1 Introduction
With 19.3 million new instances and 10 million deaths in 2020, most cancers is a number one reason behind untimely demise and a big barrier to growing life expectancy for the worldwide inhabitants (1, 2), and ends in excessive social medical bills and private monetary burden (3, 4). To this point, most cancers stays a serious public drawback that threatens the well being of the inhabitants. Elevated common life expectancy and the prevalence of unhealthy life, equivalent to sedentary habits (SB), excessive consumption of tobacco and alcohol, and non-Mediterranean Western dietary patterns, characterised by excessive sugar and calorie content material, have additional elevated most cancers danger (5). The widespread prevalence of those danger elements amongst younger adults can be a possible reason behind the progressively earlier age of most cancers onset (6). Advances in early screening and therapy applied sciences have benefited a subset of most cancers survivors who’ve longer survival instances; therefore, the necessity to guarantee the standard of life (QoL) for most cancers survivors has turn out to be a vital consideration for clinicians (7). Furthermore, lowered ranges of bodily exercise (PA) as a result of a sedentary life-style are a non-negligible reason behind most cancers (8, 9).
In recent times, researchers have begun to give attention to the importance of modifiable behavioral elements in most cancers growth and development, notably the potential associations amongst SB, PA, and most cancers. Quite a few epidemiological research have discovered that acceptable PA reduces the danger and improves the prognosis of a number of cancers, whereas SB has the precise reverse impact (10, 11). Nonetheless, SB and low PA ranges have gotten more and more widespread in trendy life, each within the wholesome inhabitants and amongst most cancers survivors. In 2018, the American School of Sports activities Medication performed a roundtable on the correlations between PA, SB, and most cancers, which reported on the unfavorable significance of SB in relation to most cancers prevalence and prognosis, whereas offering preliminary proof to assist the constructive position of PA in stopping a number of cancers and growing the life expectancy of most cancers survivors (12). Train oncology has obtained growing consideration within the discipline of most cancers therapy and supportive care (13, 14). Nonetheless, the efficient translation of train oncology into scientific observe stays a problem. Given the potential worth of those modifiable behavioral elements in major most cancers prevention and supportive most cancers care, quite a few publications have emerged; nonetheless, the buildup of publications has additionally triggered difficulties for researchers in figuring out present analysis hotspots and future frontier points. Subsequently, new patterns of literature search are urgently wanted.
Bibliometrics is a technique involving qualitative and quantitative evaluation of publications in particular fields, which makes use of a mixture of arithmetic and statistics to determine primary options, information constructions, present hotspots, and analysis frontiers (15, 16). Bibliometrics can be utilized to determine essentially the most influential nations, authors, establishments, journals, and publications, synthesizing and visualizing key data from completely different disciplines (17–20). There have been a number of scientometric research on train and most cancers, together with on the molecular mechanisms underlying the consequences of train on most cancers (21) and rehabilitation train in sufferers with most cancers (22); nonetheless, no research offering a extra complete and systematic scientometric evaluation of this discipline have been performed. We due to this fact hypothesize that bibliometrics can present a complete evaluation and evaluation of analysis hotspots and future frontiers on this discipline. To check our speculation above, we performed a information mapping research of publications associated to SB and PA within the context of most cancers to summarise (i) particulars of the highest authors, nations, establishments, and journals. (ii) insights on areas of sturdy publication and obvious deficits. (iii) rising analysis tendencies and future frontier on this discipline. Particularly, our analysis focuses on PA, and SB throughout your entire most cancers continuum, as these modifiable elements play a vital position in most cancers analysis from major prevention to therapy to survivorship. The outcomes will allow investigators to higher align their analysis inquiries and assist funding businesses perceive topical and rising analysis areas.
2 Supplies and strategies
2.1 Bibliometric search technique
Our major query involved the 20-year analysis tendencies in PA, SB, and most cancers. In our preliminary assessment, we discovered that publications associated to PA and SB within the context of most cancers are comparatively scarce earlier than 2001. Subsequently, eligible research revealed from January 2001 to October 2022 had been retrieved from the Internet of Science Core Assortment (WoSCC, Clarivate Analytics). The WoSCC database offers a complete information supply for scientometric evaluation and is at the moment essentially the most used database for this kind of analysis (17, 23). The particular search technique is introduced in Supplementary Desk 1. Solely manuscripts revealed in English had been thought-about, and publication varieties chosen had been articles and critiques; convention abstracts, editorial materials, letters to the editor, and feedback had been excluded. Titles and abstracts had been screened by two impartial reviewers. A stream chart for research identification and choice is proven in Determine 1.
2.2 Information statistics and visualization
Key information for publications that met the factors, together with analysis title, writer, analysis establishment, nation/area, journal, publication yr, variety of citations, 2021 affect issue (IF), and references, had been downloaded from WoSCC. Microsoft Excel 2020, OriginPro 2021, VOSviewer (24), the R language package deal, biblioshiny (25), and the Bibliometric on-line evaluation platform (https://bibliometric.com/) had been used for information evaluation and visualization. As well as, the H-index (numbers of each revealed and cited papers ≥ h) was used to determine high-quality authors and manuscripts (26); the H-index is a key bibliometric indicator used to evaluate the general analysis efficiency of researchers, journals, establishments, or nations (27, 28).
3 Outcomes
3.1 Annual Overview of Publications
A complete of 4,382 publications had been recognized as assembly the factors after a assessment of titles and abstracts (81% of unique research and 19% of critiques). Annual numbers of publications on SB and PA in most cancers have elevated considerably over the past twenty years, from 39 in 2001 to 477 in 2021 (Determine 2A). Primarily based on present tendencies, annual publications are anticipated to succeed in 500 in 2025. As well as, the variety of citations has step by step elevated and peaked in 2013 and 2016 (Determine 2B).
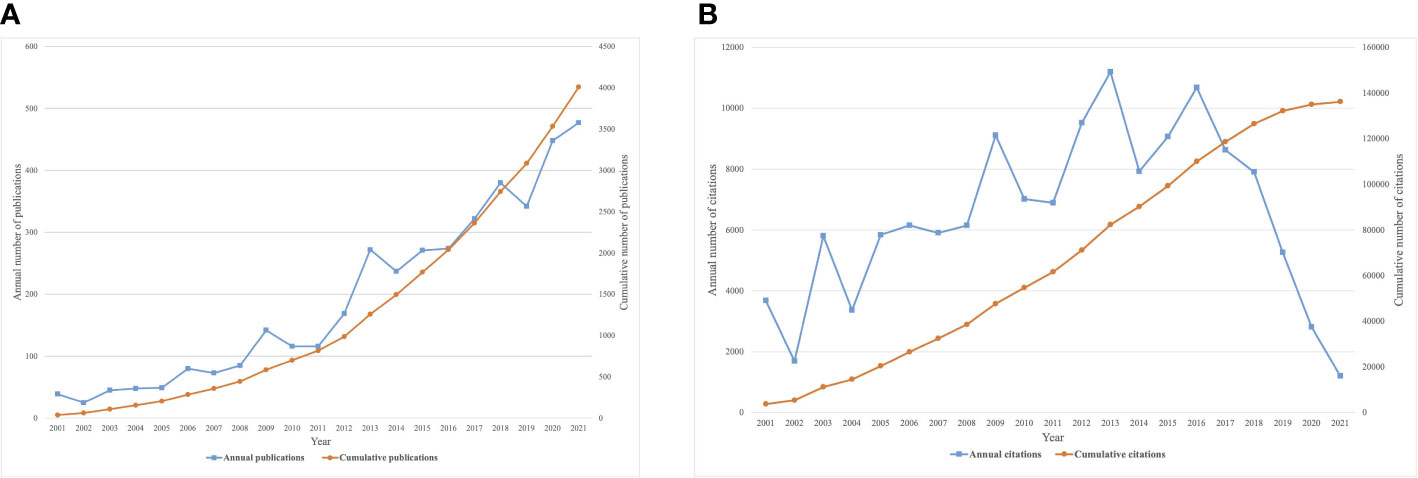
Determine 2 Variety of publications and citations of SB, PA, and most cancers. (A) Annual and cumulative variety of publications; (B) Annual and cumulative variety of citations.
3.2 Distribution of nations/areas
In complete, authors from 77 nations and territories contributed to analysis advances within the discipline of PA and SB within the context of most cancers, with the biggest variety of publications coming from the USA (39.1%), adopted by Canada (16.4%), Australia (12.5%), the UK (7.8%), China (7.8%), and Germany (6.6%). We additionally analyzed the cooperation relationships between nations (Determine 3A). The outcomes confirmed nearer collaboration between the USA, Canada, and the UK, and fewer collaboration between China and different nations. We additionally discovered that the USA and Canada have been conducting analysis on this discipline for an extended time frame than China and Australia (Determine 3B). When it comes to citations, publications from the USA had the very best quotation frequency (n = 65,133), adopted by Canada (n = 30,986), Australia (n = 17,058), and the UK (n = 14,118).
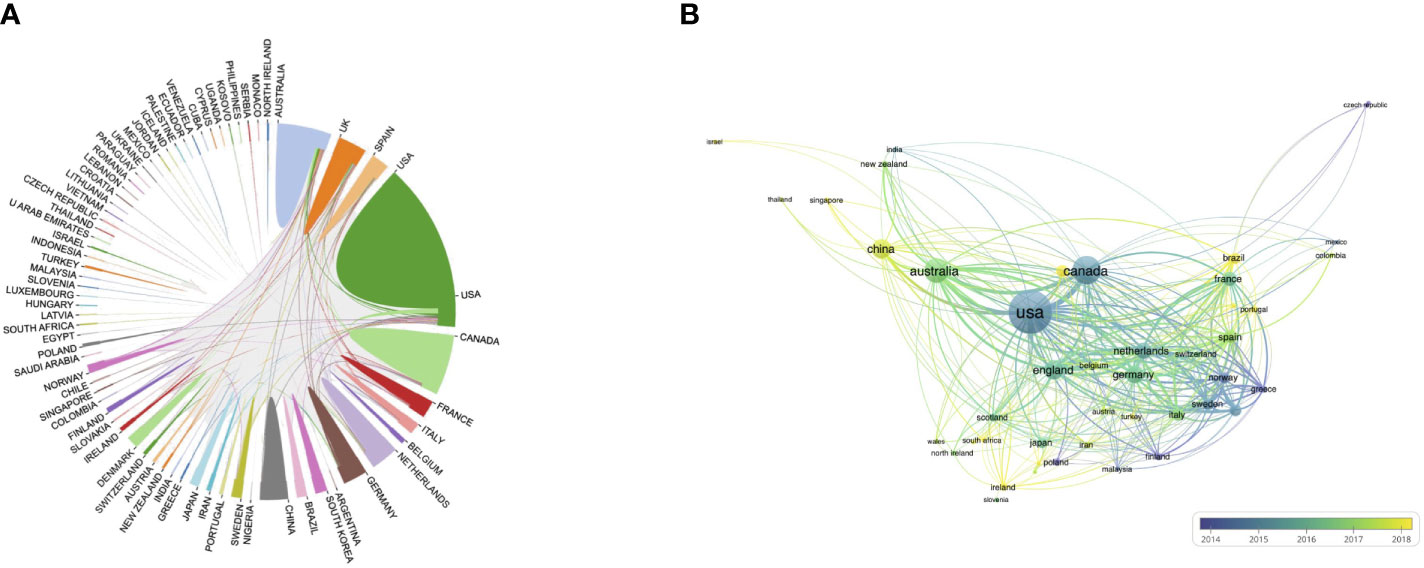
Determine 3 Distribution of nations related to SB, PA, and most cancers. (A) Worldwide collaboration between nations/areas (B) Temporal development of nation/area collaboration.
3.3 Journal distribution
A complete of 756 journals revealed analysis on PA and SB in most cancers throughout our research interval. The highest 10 main journals revealed a complete of 1207 publications. Amongst them, Supportive Care in Most cancers had the very best variety of publications (n = 329), adopted by Most cancers Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention (n = 125), and BMC Most cancers (n = 119) (Determine 4A). When it comes to citations, the Journal of Scientific Oncology, which is among the many most influential journals within the discipline of oncology, ranked first, with 46 publications receiving 8585 citations, adopted by Most cancers Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention (7215 citations), Supportive Care in Most cancers (7215 citations), and Psycho-Oncology (6435 citations) (Determine 4B). As well as, Most cancers Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention had the very best H-index, indicating the upper high quality of manuscripts revealed on this journal (Determine 4C).
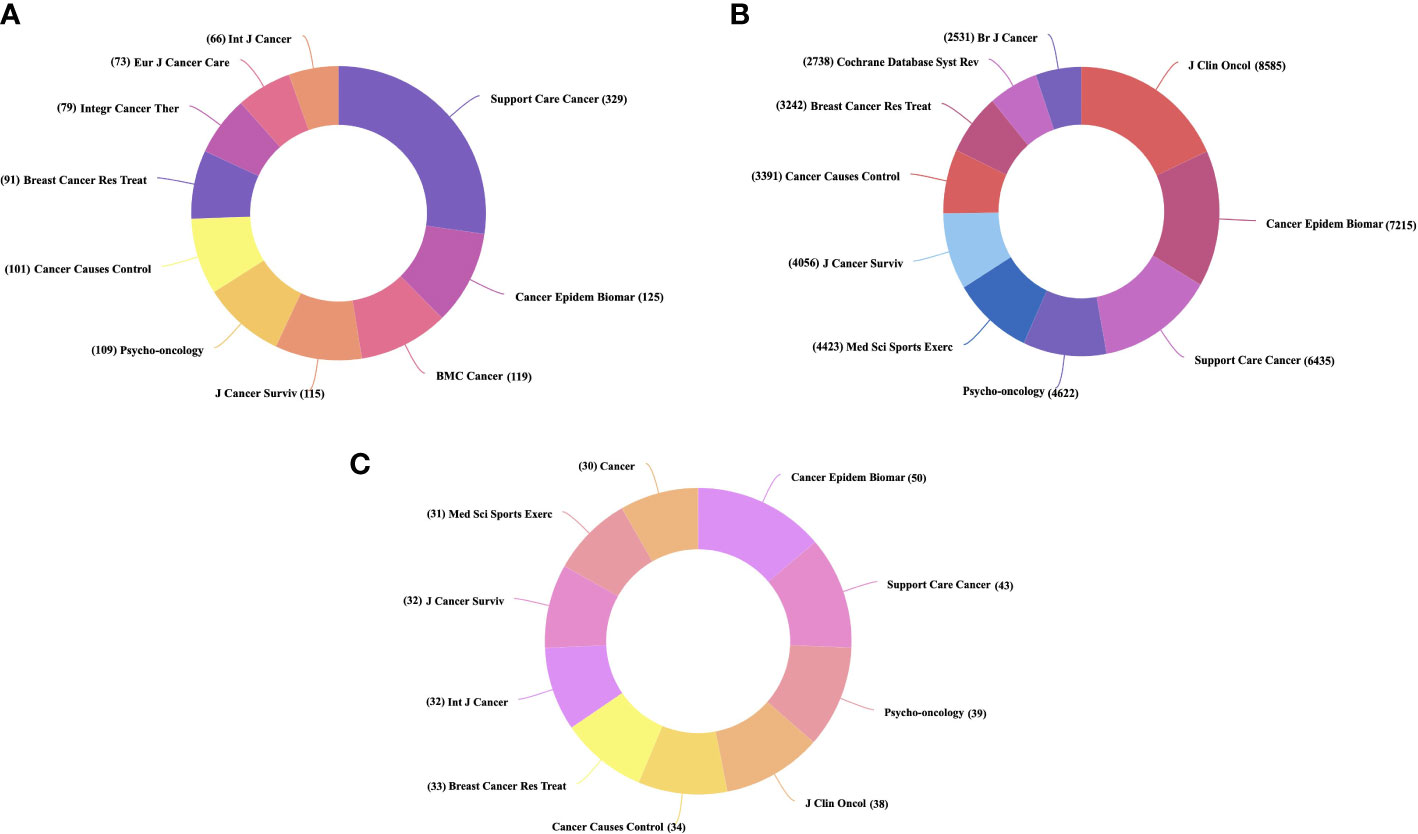
Determine 4 Distribution of Journals related to SB, PA, and most cancers. (A) Prime 10 journals with the very best variety of publications (B) Prime 10 journals with the very best variety of citations (C) Prime 10 journals with the very best H-index.
3.4 Best authors and establishments
Essentially the most influential authors recognized, based mostly on the variety of publications ≥ 40, are listed in Determine 5A; These outstanding contributors are primarily from Canada, the USA, and Australia. Essentially the most prolific writer was Ok.S. Courneya, with 240 publications over the last 20 years, who additionally obtained the very best variety of citations (7,719) and H-index (66). C.M. Friedenreich and L.W. Jones ranked second and third, respectively. As well as, we analyzed the collaborations of extremely productive authors within the discipline (Supplementary Determine 1) and recognized a number of key analysis groups, together with Ok.S. Courneya, R.U. Newton, and Ok.H. Schmitz. These authors are main impartial analysis groups that every have sturdy connections with numerous different authors. Additional, we analyzed the best establishments (Determine 5B), based mostly on the variety of publications ≥ 80, and located that the College of Alberta, the College of Calgary, and the College of Queensland had been the highest three establishments, with the very best numbers of revealed papers, with the College of Alberta had the very best H-index. Particulars of the highest 30 most efficient authors and establishments are supplied in Supplementary Tables 2, 3.

Determine 5 Distribution of essentially the most influential authors and establishments. (A)The best authors. (B) The best establishments.
3.5 Evaluation of key publications
Reference evaluation is a vital technique for assessing the affect of particular person publications/analysis. As well as, mining and evaluation of extremely cited research will help determine analysis hotspots and inform subsequent analysis. Right here, we reported the highest 10 publications with the minimal variety of complete citations over 600 (29–38). Holmes et al. performed a potential observational research to evaluate the impact of PA on the danger of demise from breast most cancers, and concluded that survivors of breast most cancers who walked a median of three–5 hours per week had the bottom danger of demise (29). As well as, PA had a big constructive impact on vanity and chemotherapy completion charges of sufferers with most cancers (34). A number of research have synthesized the potential associations of PA and SB in sufferers with most cancers; usually, they discovered that acceptable PA is helpful for each tumorigenic burden and prognosis of most cancers survivors (30, 32, 33, 35, 38). Notably, a research by Moore et al. discovered that PA was related to a excessive danger of malignant melanoma and prostate most cancers (35). Rock et al. supplied pointers and proposals of PA for sufferers with most cancers (at the very least 150 min of train per week) (31). Given the quite a few excellent publications within the discipline, Supplementary Desk 4 reveals the highest 100 most cited publications.
3.6 Evaluation of hotspots and tendencies in analysis
VOSviewer was used to investigate and visualize ‘Key phrases’ and ‘Key phrases Plus’ in publications, to determine analysis hotspots and future frontiers. Determine 6A reveals excessive frequency (> 80) key phrase co-occurrence mapping within the discipline of PA and SB in most cancers. We modified some key phrases; for instance, we unified “health-related high quality of life” and “quality-of-life” as “high quality of life”. We additionally eliminated some descriptive key phrases equivalent to “bodily exercise”, “sedentary habits”, “train”, “well being”, and “most cancers”. The remaining core key phrases could be divided into three clusters: (i) “breast most cancers”, (ii) “high quality of life”, and (iii) “cardio train”. After that, we ranked the time of prevalence of all key phrases to determine potential analysis tendencies and future frontiers. Determine 6B reveals that analysis tendencies up to now 5 years have included train oncology, distant intervention, and social assist for PA, amongst others. As well as, the analysis hotpots and tendencies matters on PA and SB within the context of most cancers had been summarized based mostly on the PICOS assertion (Supplementary Desk 5).
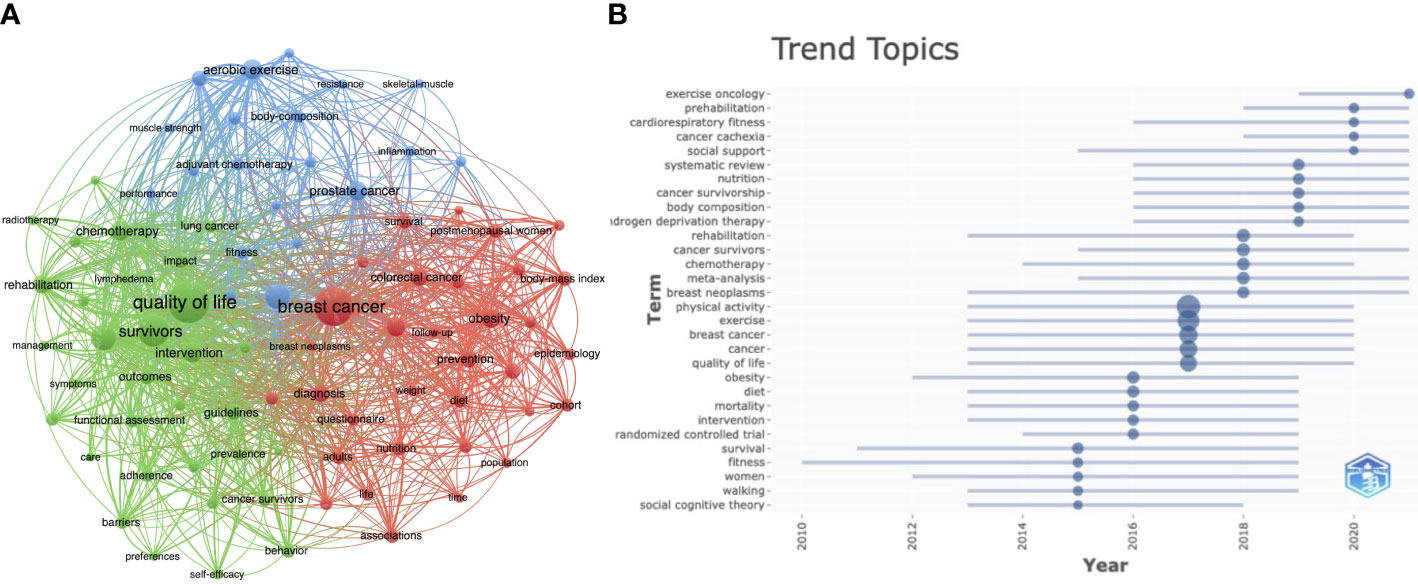
Determine 6 Evaluation of Hotspots and Developments in Analysis. (A) Key phrase co-occurrence visualization map. (B)Timeline of analysis tendencies within the discipline of PA, SB, and most cancers.
4 Dialogue
4.1 Abstract of main findings
Right here, we performed a bibliometric evaluation of publications on PA and SB within the context of most cancers over the past twenty years. Total, we discovered {that a} rising variety of research have centered on potential correlations between train and most cancers. Additional, we discovered a big improve within the variety of publications and citations on this discipline from 2001 onwards, for 2 most important causes: first, unhealthy behaviors have gotten extra prevalent within the inhabitants, resulting in a big improve in potential danger elements for most cancers in comparison with twenty years in the past (5); and second, sufferers are surviving for longer durations, benefiting from enhancements in medical care, due to this fact, how one can obtain a greater QoL for most cancers survivors has turn out to be a scorching subject (39, 40). As well as, the potential position of train within the major prevention of most cancers has obtained growing consideration, each from researchers and policymakers (41).We discovered that the USA was essentially the most influential nation, adopted by Canada, Australia, the UK, China, and Germany, with researchers from these nations contributing 90% of publications. The US dominates by way of publication numbers and citations, making outstanding contributions to development of analysis into PA and SB in most cancers. The outstanding contribution from the USA is because of its higher variety of researchers and world-leading analysis establishments. As well as, the US funding in analysis funding has led to higher analysis alternatives and wider worldwide collaborations. Most cancers stays a world problem, which requires nearer cooperation amongst nations to beat bottlenecks. When it comes to worldwide cooperation, the USA, Canada, and the UK cooperate extra carefully with different nations, which is a possible purpose for his or her excessive quotation charges. The College of Alberta, Canada, has the very best variety of publications and H-Index, indicating that the establishment publishes higher-quality articles and may very well be thought-about for additional collaboration and research. When it comes to authors, Ok.S. Courneya, C.M. Friedenreich, and L. W. Jones had the very best H-index values, indicating that they revealed higher-quality research. We discovered that these authors have a lot bigger publications and early pioneers within the discipline (10 years or extra). They’ve revealed extra articles in high journals and have due to this fact obtained extra citations. As well as, it’s straightforward to see that almost all of those authors are from the world’s main analysis establishments and should have a wonderful analysis group with extra grad college students and researchers to assist their extra in-depth research. Along with publishing many high-quality managed scientific research, their revealed complete critiques within the discipline have been well known. The journals which have revealed essentially the most articles on PA and SB in most cancers had been Supportive Care in Most cancers, Most cancers Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention, and BMC Most cancers. Most publications on this discipline give attention to supportive care points in most cancers, particularly signs and QoL, which can align with these journals’ scope. As well as, most research are managed scientific trials with small pattern sizes, which can be simpler to just accept in complete journals reasonably than high journals. We discovered that randomized managed trials (RCTs) with giant samples had been extra prone to be revealed in high journals and to obtain extra citations.
4.2 Analysis hotspots and tendencies
Primarily based on the evaluation of key phrase co-occurrence and assessment of the timelines of analysis subject publication, we categorised analysis hotspots and tendencies within the discipline of PA and SB in most cancers into the matters summarized within the following sections.
4.2.1 SB and PA in sufferers with breast most cancers
Breast most cancers is the most typical most cancers in girls, with greater than 10% of recent instances per yr (1). Earlier research have reported that SB accounts for 70% of modifiable breast most cancers danger elements (42). The standardized incidence of breast most cancers is considerably greater in sedentary girls than in those that sit for much less time (43). As well as, early prognosis and elevated consciousness have improved total survival, with the five-year survival for breast most cancers survivors in the USA to be 90% in 2022 (44). Because of this, extra researchers are specializing in symptom administration, prognosis, and QoL in feminine survivors. They’ve been granted extra particular funding alternatives centered on breast most cancers. SB and low PA ranges are widespread in survivors of breast most cancers. Phillips et al. confirmed that the period (555.7 min) of SB and proportion (66.4%) of survivors of breast most cancers performing SB actions had been 55 min and seven% greater, respectively, than these in wholesome management populations (45). Solely 11% of sufferers had a PA stage that met the guideline-recommended standards (cumulative 95 min of moderate-to-vigorous PA stage) (46). Notably, though the present meta-analysis discovered that SB elevated the danger of breast most cancers by 8-17%, the conclusions weren’t completely constant (47). The 2018 Professional Report of the World Most cancers Analysis Fund/American Institute for Most cancers Analysis indicated that the present energy of proof relating SB to breast most cancers danger are restricted (48). Extra proof assist from high-quality RCTs is required, which is why researchers regularly give attention to this analysis hotspot. Lastly, the organic mechanisms between PA and breast most cancers are usually not but clear and should contain adipokines and estrogen ranges, irritation, and oxidative stress (49), which have attracted numerous preclinical research.
4.2.2 QoL points in most cancers survivors
Well being-related high quality of survival (HRQoL) has turn out to be an vital consider assessing scientific efficacy (50). Generally, survivors of most cancers have higher psychological well being wants, greater ranges of hysteria and melancholy, and poorer HRQoL associated to bodily and psychological well being (51). Because of the instant and long-term results of most cancers and its therapy, most cancers survivors could endure bodily and psychological misery, together with fatigue, decreased bodily efficiency, melancholy, and nervousness (52, 53). QoL is a key benefit of PA, and lots of research have confirmed that PA enhances QoL (54, 55). Most cancers survivors who participated in PA actions had considerably greater QoL than those that didn’t (56). Nonetheless, extra element must be supplied on these associations. A number of research have recognized ethnic/racial variations in PA ranges in breast and colon most cancers sufferers (57, 58). Extra analysis continues to be wanted to disclose PA variations in much less widespread cancers for inhabitants subgroups. Furthermore, future research ought to contemplate the affiliation between PA and different most cancers outcomes, together with signs, therapy negative effects, and prognosis, to find out dose-response relationships between PA and QoL, and to determine mechanisms to clarify these associations. Lastly, the emotion domains are key elements of QoL. Scientific analysis ought to pay extra consideration to the psychiatric elements that affect PA in most cancers survivors, together with cancer-caused fatigue, nervousness, melancholy, self-efficacy, and well being beliefs and engagement.
4.2.3 Cardio train
Lung most cancers constantly ranks excessive amongst malignancies, by way of annual incidence and mortality (44). Train coaching is protected, possible, and efficient in bettering the prognosis of sufferers with lung most cancers, notably these with non-small cell lung most cancers (59). Inspiratory muscle coaching and cardio train enhance lung operate and respiratory muscle energy in postoperative sufferers with lung most cancers, decreasing the danger of sputum retention and postoperative pulmonary issues (60, 61). A meta-analysis confirmed that train coaching lowered total and clinically related postoperative issues in sufferers with non-small cell lung most cancers, in contrast with standard care (62). Cardio train could enhance sleep disturbance, psychological burden, and most cancers treatment-induced cognitive impairment in survivors of breast and colon most cancers (63–65). Notably, strolling (cardio) is the simplest and most most popular and accessible train for most cancers survivors. There may be nonetheless a necessity for analysis on different varieties and types of train, equivalent to high-intensity interval coaching, resistance coaching (RT), and complete coaching. An built-in train protocol could also be relevant to most cancers survivors, which requires extra exploratory research. In abstract, the event of future train packages requires the involvement of execs and group assist, together with oncologists, physiotherapists, researchers, and affected person associations (66).
4.2.4 Most cancers prehabilitation packages and cardiorespiratory health
Most cancers prehabilitation packages have turn out to be a trending subject in the latest timeline. Within the present literature, a variety of preoperative interventions are known as prehabilitation. Most cancers sufferers present process surgical procedure are in danger for delayed restoration. Prehabilitation goals to enhance the affected person’s preoperative operate for higher surgical tolerance and promote restoration (67). Most supporting proof got here from sufferers present process resection for colorectal, lung, and breast most cancers (68–70). Earlier research have demonstrated the restricted affect of exercise-only prehabilitation packages, whereas multimodal prehabilitation, together with dietary optimization, mixed train packages (cardiorespiratory health and RT), and psychological well-being, have turn out to be the popular possibility (71). This multimodal prehabilitation program appears to be additional vital in pancreatic most cancers, the place the prognosis is commonly carefully related to cachexia and malnutrition (72). Nonetheless, researchers have but to be a consensus about what and when a prehabilitation program ought to happen. Subsequently, extra analysis ought to give attention to the opportune time and actual protocols for preventative interventions. Contemplating the person heterogeneity of affected person bodily and psychological standing, an individualized train rehabilitation protocol is important to acquire long-term PA ranges (73, 74).
4.2.5 Distant intervention and social assist for PA
PA of most cancers survivors is a long-term, continuous course of. PA can cut back most cancers negative effects, however participation charges amongst most cancers survivors are weak (13%–40%) (75). Telemedicine fashions, together with cell well being (mHealth) and digital well being (eHealth), are rising ideas in trendy medical care that provide alternatives to enhance PA for most cancers survivors and cut back SB (76, 77). Within the background of sudden public well being occasions (e.g., the emergence of Covid-19 and Monkeypox virus), sufferers present process most cancers therapy could also be unable to participate in bodily train. Many healthcare organizations have adopted telemedicine to keep away from interruptions in therapy companies, as a result of social distancing measures, isolation, self-isolation, and hospital customer restrictions (78). In contrast with the wholesome inhabitants, sufferers with most cancers could also be extra inclined to novel coronavirus infections and critical issues (79, 80). Subsequently, the usage of telerehabilitation packages for sufferers with persistent ailments is extremely really helpful (81). A transparent benefit of telemedicine is that most cancers survivors can obtain skilled steerage from a bodily therapist at dwelling, thereby decreasing the necessity for nonessential contact (82). Telemedicine could be divided into 4 most important areas: web-based, phone interventions, cell purposes, and SMS messaging. A scientific assessment that included 3,698 topics revealed that individuals confirmed good compliance and symptom reduction from telemedicine (83); nonetheless, current scientific trials have limitations, equivalent to small pattern dimension, non-randomized design, topic bias, single tumor kind (largely breast most cancers survivors), and poor PA measurements (84), which can lead to non-significant findings when extra stringent inclusion standards are utilized in meta-analysis (85). New strategies are wanted sooner or later to advertise and assist PA ranges in most cancers survivors.
5 Limitations
This research has some limitations. (i) As a result of software program limitations, we had been unable to carry out cross-check evaluation of different high-quality databases (e.g., PubMed, Scopus). (ii) We solely included research in English, and a few related articles in different languages could have been excluded. (iii) Solely research since 2001 had been included, which can trigger some omissions. (iv) Along with the “key phrases” supplied by the writer, we now have included “key phrases plus” to direct the searches, which can restrict the outcomes discovered. (v) Because of the existence of some synonymous key phrases, bias should still exist, regardless of our efforts to standardize them.
6 Conclusions
This research analyzes publications associated to PA and SB analysis within the context of most cancers, and summarises essentially the most influential authors, nations, establishments, and journals. In a phrase, proof from the research outcomes helps our speculation. Train oncology is a broad analysis subject specializing in most cancers prevention, administration, and supportive care. The present analysis centered on train and sedentariness in breast most cancers sufferers and the position of PA in bettering high quality of life in survivorship. Rising analysis foci had been usually round most cancers prehabilitation packages and distant intervention points for PA. Moreover, this evaluation serves to assist the prioritization of analysis matters on this discipline because it offers perception on gaps and deficiencies within the present literature. Future analysis ought to contemplate these shortcomings as a elementary foundation for research design.
Information availability assertion
The unique contributions introduced within the research are included within the article/Supplementary Materials. Additional inquiries could be directed to the corresponding authors.
Writer contributions
Conceptualization, JG. Methodology, MH. Software program, YC. Information Curation, JY, YJ, and JH. Writing – Authentic Draft Preparation, JG. Writing – Evaluation & Enhancing, GW. Supervision, JH. Funding Acquisition, JH and YJ. All authors contributed to the article and accredited the submitted model.
Funding
This analysis was supported by the Nationwide Pure Science Basis of China (Reference: 82004288), Jiangsu Science and Expertise Division Social Improvement-Scientific Frontier Expertise (Reference: BE2019767 and BRA2019100), and Jiangsu Scientific Innovation Middle of Digestive Most cancers of Conventional Chinese language Medication (Reference: 2021.6).
Battle of curiosity
The authors declare that the analysis was performed within the absence of any business or monetary relationships that may very well be construed as a possible battle of curiosity.
Writer’s observe
All claims expressed on this article are solely these of the authors and don’t essentially characterize these of their affiliated organizations, or these of the writer, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that could be evaluated on this article, or declare that could be made by its producer, will not be assured or endorsed by the writer.
Supplementary materials
The Supplementary Materials for this text could be discovered on-line at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2023.1095852/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary FIGURE 1 | The collaborative relationships between completely different authors.
References
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. World most cancers statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 nations. CA Most cancers J Clin (2021) 71(3):209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
2. Bray F, Laversanne M, Weiderpass E, Soerjomataram I. The ever-increasing significance of most cancers as a number one reason behind untimely demise worldwide. Most cancers (2021) 127(16):3029–30. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33587
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
3. Carrera PM, Kantarjian HM, Blinder VS. The monetary burden and misery of sufferers with most cancers: Understanding and stepping-up motion on the monetary toxicity of most cancers therapy. CA Most cancers J Clin (2018) 68(2):153–65. doi: 10.3322/caac.21443
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
4. Huang M, Haiderali A, Fox GE, Frederickson A, Cortes J, Fasching PA, et al. Financial and humanistic burden of triple-negative breast most cancers: A scientific literature assessment. Pharmacoeconomics (2022) 40(5):519–58. doi: 10.1007/s40273-021-01121-7
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
6. Gu J, Li Y, Yu J, Hu M, Ji Y, Li L, et al. A danger scoring system to foretell the person incidence of early-onset colorectal most cancers. BMC Most cancers (2022) 22(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09238-4
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
7. Firkins J, Hansen L, Driessnack M, Dieckmann N. High quality of life in “persistent” most cancers survivors: a meta-analysis. J Most cancers Surviv (2020) 14(4):504–17. doi: 10.1007/s11764-020-00869-9
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
8. Kerr J, Anderson C, Lippman SM. Bodily exercise sedentary behaviour food regimen and most cancers: an replace and rising new proof. Lancet Oncol (2017) 18(8):e457–71. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30411-4
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
9. Liu L, Shi Y, Li T, Qin Q, Yin J, Pang S, et al. Leisure time bodily exercise and most cancers danger: analysis of the WHO’s suggestion based mostly on 126 high-quality epidemiological research. Br J Sports activities Med (2016) 50(6):372–8. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2015-094728
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
10. Rezende LFM, Sa TH, Markozannes G, Rey-Lopez JP, Lee IM, Tsilidis KK, et al. Bodily exercise and most cancers: an umbrella assessment of the literature together with 22 main anatomical websites and 770 000 most cancers instances. Br J Sports activities Med (2018) 52(13):826–33. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2017-098391
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
11. Hermelink R, Leitzmann MF, Markozannes G, Tsilidis Ok, Pukrop T, Berger F, et al. Sedentary habits and cancer-an umbrella assessment and meta-analysis. Eur J Epidemiol (2022) 37(5):447–60. doi: 10.1007/s10654-022-00873-6
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
12. Patel AV, Friedenreich CM, Moore SC, Hayes SC, Silver JK, Campbell KL, et al. American School of sports activities drugs roundtable report on bodily exercise sedentary habits and most cancers prevention and management. Med Sci Sports activities Exerc (2019) 51(11):2391–402. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000002117
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
13. Watson G, Coyne Z, Houlihan E, Leonard G. Train oncology: an rising self-discipline within the most cancers care continuum. Postgrad Med (2022) 134(1):26–36. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2021.2009683
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
14. Stout NL, Brown JC, Schwartz AL, Marshall TF, Campbell AM, Nekhlyudov L, et al. An train oncology scientific pathway: Screening and referral for personalised interventions. Most cancers (2020) 126(12):2750–8. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32860
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
17. Wang J, Maniruzzaman M. A worldwide bibliometric and visualized evaluation of bacteria-mediated most cancers remedy. Drug Discovery At this time (2022) 27(10):103297. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2022.05.023
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
18. Gu J, Hu M, Gu Z, Yu J, Ji Y, Li L, et al. Bibliometric evaluation reveals a 20-year analysis development for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Entrance Neurol (2021) 12:793663. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.793663
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
19. Wilson M, Sampson M, Barrowman N, Doja A. Bibliometric evaluation of neurology articles revealed usually drugs journals. JAMA Netw Open (2021) 4(4):e215840. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.5840
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
20. You Y, Shou X, Zhang X, Fan S, Chai R, Xue W, et al. Psycho-cardiological illness: A bibliometric assessment from 2001 to 2021. Entrance Cardiovasc Med (2022) 9:890329. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.890329
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
21. Zhong D, Li Y, Huang Y, Hong X, Li J, Jin R. Molecular mechanisms of train on most cancers: A bibliometrics research and visualization evaluation by way of CiteSpace. Entrance Mol Biosci (2021) 8:797902. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.797902
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
22. Pan Y, Deng X, Zhuang Y, Li J. Analysis tendencies round train rehabilitation amongst most cancers sufferers: A bibliometrics and visualized information graph evaluation. BioMed Res Int (2022) 2022:3755460. doi: 10.1155/2022/3755460
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
23. Gao Y, Shi S, Ma W, Chen J, Cai Y, Ge L, et al. Bibliometric evaluation of worldwide analysis on PD-1 and PD-L1 within the discipline of most cancers. Int Immunopharm (2019) 72:374–84. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.03.045
24. Perianes-Rodriguez A, Waltman L, van Eck NJ. Setting up bibliometric networks: A comparability between full and fractional counting. J Informetrics (2016) 10(4):1178–95. doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2016.10.006
25. Aria M, Cuccurullo C. Bibliometrix: An r-tool for complete science mapping evaluation. J Informetrics (2017) 11(4):959–75. doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
27. Hodge DR, Lacasse JR. Evaluating journal high quality: Is the h-index a greater measure than affect elements? Res Soc Work Pract (2010) 21(2):222–30. doi: 10.1177/1049731510369141
28. Bertoli-Barsotti L, Lando T. A theoretical mannequin of the connection between the h-index and different easy quotation indicators. Scientometrics (2017) 111(3):1415–48. doi: 10.1007/s11192-017-2351-9
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
29. Holmes MD, Chen WY, Feskanich D, Kroenke CH, Colditz GA. Bodily exercise and survival after breast most cancers prognosis. JAMA (2005) 293(20):2479–86. doi: 10.1001/jama.293.20.2479
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
30. Katzmarzyk PT, Church TS, Craig CL, Bouchard C. Sitting time and mortality from all causes heart problems and most cancers. Med Sci Sports activities Exerc (2009) 41(5):998–1005. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181930355
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
31. Rock CL, Doyle C, Demark-Wahnefried W, Meyerhardt J, Courneya KS, Schwartz AL, et al. Diet and bodily exercise pointers for most cancers survivors. CA Most cancers J Clin (2012) 62(4):243–74. doi: 10.3322/caac.21142
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
32. Speck RM, Courneya KS, Masse LC, Duval S, Schmitz KH. An replace of managed bodily exercise trials in most cancers survivors: a scientific assessment and meta-analysis. J Most cancers Surviv (2010) 4(2):87–100. doi: 10.1007/s11764-009-0110-5
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
33. McNeely ML, Campbell KL, Rowe BH, Klassen TP, Mackey JR, Courneya KS. Results of train on breast most cancers sufferers and survivors: a scientific assessment and meta-analysis. CMAJ (2006) 175(1):34–41. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.051073
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
34. Courneya KS, Segal RJ, Mackey JR, Gelmon Ok, Reid RD, Friedenreich CM, et al. Results of cardio and resistance train in breast most cancers sufferers receiving adjuvant chemotherapy: a multicenter randomized managed trial. J Clin Oncol (2007) 25(28):4396–404. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.08.2024
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
35. Moore SC, Lee IM, Weiderpass E, Campbell PT, Sampson JN, Kitahara CM, et al. Affiliation of leisure-time bodily exercise with danger of 26 kinds of most cancers in 1.44 million adults. JAMA Intern Med (2016) 176(6):816–25. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.1548
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
36. Wareham NJ, Jakes RW, Rennie KL, Schuit J, Mitchell J, Hennings S, et al. Validity and repeatability of a easy index derived from the brief bodily exercise questionnaire used within the European potential investigation into most cancers and vitamin (EPIC) research. Public Well being Nutr (2003) 6(4):407–13. doi: 10.1079/PHN2002439
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
37. Meyerhardt JA, Giovannucci EL, Holmes MD, Chan AT, Chan JA, Colditz GA, et al. Bodily exercise and survival after colorectal most cancers prognosis. J Clin Oncol (2006) 24(22):3527–34. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.06.0855
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
38. Kyu HH, Bachman VF, Alexander LT, Mumford JE, Afshin A, Estep Ok, et al. Bodily exercise and danger of breast most cancers colon most cancers diabetes ischemic coronary heart illness and ischemic stroke occasions: systematic assessment and dose-response meta-analysis for the worldwide burden of illness research 2013. BMJ (2016) 354:i3857. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i3857
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
40. Schmidt ME, Goldschmidt S, Hermann S, Steindorf Ok. Late results long-term issues and unmet wants of most cancers survivors. Int J Most cancers (2022) 151(8):1280–90. doi: 10.1002/ijc.34152
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
42. Protani M, Web page A, Taylor R, Glazebrook R, Lahmann PH, Department E, et al. Breast most cancers danger elements in Queensland girls attending population-based mammography screening. Maturitas (2012) 71(3):279–86. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2011.12.008
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
43. Godinho-Mota JCM, Goncalves LV, Mota JF, Soares LR, Schincaglia RM, Martins KA, et al. Sedentary habits and alcohol consumption improve breast most cancers danger no matter menopausal standing: A case-control research. Vitamins (2019) 11(8):1871. doi: 10.3390/nu11081871
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
45. Phillips SM, Dodd KW, Steeves J, McClain J, Alfano CM, McAuley E. Bodily exercise and sedentary habits in breast most cancers survivors: New perception into exercise patterns and potential intervention targets. Gynecol Oncol (2015) 138(2):398–404. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2015.05.026
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
46. Thraen-Borowski KM, Gennuso KP, Cadmus-Bertram L. Accelerometer-derived bodily exercise and sedentary time by most cancers kind in the usa. PloS One (2017) 12(8):e0182554. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182554
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
47. Jochem C, Wallmann-Sperlich B, Leitzmann MF. The affect of sedentary habits on most cancers danger: Epidemiologic proof and potential molecular mechanisms. Curr Nutr Rep (2019) 8(3):167–74. doi: 10.1007/s13668-019-0263-4
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
48. Clinton SK, Giovannucci EL, Hursting SD. The world most cancers analysis Fund/American institute for most cancers analysis third professional report on food regimen vitamin bodily exercise and most cancers: Affect and future instructions. J Nutr (2020) 150(4):663–71. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxz268
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
49. Orlandella FM, De Stefano AE, Iervolino PLC, Buono P, Soricelli A, Salvatore G. Dissecting the molecular pathways concerned within the results of bodily exercise on breast cancers cells: A story assessment. Life Sci (2021) 265:118790. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118790
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
50. Kovic B, Jin X, Kennedy SA, Hylands M, Pedziwiatr M, Kuriyama A, et al. Evaluating progression-free survival as a surrogate end result for health-related high quality of life in oncology: A scientific assessment and quantitative evaluation. JAMA Intern Med (2018) 178(12):1586–96. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.4710
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
51. Elliott J, Fallows A, Staetsky L, Smith PW, Foster CL, Maher EJ, et al. The well being and well-being of most cancers survivors within the UK: findings from a population-based survey. Br J Most cancers (2011) 105 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S11–20. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.418
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
52. Hewitt M, Rowland JH, Yancik R. Most cancers survivors in the usa: age well being and incapacity. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci (2003) 58(1):82–91. doi: 10.1093/gerona/58.1.m82
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
53. Harrington CB, Hansen JA, Moskowitz M, Todd BL, Feuerstein M. It’s not over when it’s over: long-term signs in most cancers survivors–a scientific assessment. Int J Psychiatry Med (2010) 40(2):163–81. doi: 10.2190/PM.40.2.c
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
54. Mishra SI, Scherer RW, Geigle PM, Berlanstein DR, Topaloglu O, Gotay CC, et al. Train interventions on health-related high quality of life for most cancers survivors. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (2012) 2012(8):CD007566. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007566.pub2
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
55. Friedenreich CM, Stone CR, Cheung WY, Hayes SC. Bodily exercise and mortality in most cancers survivors: A scientific assessment and meta-analysis. JNCI Most cancers Spectr (2020) 4(1):pkz080. doi: 10.1093/jncics/pkz080
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
56. Penttinen H, Utriainen M, Kellokumpu-Lehtinen PL, Raitanen J, Sievanen H, Nikander R, et al. Effectiveness of a 12-month train intervention on bodily exercise and high quality of lifetime of breast most cancers survivors; five-year outcomes of the BREX-study. In Vivo (2019) 33(3):881–8. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11554
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
57. Paxton RJ, Phillips KL, Jones LA, Chang S, Taylor WC, Courneya KS, et al. Associations amongst bodily exercise physique mass index and health-related high quality of life by race/ethnicity in a various pattern of breast most cancers survivors. Most cancers (2012) 118(16):4024–31. doi: 10.1002/cncr.27389
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
58. Lewis C, Xun P, He Ok. Bodily exercise in relation to high quality of life in newly recognized colon most cancers sufferers: a 24-month follow-up. Qual Life Res (2014) 23(8):2235–46. doi: 10.1007/s11136-014-0679-7
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
60. Liu JF, Kuo NY, Fang TP, Chen JO, Lu HI, Lin HL. A six-week inspiratory muscle coaching and cardio train improves respiratory muscle energy and train capability in lung most cancers sufferers after video-assisted thoracoscopic surgical procedure: A randomized managed trial. Clin Rehabil (2021) 35(6):840–50. doi: 10.1177/0269215520980138
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
61. Messaggi-Sartor M, Marco E, Martinez-Tellez E, Rodriguez-Fuster A, Palomares C, Chiarella S, et al. Mixed cardio train and high-intensity respiratory muscle coaching in sufferers surgically handled for non-small cell lung most cancers: a pilot randomized scientific trial. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med (2019) 55(1):113–22. doi: 10.23736/S1973-9087.18.05156-0
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
62. Gravier FE, Smondack P, Prieur G, Medrinal C, Combret Y, Muir JF, et al. Results of train coaching in individuals with non-small cell lung most cancers earlier than lung resection: a scientific assessment and meta-analysis. Thorax (2022) 77(5):486–96. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2021-217242
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
63. Roveda E, Vitale JA, Bruno E, Montaruli A, Pasanisi P, Villarini A, et al. Protecting impact of cardio bodily exercise on sleep habits in breast most cancers survivors. Integr Most cancers Ther (2017) 16(1):21–31. doi: 10.1177/1534735416651719
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
64. Brown JC, Damjanov N, Courneya KS, Troxel AB, Zemel BS, Rickels MR, et al. A randomized dose-response trial of cardio train and health-related high quality of life in colon most cancers survivors. Psychooncology (2018) 27(4):1221–8. doi: 10.1002/pon.4655
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
65. Bekhet AH, Abdallah AR, Ismail HM, Genena DM, Osman NA, El Khatib A, et al. Advantages of cardio train for breast most cancers survivors: A scientific assessment of randomized managed trials. Asian Pac J Most cancers Prev (2019) 20(11):3197–209. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.11.3197
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
66. Avancini A, Belluomini L, Tregnago D, Trestini I, Lanza M, Milella M, et al. Train oncology: It’s time to make a change. Affected person Educ Couns (2022) 105(7):2629–31. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2022.01.019
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
67. Carli F, Silver JK, Feldman LS, McKee A, Gilman S, Gillis C, et al. Surgical prehabilitation in sufferers with most cancers: State-of-the-Science and proposals for future analysis from a panel of subject material specialists. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am (2017) 28(1):49–64. doi: 10.1016/j.pmr.2016.09.002
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
68. Trepanier M, Minnella EM, Paradis T, Awasthi R, Kaneva P, Schwartzman Ok, et al. Improved disease-free survival after prehabilitation for colorectal most cancers surgical procedure. Ann Surg (2019) 270(3):493–501. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003465
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
69. Ferreira V, Minnella EM, Awasthi R, Gamsa A, Ferri L, Mulder D, et al. Multimodal prehabilitation for lung most cancers surgical procedure: A randomized managed trial. Ann Thorac Surg (2021) 112(5):1600–8. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2020.11.022
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
70. Brahmbhatt P, Sabiston CM, Lopez C, Chang E, Goodman J, Jones J, et al. Feasibility of prehabilitation previous to breast most cancers surgical procedure: A mixed-methods research. Entrance Oncol (2020) 10:571091. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.571091
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
71. Scheede-Bergdahl C, Minnella EM, Carli F. Multi-modal prehabilitation: addressing the why when what how who and the place subsequent? Anaesthesia (2019) 74 Suppl 1(S1):20–6. doi: 10.1111/anae.14505
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
72. De Luca R, Gianotti L, Pedrazzoli P, Brunetti O, Rizzo A, Sandini M, et al. Immunonutrition and prehabilitation in pancreatic most cancers surgical procedure: A brand new idea within the period of ERAS(R) and neoadjuvant therapy. Eur J Surg Oncol (2022). doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2022.12.006
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
73. Avancini A, Tregnago D, Rigatti L, Sartori G, Yang L, Trestini I, et al. Components influencing bodily exercise in most cancers sufferers throughout oncological therapies: A qualitative research. Integr Most cancers Ther (2020) 19:1534735420971365. doi: 10.1177/1534735420971365
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
74. Avancini A, Sartori G, Gkountakos A, Casali M, Trestini I, Tregnago D, et al. Bodily exercise and train in lung most cancers care: Will guarantees be fulfilled? Oncologist (2020) 25(3):e555–69. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0463
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
75. Eng L, Pringle D, Su J, Shen X, Mahler M, Niu C, et al. Patterns perceptions and perceived obstacles to bodily exercise in grownup most cancers survivors. Help Care Most cancers (2018) 26(11):3755–63. doi: 10.1007/s00520-018-4239-5
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
76. Penedo FJ, Oswald LB, Kronenfeld JP, Garcia SF, Cella D, Yanez B. The growing worth of eHealth within the supply of patient-centred most cancers care. Lancet Oncol (2020) 21(5):e240–51. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30021-8
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
77. Jiang Y, West BT, Barton DL, Harris MR. Acceptance and use of eHealth/mHealth purposes for self-management amongst most cancers survivors. Stud Well being Technol Inform (2017) 245:131–5. doi: 10.3233/978-1-61499-830-3-131
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
78. Smith AC, Thomas E, Snoswell CL, Haydon H, Mehrotra A, Clemensen J, et al. Telehealth for world emergencies: Implications for coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID-19). J Telemed Telecare (2020) 26(5):309–13. doi: 10.1177/1357633X20916567
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
80. Hanna TP, Evans GA, Sales space CM. Most cancers COVID-19 and the precautionary precept: prioritizing therapy throughout a world pandemic. Nat Rev Clin Oncol (2020) 17(5):268–70. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-0362-6
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
81. Scherrenberg M, Wilhelm M, Hansen D, Voller H, Cornelissen V, Frederix I, et al. The longer term is now: a name for motion for cardiac telerehabilitation within the COVID-19 pandemic from the secondary prevention and rehabilitation part of the European affiliation of preventive cardiology. Eur J Prev Cardiol (2020) 28(5):2047487320939671. doi: 10.1177/2047487320939671
82. Bland KA, Bigaran A, Campbell KL, Trevaskis M, Zopf EM. Exercising in isolation? the position of telehealth in train oncology throughout the COVID-19 pandemic and past. Phys Ther (2020) 100(10):1713–6. doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzaa141
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
83. Morrison KS, Paterson C, Toohey Ok. The feasibility of train interventions delivered by way of telehealth for individuals affected by most cancers: A speedy assessment of the literature. Semin Oncol Nurs (2020) 36(6):151092. doi: 10.1016/j.soncn.2020.151092
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
84. Groen WG, van Harten WH, Vallance JK. Systematic assessment and meta-analysis of distance-based bodily exercise interventions for most cancers survivors (2013-2018): We nonetheless haven’t discovered what we’re on the lookout for. Most cancers Deal with Rev (2018) 69:188–203. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2018.07.012
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
85. Ibeggazene S, Turner R, Rosario D, Bourke L. Distant interventions to enhance train behaviour in sedentary individuals dwelling with and past most cancers: a scientific assessment and meta-analysis. BMC Most cancers (2021) 21(1):308. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-07989-0
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar

