopted by a lower in mobile senescence 144 h from therapies (Supplementary Fig. 1C). These observations point out that the BT474 cell line might harbor an intrinsic resistance to CDK4/6 inhibition +/− fulvestrant in comparison with the T47D and MCF7 cell strains.
Results of CDK4/6 inhibition on gene expression in breast most cancers cell strains
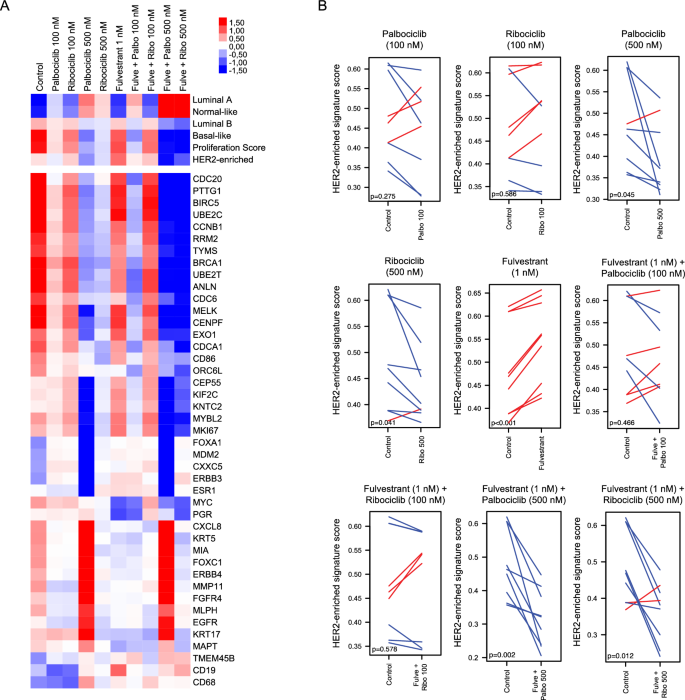
Gene expression profiling was carried out in untreated cells and upon therapy in an effort to establish adjustments within the PAM50 biology induced by CDK4/6 inhibitors in T47D, MCF7, and BT474 cell strains handled with totally different doses of palbociclib and ribociclib (100 or 500 nM) +/− fulvestrant (1 nM). The expression of the 50 genes of the PAM50 intrinsic subtype predictor and 6 signatures (Basal-like, HER2-enriched, Luminal A, Luminal B, Regular-like, and the 11-gene proliferation rating) have been explored at each therapy situations. Paired t-tests and multiclass SAM confirmed that each CDK4/6 inhibitors (100 or 500 nM) +/− fulvestrant (1 nM) considerably elevated (FDR < 5%) the Luminal A and Regular-like signatures and considerably decreased (FDR < 5%) the Basal-like and proliferation signatures (Fig. 2A, Supplementary Fig. 4). Apparently, the HER2-enriched signature was solely considerably lowered when the CDK4/6 inhibitors got at 500 nM both alone (palbociclib p = 0.045, ribociclib p = 0.041) or together with fulvestrant (palbociclib p = 0.002, ribociclib p = 0.012), whereas no important adjustments have been noticed with 100 nM CDK4/6 inhibitor monotherapy (palbociclib p = 0.275, ribociclib p = 0.596) or together with fulvestrant (palbociclib p = 0.466, ribociclib p = 0.613) (Fig. 2A,B). Therapy with fulvestrant alone considerably elevated the HER2-enriched signature (p < 0.001) (Fig. 2A,B).
Modifications within the HER2-enriched signature upon therapy with CDK4/6 inhibitors +/− fulvestrant in vitro. (A) Heatmap of a multiclass SAM representing the PAM50 molecular subtypes, proliferation rating and genes which might be differentially expressed (FDR < 5%) in T47D, MCF7, and BT474 cells handled with CDK4/6 inhibitors (100 or 500 nM) +/− fulvestrant (1 nM). Three impartial mRNA extractions per cell line have been carried out. (B) Paired samples t-test analyses displaying adjustments within the HER2-enriched signature following therapy of T47D, MCF7, and BT474 cells with CDK4/6 inhibitors (100 or 500 nM) +/− fulvestrant (1 nM). Three impartial mRNA extractions and gene expression analyses have been carried out for every cell line.
Subsequent, we assessed particular person gene expression throughout therapies utilizing multiclass SAM. Forty-three (64.2%) genes have been differentially expressed throughout therapy teams (FDR < 5%). Notably, each inhibitors, particularly at 500 nM, led to a decrease expression of proliferative genes (e.g.: CDC20, UBE2C, KNTC2, MKI67, BIRC5, CDCA1, PTTG1, CEP55, TYMS, and RRM2). Apparently, in decrease doses of CDK4/6 inhibitors (100 nM) the mix of fulvestrant and palbociclib had a stronger inhibitory impact over cell proliferation than the mix of fulvestrant and ribociclib. Moreover, we carried out a paired SAM evaluation to examine the variations between 500 nM of palbociclib vs 500 nM ribociclib with or with out fulvestrant. A proportion of 19.4% and 25.3% of genes have been differentially expressed after therapy with 500 nM of palbociclib vs 500 nM ribociclib with or with out fulvestrant, respectively (Supplementary Desk 1). Apparently, a better expression of the HER2-enriched genes FGFR4 and TMEM45B was noticed in cells handled with 500 nM palbociclib in comparison with these handled with 500 nM ribociclib with and with out fulvestrant (Fig. 2A).
Early in vivo organic adjustments throughout CDK4/6 inhibitor in tumor samples from CORALLEEN and NeoPalAna section II research
To establish molecular adjustments induced by CDK4/6 inhibitors, we carried out gene expression analyses in baseline, day 15, and surgical procedure tumor samples of sufferers handled with ribociclib plus letrozole within the CORALLEEN trial (Fig. 3A) in addition to in baseline, day 15, and surgical procedure samples of sufferers handled with palbociclib plus anastrazole within the NeoPalAna trial (Fig. 3B).
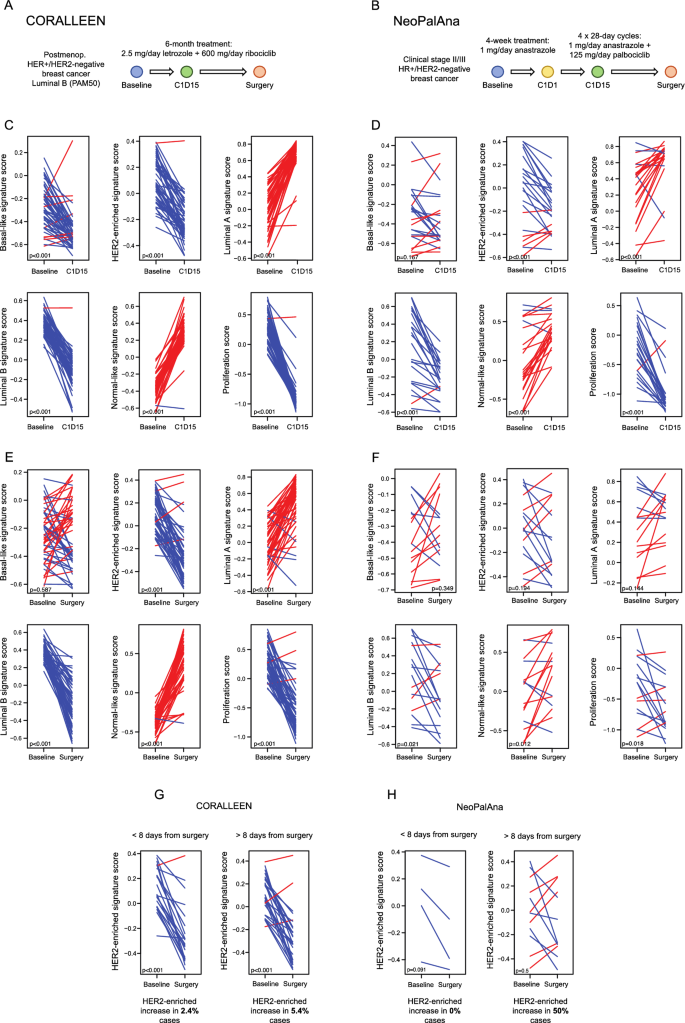
Modifications within the PAM50 signatures within the CORALLEEN and NeoPalAna research. Schematic summaries of the samples analyzed from (A) the CORALLEEN trial design and (B) the NeoPalAna trial design. (C) Paired samples t-test analyses displaying adjustments in the PAM50 signatures at cycle 1 day 15 (C1D15) in tumor samples from CORALLEEN and (D) NeoPalAna section II research. (E) Modifications within the PAM50 signatures at surgical procedure in tumor samples from CORALLEEN and (F) NeoPalAna. (G) Modifications within the HER2-enriched signature in tumor samples from CORALLEEN and (H) NeoPalAna from sufferers who underwent surgical procedure ≤ 8 or > 8 days from the final dose of CDK4/6 inhibitors + endocrine remedy.
First, we assessed early adjustments in 49 paired baseline and day 15 tumor samples from the CORALLEEN trial (Fig. 3C) and 23 paired baseline and day 15 tumor samples from the NeoPalAna trial (Fig. 3D). Therapy with ribociclib and endocrine remedy led to a major enhance in Luminal A (p < 0.001) and Regular-like (p < 0.001) signatures and a major lower in Basal-like (p < 0.001), HER2-enriched (p < 0.001), Luminal B (p < 0.001) and proliferation (p < 0.001) signatures (Fig. 3C). Equally, therapy with palbociclib plus endocrine remedy led to a major enhance in Luminal A (p < 0.001) and Regular-like (p < 0.001) signatures and a major lower in HER2-enriched (p < 0.001), Luminal B (p < 0.001) and proliferation (p < 0.001) signatures (Fig. 3D).
Organic adjustments after CDK4/6 inhibitor in tumor samples from CORALLEEN and NeoPalAna section II research
Subsequent, we assessed adjustments in 49 paired baseline and surgical procedure tumor samples from the CORALLEEN (Fig. 3E) and 16 paired baseline and surgical procedure tumor samples from the NeoPalAna (Fig. 3F).
Therapy with ribociclib and endocrine remedy led to a major enhance in Luminal A (p < 0.001) and Regular-like (p < 0.001) signatures and a major lower in HER2-enriched (p < 0.001), Luminal B (p < 0.001), and proliferation (p < 0.001) signatures (Fig. 3E). Therapy with palbociclib plus endocrine remedy led to a major enhance within the Regular-like (p = 0.012) signature and a major lower within the Luminal B (p = 0.021) and proliferation signature (p = 0.018) (Fig. 3F). Importantly, the HER2-enriched signature didn’t lower in surgical samples of sufferers handled with palbociclib (p = 0.194), though a distinction in pattern measurement may clarify this consequence (Figs. 3F).
In CORALLEEN, the median variety of days between the final dose of ribociclib and surgical procedure was 13.1 days (vary: 1–78)36, whereas in NeoPalAna the median variety of days between the final dose of palbociclib and surgical procedure was 29 days (vary: 8–49), aside from 8 sufferers who obtained further 10–12 days of palbociclib instantly earlier than surgical procedure17. In sufferers from CORALLEEN, the HER2-enriched signature was considerably decreased in sufferers who underwent surgical procedure at 8 days from the final dose of ribociclib or earlier than (p < 0.001), in addition to in those that underwent surgical procedure after > 8 days from the final dose of ribociclib (p < 0.001) (Fig. 3G). In 4 sufferers from NeoPalAna who underwent surgical procedure at 8 days from the final dose of palbociclib or earlier than, a bent of discount within the HER2-enriched signature was additionally noticed. Nevertheless, in sufferers who underwent surgical procedure after > 8 days from the final dose of palbociclib, the HER2-enriched signature elevated in 50% of the circumstances (Fig. 3H).