1 Introduction
The incidence and mortality of colorectal most cancers (CRC) have been vastly decreased by large-scale screening for lesions in colon and rectum amongst average-risk populations (1). Many nations and areas have supplied organized CRC screening for middle-aged and aged populations as native or nationwide public well being service packages (2). The triage screening technique, principally colonoscopy referral for people with optimistic fecal immunochemical take a look at (FIT) outcomes, was broadly adopted within the packages (3, 4). Nonetheless, FIT isn’t delicate to non-bleeding lesions. Due to this fact, a number of danger scoring methods have been developed and used combinatorically with FIT to establish high-risk people for subsequent colonoscopy, significantly in Asia-Pacific nations with a low incidence of the most cancers (5).
In China, the questionnaire-based danger evaluation (RA) and two-sample qualitative FIT has been parallel used to detect CRC since 2005 (6). The parallel checks have been proved cost-effective in Chinese language populations (7), and had been beneficial as preliminary checks for CRC screening packages in China. To this point, nonetheless, the general public well being service packages had been supplied solely in Shanghai (8), Guangzhou (9), Tianjin (10), Hangzhou (11), and different city areas, together with the population-based Most cancers Screening Program in City China (CanSPUC) program that lined 22 cities in 16 provinces and used a danger scoring system incorporating earlier fecal occult blood take a look at outcomes (12). The utility of the RA instruments, nonetheless, has been persistently noticed to lead to suboptimal adherence to colonoscopy, which vastly jeopardized the effectivity of CRC screening (11–14). In our earlier research, we discovered that the colonoscopy adherence was lower than 40%, and positively associated with the specificity of preliminary screening checks (14, 15).
With the event of biotechnology, plenty of novel checks have been developed lately, during which colon capsule endoscopy, computed tomographic colonography, and molecular biomarkers in stool or blood at DNA, RNA and protein ranges are promising in CRC screening (16, 17). Of the novel biomarkers, multi-target stool DNA take a look at (mt-sDNA) and methylated SEPT9 DNA plasma assay (mSEPT9) have been beneficial as complementary checks for FIT within the 2016 USPSTF guideline (18). These rising applied sciences present a number of selections of screening checks, which can break the bottlenecks of the present screening modalities and promote optimization and diversification of screening methods.
To raised perceive the benefits and downsides of the currently-used screening checks for CRC in China, and the potential functions of the novel checks in large-scale CRC screening practices, we carried out a qualitative research primarily based on grounded idea. The grounded idea focuses on revealing the method of a phenomenon and the various views concerning the phenomenon, thereby creating an explanatory idea for this phenomenon (19). The speculation emphasizes the theoretical sampling, fixed comparability of information, and theoretical saturation. The simultaneous information assortment and evaluation permit theoretical sampling of interviewees who can present info to develop a idea and eventually attain theoretical saturation (20).
The grounded idea supplies a super qualitative methodological framework to discover viewpoints of consultants on the scenario of CRC screening and the utility of novel screening checks in China, which can assist to optimize and replace the screening tips, facilitate identification of high-risk people for colonoscopy, and enhance effectivity of CRC screening packages in China.
2 Strategies
2.1 Research design
On this qualitative research using an exploring analysis expertise of grounded idea (19), a semi-structured open-ended particular person interview was carried out in China from October to November of 2020. The research was reported in response to the Consolidated Standards for Reporting Qualitative Analysis (COREQ) reporting guideline (21).
This research was accredited by the Ethics Committee of Fudan College College of Public Well being (IRB00002408 & FWA00002399) (Registration quantity: 2019-TYSQ-03-29). Previous to the graduation of every interview, every participant was knowledgeable of the aim of the research and the voluntary, nameless, and confidential nature of the interview utilizing an info sheet. All contributors had been additionally knowledgeable of that the lengthy interview interval would trigger minimal discomfort, and their withdrawal from the research could be permitted with none opposed outcomes. The contributors had been required to signal an knowledgeable consent type earlier than collaborating. The authors declare that the research was carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki for analysis involving human topics (22).
2.2 Research contributors
To make sure ample representativeness and variety of the viewpoints, the research contributors had been chosen from totally different well being sections of presidency, analysis institutes, facilities for illness prevention and management (CDC), hospitals, and group healthcare facilities in China utilizing a purposive sampling technique. Their career, place, expertise, and data in CRC screening had been additionally thought of to make sure the total protection of the service supply (i.e., policy-making, administration, supervision, group, implementation, follow-up, analysis and remedy, and analysis). The potential consultants had been invited to take part the interview by phone-call or sending an e-mail, after which contributors had been scheduled for an interview at a handy time. A complete of 15 contributors had been interviewed. The contributors’ traits are introduced in Desk 1.
2.3 Information assortment
In-depth interviews had been carried out utilizing an interview define conceptualized and developed primarily based on the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Analysis (CFIR) (23), which has been broadly utilized in well being service analysis (24). The 5 main domains of CFIR-intervention traits, outer setting, internal setting, traits of people, and implementation course of—have been used to virtually information the analysis of limitations and facilitators of interventions (23), and subsequently could also be appropriate for the evaluation of the CRC screening.
Based mostly on systematic iterations of scientific literature evaluations and cautious choice and rephrasing of the objects, we developed an interview define together with 12 best suited probing questions regarding the present CRC screening protocol, limitations and facilitators for screening effectiveness, current issues and potential optimization of screening protocol, and future prospects of CRC screening packages (Determine 1). Additional dialogue was carried out together with the probing questions. We additionally collected reported sensitivity, specificity and value of currently-used preliminary screening checks by means of complete literature evaluations and consults with associated consultants. The data summarized in Desk 2 was supplied to the contributors as a reference on the interview, which was supplemented on the similar time by the consultants interviewed. The protocol of the interview was pilot-tested with one knowledgeable (ID11) to find out the readability, reliability, and convergent validity of the questions. Because the pilot interview simply indicated minor adjustment of the merchandise order and language expression, however didn’t reveal any want for main modifications to the interview schedule, the outcomes of the pilot take a look at had been included on this evaluation.

Determine 1. Interview information to discover viewpoints of consultants on CRC screening. CRC: colorectal most cancers; FIT: fecal immunochemical take a look at; mSEPT9: methylated SEPT DNA plasma assay; mt-sDNA: multi-target stool DNA take a look at.
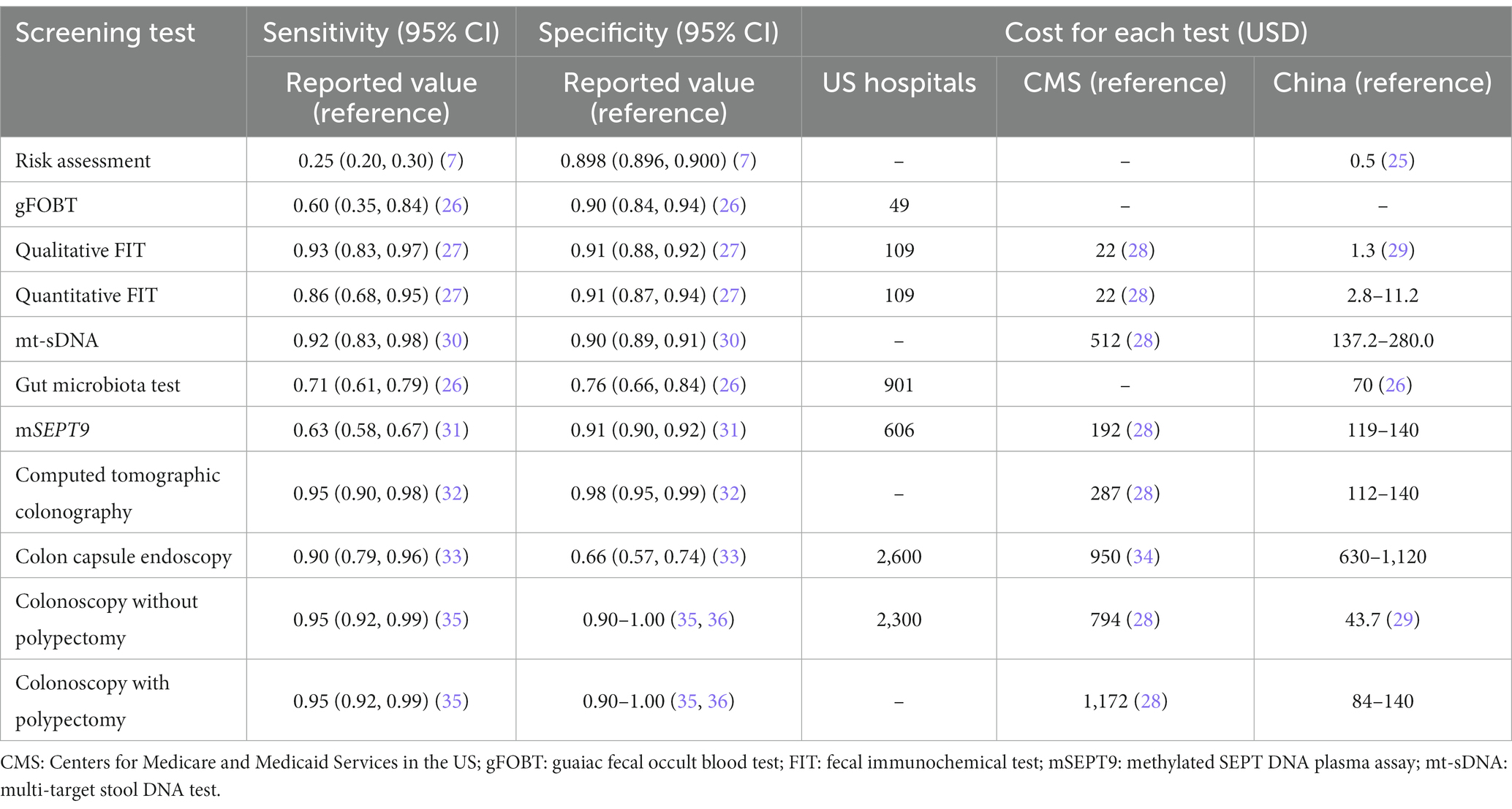
Desk 2. Earlier reported sensitivity, specificity, and price of every screening take a look at for colorectal most cancers.
The face-to-face interviews had been carried out with 5 consultants at their workplaces or a personal room the place nobody may observe or overhear the discussions. On-line interviews had been additionally carried out for 10 consultants utilizing Zoom, Tencent, or WeChat. The primary researcher (W.M.W.) moderated the interviews utilizing follow-up prompts for readability, and requested for extra info when wanted. The second researcher (S.S.T.) took subject notes to evaluate gestures, facial expressions and different non-verbal communications of the contributors, and supplied technical help through the interviews. The interviews had been audio-recorded utilizing a smartphone. The interviews lasted for 40 min roughly, which ranged from 30 to 60 min. Following rigorous standardized method for qualitative analysis, the info assortment was terminated when information saturation was achieved.
After the interviews, a self-administered questionnaire was used to gather demographic traits of consultants, together with age, intercourse, instructional stage, occupation, skilled title, length of working within the space of CRC screening, and their roles within the space of CRC screening.
2.4 Information evaluation
Audio recordings of the interviews had been transcribed verbatim utilizing iflyrec software program. The transcripts had been double-checked and transferred to MAXQDA 2020 software program by the researchers. An iterative information assortment and evaluation had been employed utilizing a relentless comparability method to construct ideas and classes in response to the grounded idea method, which supplies a radical procedure-oriented technique for coding, together with open, axial, and selective coding phases.
Open coding includes breaking down, analyzing, evaluating, conceptualizing, and classifying information, by means of which the central ideas and classes had been created. Axial coding additional categorized, condensed, and refined the classes to develop subcategories associated to every major class. Selective coding, the third section, additional abstracted and summarized the primary classes to type the core classes, and eventually construct a grounded theoretical mannequin protecting all of the collected information (37). A theoretical saturation take a look at was carried out throughout and after the method of coding till no extra points or insights had been recognized (17). On this interview, no new idea or class was discovered when the transcripts of the eleventh respondent had been coded. Further 4 consultants had been interviewed to substantiate the theoretical saturation. To extend the reliability of our findings, two researchers coded all of the transcripts independently. A 3rd researcher checked the unique information, coding, extracted ideas and classes, and in contrast and mentioned any controversy to succeed in a consensus.
3 Outcomes
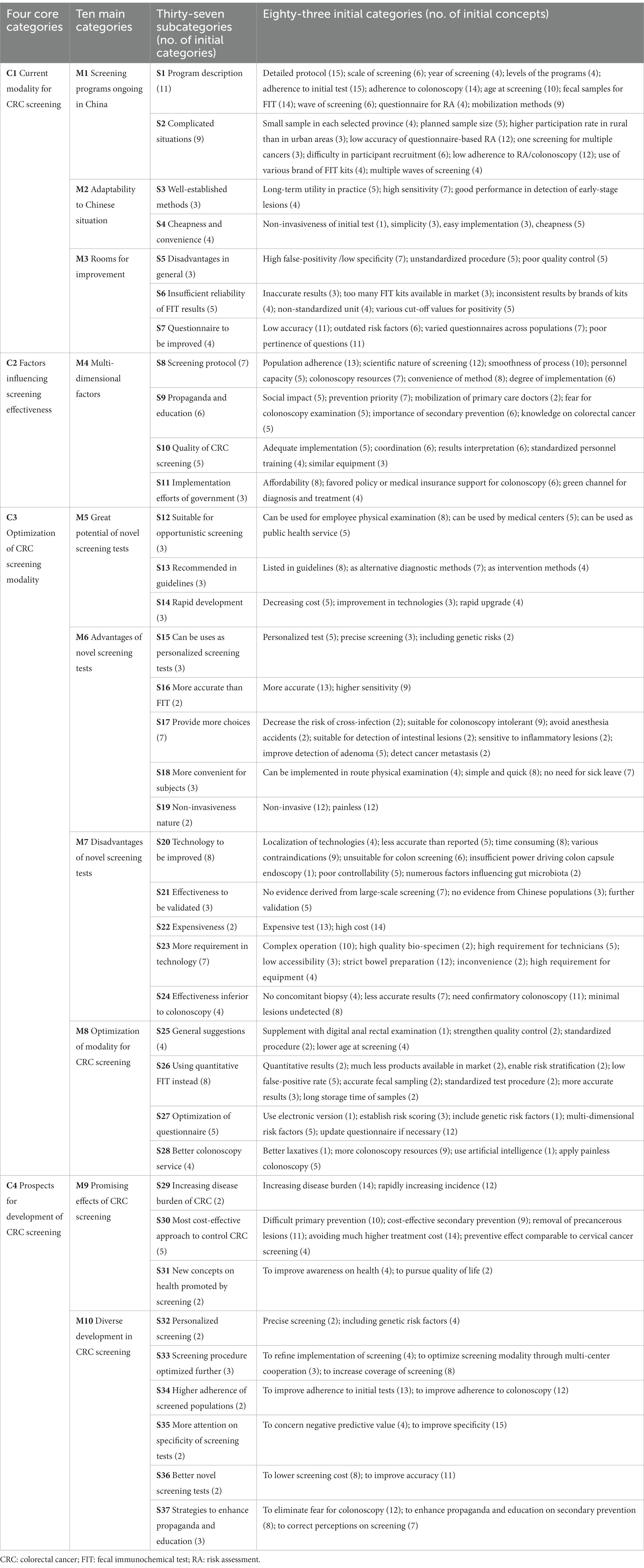
Greater than 600 min of audio recordings had been collected and transcribed verbatim, from which the ideas associated to the goals of this research had been extracted. After which 83 preliminary classes had been derived from the ideas within the open coding section. Then 37 subcategories and 10 major classes had been summarized from the preliminary classes by means of axial coding. Within the selective coding, 4 core classes had been recognized, together with present modality for CRC screening (C1), elements influencing screening effectiveness (C2), optimization of CRC screening modality (C3), and prospects for growth (C4) (Desk 3).
3.1 Classes and sub-categories
3.1.1 C1: present CRC screening modality in China
The nationwide guideline of China for CRC screening beneficial parallel use of RA and two-sample qualitative FIT as preliminary checks, adopted by a colonoscopy follow-up (6). This triage screening technique is being carried out as a significant public well being service in Shanghai (8), Guangzhou (9), and Hangzhou (11). Within the CanSPUC program initiated in 2012 in mainland China, a danger scoring system was used as an preliminary take a look at (12). In Taiwan and Hong Kong, one-sample quantitative FIT was used to establish high-risk people for subsequent colonoscopy (38, 39). Nearly all consultants expressed their issues on the excessive false-positive charges of the preliminary checks, and proposed a number of potential contributors to the opposed scenario.
First, numerous qualitative FIT merchandise had been utilized in screening packages as an preliminary take a look at. Qualitative FIT is often utilized in China resulting from its comfort and cheapness. Nonetheless, greater than 10 manufacturers of qualitative FIT kits produced by totally different producers can be found in China, however with low consistency in take a look at outcomes. For the quantitative FIT, quite the opposite, just one product with a model of OC-MICRO is obtainable dominantly in China.
“Quantitative FIT is broadly utilized in developed nations or areas, whereas qualitative FIT is extra commonly-used in China. The low consistency of the outcomes examined by totally different manufacturers of qualitative FIT kits have develop into a giant downside within the observe of CRC screening.” (Male, researcher, ID14)
“The outcomes of qualitative checks usually are not constant for FIT kits produced by totally different producers. Nonetheless, totally different FIT kits had been used throughout screening packages; even in a CRC screening program, the FIT kits might change yr by yr.” (Feminine, CDC employees, ID7)
Second, the beneficial RA instruments haven’t been up to date. The danger elements of CRC might have modified together with the social growth and dietary transition in China. Nonetheless, the RA instruments haven’t been up to date primarily based on newly-established danger predictive fashions or danger scoring methods.
“The questionnaire at the moment used was derived from a number of case-control research carried out in Jiashan County, Zhejiang Province, a number of many years in the past, and was simply simplified in a large-scale nationwide most cancers screening program lately. Clearly, the questionnaire is outdated. We’ve instructed to replace the questionnaire through the previous years.” (Male, major care supplier, ID1)
“Typically, individuals had been much less more likely to attend follow-up colonoscopy in the event that they had been recognized as high-risk people by questionnaire-based RA solely. The danger stratification primarily based on the outcomes of the questionnaire was not convincing for our topics.” (Feminine, major care supplier, ID9)
Lastly, numerous misconducts might occur in every a part of the entire process of screening, which can have led to inaccurate take a look at outcomes.
“Most topics would report having constipation or diarrhea even when that they had the signs often, if medical doctors didn’t clarify associated definitions very clearly through the survey. This might result in low high quality of the collected information and incorrect danger stratifications” (Male, gastroenterologist, ID2)
“The contributors had been requested to gather fecal samples by themselves. Nonetheless, it’s tough for them to gather applicable quantity of stool samples. Some contributors even added water into the tubes …. The operation was positively unstandardized and incorrect.” (Feminine, researcher, ID12)
3.1.2 C2: elements influencing screening effectiveness
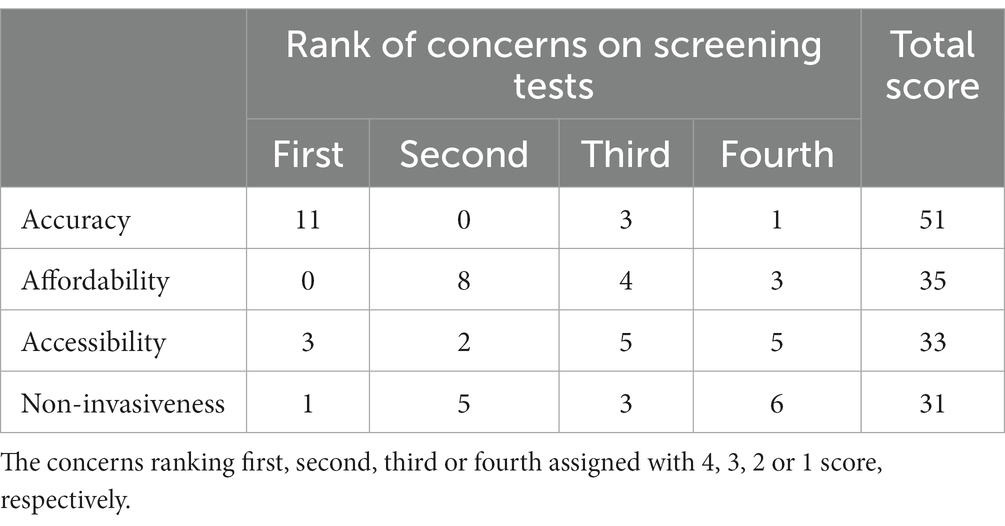
The consultants’ opinions on limitations and facilitators for effectiveness of CRC screening had been additionally collected. Particularly, the consultants had been extremely involved concerning the inhabitants adherence, rationality, and affordability of CRC screening checks. As introduced in Desk 4, the accuracy and the affordability ranked the primary and the second of the 4 essential traits of screening checks (accuracy, affordability, accessibility and non-invasiveness) in response to the viewpoints of the consultants.
As proven in Determine 2, a complete of 13 consultants believed that adherence to subsequent colonoscopy was associated to the accuracy of FIT. Amongst them, 7 consultants proposed that the specificity of FIT was extra essential than different indices of accuracy, 6 consultants thought that top false-positive price of FIT might have led to the mistrust of screening ends in screened populations, 4 consultants believed that larger accuracy of preliminary take a look at outcomes strengthen confidence for attending the following colonoscopy examination, and 4 consultants talked about the doable group impact in attending subsequent colonoscopy.
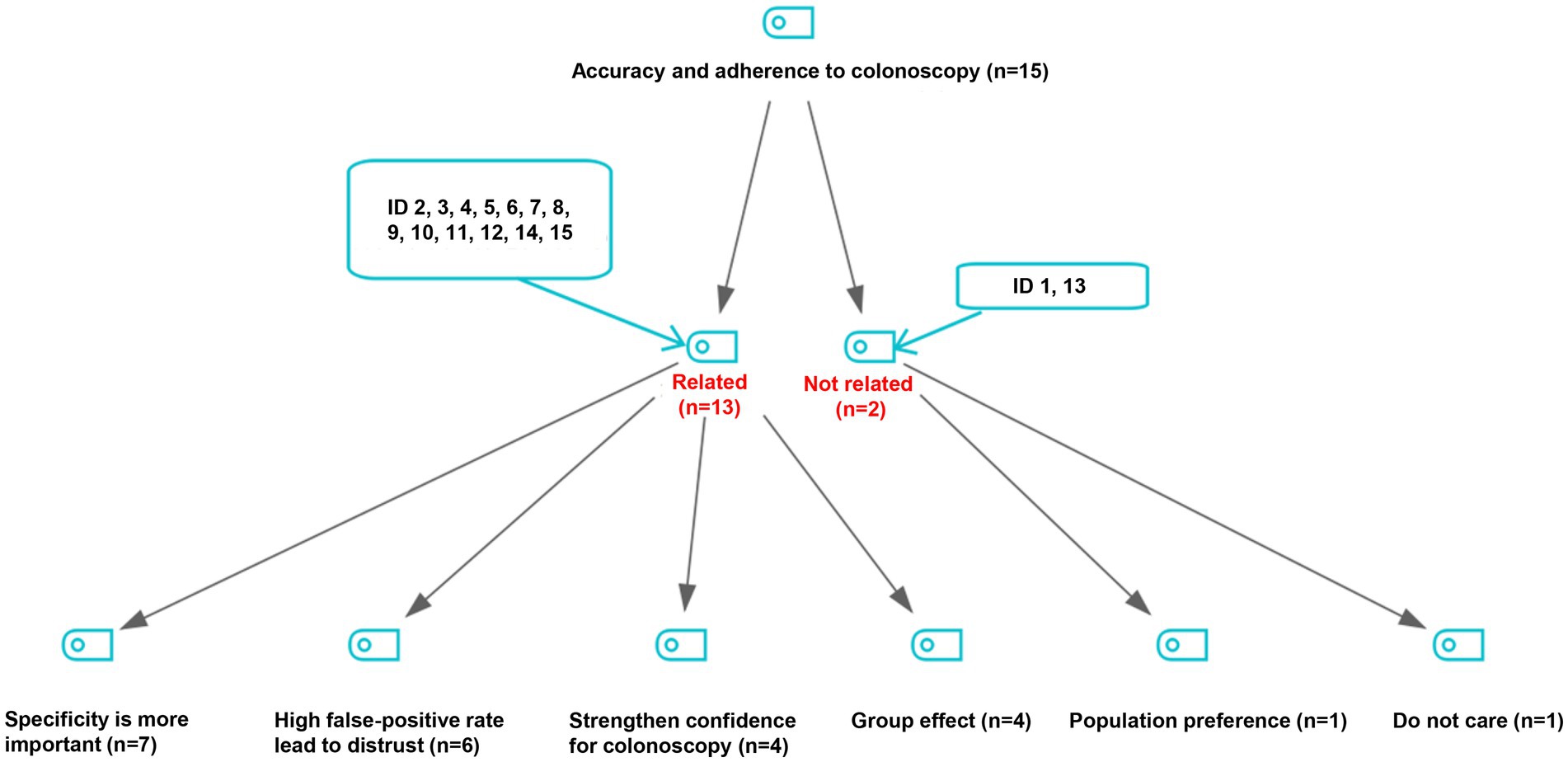
Determine 2. Viewpoints on the connection of accuracy of preliminary screening checks with adherence to follow-up colonoscopy.
“The CRC screening was carried out spherical by spherical, and a number of waves of screening have been carried out in lots of locations. Sadly, a vicious circle was noticed resulting from excessive false-positive price of the preliminary screening take a look at: a excessive false-positive price of an preliminary take a look at might lower the adherence to subsequent colonoscopy, and additional impedes the sustainability of CRC screening packages.” (Feminine, researcher, ID6)
“For instance, a topic recognized as high-risk by preliminary screening checks might really feel tricked, if he/she was not discovered any lesions in subsequent colonoscopy examination. Then he/she would categorical his/her mistrust of the preliminary take a look at outcomes to his/her friends, which can additional lower adherence to colonoscopy in the neighborhood” (Feminine, CDC employees, ID11)
3.1.3 C3: optimization of CRC screening modality
Regardless of the issues current in present screening modality, the consultants believed that the modality could possibly be optimized by means of enhancing course of administration (S25), making use of quantitative FIT (S26), updating RA instruments (S27), and offering higher colonoscopy service (S28) (Desk 3). Notably, the consultants instructed to reinforce the pertinence of things for RA by excluding outdated questions like continual appendicitis or appendectomy, continual cholecystitis or cholecystectomy, continual constipation and continual diarrhea, and including a number of essential danger elements into the system, equivalent to physique mass index (BMI), bodily exercise, aspirin use, eating regimen and smoking.
“We now use the questionnaire-based RA derived from the surveys in Jiashan County and Haining Metropolis of Zhejiang Province within the Nineteen Nineties. The RA instrument could also be outdated, and didn’t precisely mirror the chance exposures these days. The danger elements of CRC have been altering over time, and BMI, bodily actions and smoking needs to be included within the questionnaire now.” (Feminine, CDC employees, ID7)
The consultants additionally proposed to make use of 1-sample FIT as a substitute of 2-sample checks, or apply quantitative FIT as a substitute of inaccurate qualitative checks. Concerning the affordability, most consultants thought that the price of 20 CNY per quantitative take a look at is appropriate in China.
“For the FIT, I like to recommend 1-sample FIT as a substitute of 2-sample checks in response to the outcomes of our screening program, and as most nations did.” (Male, researcher, ID14)
“Just lately, I heard that an company of OC-MICRO (a model of FIT) in Hangzhou supplied the fee per capita of 20 CNY. The federal government of Zhejiang Province has launched a program for early detection of most cancers, and intends to make use of quantitative FIT, however I do not know whether or not they’re utilizing it this yr.” (Male, major care supplier, ID1)
“In my view, there is no such thing as a downside with CRC screening checks and the hot button is to totally notice the effectiveness of every half in the entire screening course of. Nonetheless, a giant hole existed between the noticed and the anticipated effectiveness of a sure screening program. I believe crucial is to totally notice the anticipated effectiveness of every take a look at in CRC screening observe.” (Feminine, researcher, ID12)
3.1.4 C4: prospects for growth of CRC screening
The a lot larger prices of the novel screening checks for CRC than RA, FIT and even colonoscopy would restrict the widespread use of those novel checks in China, a rustic with an enormous inhabitants and inadequate medical assets. As proven in Desk 2, the price of colonoscopy is much decrease in China (44 USD) than in the USA (2,300 USD), which devalue and limit the applying of the accessible novel CRC screening checks in China.
On this research, 9 consultants (ID 1, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 12, 13, 14) believed that not one of the accessible novel CRC screening checks is sweet sufficient to switch the triage screening strategies which might be at the moment used. Nonetheless, they acknowledged that a number of novel checks can be utilized instead screening technique, and have nice potential in opportunistic screening. 5 consultants (ID 2, 3, 10, 11, 15) believed that mt-sDNA take a look at is probably the most promising novel technique for CRC screening within the close to future.
“Because of the comparatively excessive value, the novel checks could also be used as the choice strategies in personalised service. Nonetheless, the federal government can merely present primary public well being companies however not the personalised ones. We are able to present the residents with totally different alternate options, however it isn’t economically sensible for presidency to cowl all of the bills.” (Male, well being official, ID5)
“The mt-sDNA take a look at may help to enhance sensitivity and enhance participation price of screening … you possibly can modify threshold of mt-sDNA take a look at for extra focused screening, which I believe is an effective factor. The mt-sDNA take a look at contains quantitative molecular assays for hemoglobin, genetic mutations, methylation, and so forth. I believe it’s of nice significance for CRC screening.” (Male, gastroenterologist, ID3)
3.2 Mannequin development
Based mostly on the subcategories, major classes and core classes recognized in Desk 3, the important points in CRC screening in China may be summarized right into a grounded theoretical mannequin in Determine 3. Over the previous many years, the triage screening modality utilized in CRC screening packages (M1) has been discovered fairly appropriate for China and broadly adopted within the nation resulting from its cheapness and comfort (M2). Nonetheless, there are a number of challenges (M3), significantly the suboptimal adherence to colonoscopy that has vastly lowered the effectiveness of screening packages. Components concerning well being propaganda and schooling, high quality management and authorities may additionally affect the effectiveness of screening packages (M4). Luckily, the CRC screening packages may be improved by making use of novel screening checks (M5) or optimizing present screening modality (M8). Regardless of the benefits and good prospects of the novel screening checks (M6), their excessive prices and excessive technical requirement have restricted their utility in large-scale screening packages (M7). Due to this fact, optimization of present screening modality (M8) is very anticipated, which may be achieved through the use of extra correct danger stratification, making use of quantitative FIT, and offering higher colonoscopy service. Within the opinions of the consultants interviewed, contemplating the commonly acknowledged effectiveness of CRC screening (M9), the various growth in CRC screening is very anticipated, together with personalised screening, optimized screening process, larger inhabitants adherence, larger specificity of preliminary checks, use of novel screening checks, and improved well being schooling (M10).
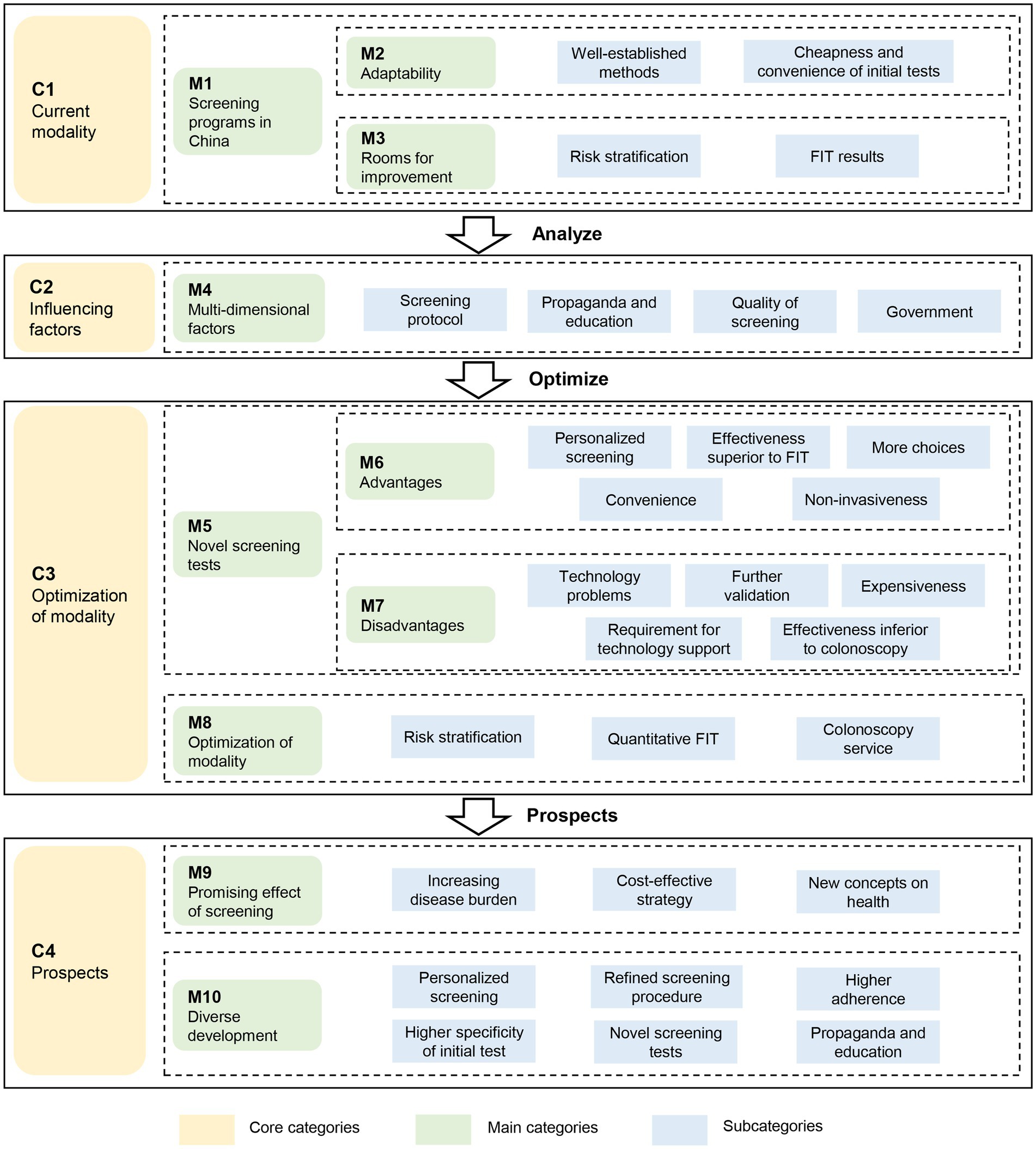
Determine 3. The grounded theory-based framework to guage the screening methods for colorectal most cancers. FIT: fecal immunochemical take a look at.
4 Dialogue
On this research, we explored the viewpoints of 15 consultants concerning the CRC screening modality in China by means of semi-structured interviews. Typically, the consultants responded positively to the triage screening modality adopted in China, but additionally expressed issues on the low adherence to colonoscopy amongst high-risk topics who had been recognized by preliminary screening checks. The consultants instructed to optimize the preliminary screening take a look at through the use of quantitative FIT as a substitute of the qualitative one, and by updating the RA instruments currently-used in China. For the rising screening applied sciences, the consultants proposed to make use of the novel checks as supplementary strategies to the triage screening modalities. The opinions might assist to optimize the currently-used screening modality for CRC, enhance adherence to follow-up colonoscopy, and absolutely obtain the effectiveness of screening packages in China.
The effectiveness of CRC screening packages relies on the accuracy of screening checks and the adherence of screened populations (40). A low adherence to colonoscopy was persistently noticed amongst high-risk topics recognized by preliminary checks in China (8, 12). On this research, most consultants believed that adherence to colonoscopy was influenced by the accuracy of FIT, probably the most generally used preliminary take a look at in triage screening for CRC globally. In our earlier research, we discovered that adherence to colonoscopy was positively related to specificity and optimistic predictive worth of preliminary screening checks (14, 15), which was in step with the findings in different populations (41, 42). Due to this fact, the excessive false-positive price of preliminary checks in China was the frequent concern of the consultants on this research.
To launch the priority, the consultants proposed two approaches to lower false-positive price of the preliminary checks, which can assist to enhance the adherence to subsequent colonoscopy in China. First, the knowledgeable beneficial to make use of quantitative FIT as a substitute of the qualitative one. The quantitative FITs outperform the qualitative ones not solely resulting from its larger accuracy, but additionally for its versatile cut-off values (43). Nonetheless, quantitative FIT stays to be developed for the large-scale screening practices in China resulting from its comparatively larger value. Furthermore, the sensitivity and specificity of one-sample qualitative FIT was discovered just like these of multiple-sample checks, whatever the model of FIT merchandise (27). Evidently, one-sample FIT needs to be adopted in China to simplify the screening process, enhance participation price, and scale back calls for for colonoscopy (44). Second, the consultants proposed to replace the RA instruments. The currently-used RA instrument didn’t embrace age, intercourse, smoking, ingesting, BMI, eating regimen, bodily exercise, analysis of diabetes, use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicine or aspirin (8, 11, 12), the frequent danger elements of CRC included in different danger scoring methods (45, 46) and beneficial within the up to date Chinese language guideline for CRC screening (32). It was additionally discovered that a number of elements for RA may be faraway from questionnaire with none extra missed CRC circumstances (47). Thus, the RA instruments is urgently wanted to be up to date utilizing population-and period-specific danger elements of CRC for higher accuracy and applicability.
Lately, many novel CRC screening checks have been developed to switch or scale back invasive examination like colonoscopy. Nonetheless, the inconsistent efficiency of those checks in populations has restricted their widespread functions (32, 48). In spite of everything, the accuracy is crucial characteristic of a screening take a look at. On this research, we discovered that the consultants ranked affordability the second most essential characteristic of screening checks, significantly for large-scale screening packages. Most novel screening checks are costly and typically require extra technical help. For instance, about 512 USD is required for one mt-sDNA take a look at, a lot decrease than 1,172 USD for a colonoscopy within the US. Due to this fact, mt-sDNA take a look at is beneficial within the guideline in all probability for the consideration of cost-effectiveness. In China, nonetheless, solely 44 USD is required for a colonoscopy examination, a lot decrease than the prices in western nations (28, 29). Due to this fact, it’s more cost effective to use colonoscopy in China, the reference take a look at in CRC screening. To this point, the novel checks are instructed for use in opportunistic screening in bodily examination establishments or hospitals.
This research has a number of limitations. First, we didn’t interview the contributors of CRC screening packages, who might present extra opinions on the CRC screening packages in China. Nonetheless, as this qualitative interview research was designed from the attitude of service suppliers, and the opinions of the consultants had been derived from their expertise and interactions with the screened topics, our outcomes have nice values for evidence-based coverage making. Second, the interview was carried out within the Chinese language setting with country-specific coverage, practical situation, and educational points, which inevitably brings the query of whether or not the mannequin was common and relevant in different nations. Lastly, the conclusions of this research had been made by means of a theoretical dialogue, not primarily based on a real-world screening information evaluation. Nonetheless, we summarized the sensitivity, specificity and value of every currently-used preliminary screening checks by means of complete literature evaluations, and supplied the knowledge to our topics on the interview, which can have made the dialogue evidence-based.
5 Conclusion
Within the opinions of consultants in China, the triage screening modality, if improved, stays the optimum selection for Chinese language populations. To make use of quantitative FIT or replace RA instruments might assist to establish high-risk people extra precisely, enhance adherence to subsequent colonoscopy, and thus absolutely obtain the effectiveness of screening. The rising novel applied sciences have nice potentials in opportunistic CRC screening in China as supplementary checks. Additional research are wanted to confirm and enhance the grounded theoretical mannequin developed on this research, and apply the theoretical outcomes into the real-world screening practices.
Information availability assertion
The uncooked information supporting the conclusions of this text will likely be made accessible by the authors, with out undue reservation.
Creator contributions
WX conceived and designed the research. WW, YC, and MCW made substantial contributions to the research design. WW drafted the manuscript. WW and ST contributed to information assortment and information sorting. ST and JH contributed to information evaluation. All authors contributed to the article and accredited the submitted model.
Funding
This research was supported by the Well being Fee of Pudong New Space of Shanghai (no. PW2019A-5).
Acknowledgments
We thank the consultants taking part the qualitative interview.
Battle of curiosity
The authors declare that the analysis was carried out within the absence of any industrial or monetary relationships that could possibly be construed as a possible battle of curiosity.
Writer’s be aware
All claims expressed on this article are solely these of the authors and don’t essentially signify these of their affiliated organizations, or these of the writer, the editors and the reviewers. Any product which may be evaluated on this article, or declare which may be made by its producer, isn’t assured or endorsed by the writer.
Abbreviations
BMI, physique mass index; CMS, facilities for medicare and medicaid companies; CDC, facilities for illness prevention and management; CRC, colorectal most cancers; FIT, fecal immunochemical take a look at; gFOBT, guaiac fecal occult blood take a look at; mSEPT9, methylated SEPT9 DNA plasma assay; mt-sDNA, multi-target stool DNA take a look at; RA, danger evaluation.
References
1. Lin, JS, Perdue, LA, Henrikson, NB, Bean, SI, and Blasi, PR. Screening for colorectal Most cancers: up to date proof report and systematic evaluation for the US preventive companies process power. JAMA. (2021) 325:1978–97. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.4417
2. Benard, F, Barkun, AN, Martel, M, and von Renteln, D. Systematic evaluation of colorectal most cancers screening tips for average-risk adults: summarizing the present world suggestions. World J Gastroenterol. (2018) 24:124–38. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i1.124
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
3. Navarro, M, Nicolas, A, Ferrandez, A, and Lanas, A. Colorectal most cancers inhabitants screening packages worldwide in 2016: an replace. World J Gastroenterol. (2017) 23:3632–42. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i20.3632
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
4. Schreuders, EH, Ruco, A, Rabeneck, L, Schoen, RE, Sung, JJ, Younger, GP, et al. Colorectal most cancers screening: a world overview of current programmes. Intestine. (2015) 64:1637–49. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-309086
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
5. Sung, JJ, Ng, SC, Chan, FK, Chiu, HM, Kim, HS, Matsuda, T, et al. An up to date Asia Pacific consensus suggestions on colorectal most cancers screening. Intestine. (2015) 64:121–32. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-306503
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
6. Dong, ZW
. Pointers of most cancers screening, early detection and early remedy of China. 1st ed. Peking: Peking College Medical Press (2005).
7. Ye, D, Huang, Q, Li, Q, Jiang, X, Mamat, M, Tang, M, et al. Comparative analysis of preliminary screening strategies for colorectal Most cancers in a mass program. Dig Dis Sci. (2017) 62:2532–41. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4648-1
8. Gong, Y, Peng, P, Bao, P, Zhong, W, Shi, Y, Gu, Okay, et al. The implementation and first-round outcomes of a community-based colorectal Most cancers screening program in Shanghai. China Oncologist. (2018) 23:928–35. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0451
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
9. Liao, Y, Li, S, Chen, C, He, X, Lin, F, Wang, J, et al. Screening for colorectal most cancers in Tianhe, Guangzhou: outcomes of mixing fecal immunochemical checks and danger elements for choosing sufferers requiring colonoscopy. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). (2018) 6:132–6. doi: 10.1093/gastro/gox030
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
10. Zhang, M, Zhao, L, Zhang, Y, Jing, H, Wei, L, Li, Z, et al. Colorectal Most cancers screening with excessive risk-factor questionnaire and fecal immunochemical checks amongst 5, 947, 986 asymptomatic inhabitants: a population-based research. Entrance Oncol. (2022) 12:893183. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.893183
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
11. Meng, W, Cai, SR, Zhou, L, Dong, Q, Zheng, S, and Zhang, SZ. Efficiency worth of excessive danger elements in colorectal most cancers screening in China. World J Gastroenterol. (2009) 15:6111–6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.6111
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
12. Chen, H, Li, N, Ren, J, Feng, X, Lyu, Z, Wei, L, et al. Participation and yield of a population-based colorectal most cancers screening programme in China. Intestine. (2019) 68:1450–7. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317124
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
13. Zheng, S, Chen, Okay, Liu, X, Ma, X, Yu, H, Chen, Okay, et al. Cluster randomization trial of sequence mass screening for colorectal most cancers. Dis Colon Rectum. (2003) 46:51–8. doi: 10.1007/s10350-004-6496-2
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
14. Wu, WM, Wang, Y, Jiang, HR, Yang, C, Li, XQ, Yan, B, et al. Colorectal Most cancers screening modalities in Chinese language inhabitants: observe and classes in Pudong new space of Shanghai, China. Entrance Oncol. (2019) 9:399. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00399
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
15. Wu, W, Huang, J, Yang, Y, Gu, Okay, Luu, HN, Tan, S, et al. Adherence to colonoscopy in cascade screening of colorectal most cancers: a scientific evaluation and meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 37:620–31. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15762
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
16. Money, BD, Fleisher, MR, Fern, S, Rajan, E, Haithcock, R, Kastenberg, DM, et al. Multicentre, potential, randomised research evaluating the diagnostic yield of colon capsule endoscopy versus CT colonography in a screening inhabitants (the TOPAZ research). Intestine. (2021) 70:2115–22. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322578
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
17. Davidson, KW, Barry, MJ, Mangione, CM, Cabana, M, Caughey, AB, Davis, EM, et al. Screening for colorectal Most cancers: US preventive companies process power suggestion assertion. JAMA. (2021) 325:1965–77. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.6238
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
18. Bibbins-Domingo, Okay, Grossman, DC, Curry, SJ, Davidson, KW, Epling, JW Jr, Garcia, FAR, et al. Screening for colorectal Most cancers: US preventive companies process power suggestion assertion. JAMA. (2016) 315:2564–75. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.5989
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
19. Corbin, JM, and Strauss, A. Grounded idea analysis: procedures, canons, and evaluative standards. Qual Sociol. (1990) 13:3–21. doi: 10.1007/BF00988593
20. Starks, H, and Trinidad, SB. Select your technique: a comparability of phenomenology, discourse evaluation, and grounded idea. Qual Well being Res. (2007) 17:1372–80. doi: 10.1177/1049732307307031
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
21. Tong, A, Sainsbury, P, and Craig, J. Consolidated standards for reporting qualitative analysis (COREQ): a 32-item guidelines for interviews and focus teams. Int J Qual Well being Care. (2007) 19:349–57. doi: 10.1093/intqhc/mzm042
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
22. World Medical Affiliation declaration of Helsinki
. Suggestions guiding physicians in biomedical analysis involving human topics. JAMA. (1997) 277:925–6. doi: 10.1001/jama.277.11.925
23. Damschroder, LJ, Aron, DC, Keith, RE, Kirsh, SR, Alexander, JA, and Lowery, JC. Fostering implementation of well being companies analysis findings into observe: a consolidated framework for advancing implementation science. Implement Sci. (2009) 4:50. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-4-50
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
24. Kirk, MA, Kelley, C, Yankey, N, Birken, SA, Abadie, B, and Damschroder, L. A scientific evaluation of using the consolidated framework for implementation analysis. Implement Sci. (2016) 11:72. doi: 10.1186/s13012-016-0437-z
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
25. Cenin, D, Li, P, Wang, J, de Jonge, L, Yan, B, Tao, S, et al. Optimising colorectal most cancers screening in Shanghai, China: a modelling research. BMJ Open. (2022) 12:e048156. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-048156
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
26. Peng, BJ, Cao, CY, Li, W, Zhou, YJ, Zhang, Y, Nie, YQ, et al. Diagnostic efficiency of intestinal Fusobacterium nucleatum in colorectal Most cancers: a Meta-analysis. Chin Med J. (2018) 131:1349–56. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.232814
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
27. Lee, JK, Liles, EG, Bent, S, Levin, TR, and Corley, DA. Accuracy of fecal immunochemical checks for colorectal most cancers: systematic evaluation and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. (2014) 160:171. doi: 10.7326/m13-1484
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
28. Peterse, EFP, Meester, RGS, de Jonge, L, Omidvari, AH, Alarid-Escudero, F, Knudsen, AB, et al. Evaluating the cost-effectiveness of revolutionary colorectal Most cancers screening checks. J Natl Most cancers Inst. (2021) 113:154–61. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djaa103
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
29. Cai, SR, Huang, YQ, Zhang, SZ, Li, QR, Ma, XY, and Zheng, S. Results of subitems within the colorectal most cancers screening protocol on the Chinese language colorectal most cancers screening program: an evaluation primarily based on pure group screening outcomes. BMC Most cancers. (2019) 19:47. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-5191-y
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
30. Yau TOTang, CM, Harriss, EK, Dickins, B, and Polytarchou, C. Faecal microRNAs as a non-invasive instrument within the analysis of colonic adenomas and colorectal most cancers: a meta-analysis. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:9491. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45570-9
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
31. Gachabayov, M, Lebovics, E, Rojas, A, Felsenreich, DM, Latifi, R, and Bergamaschi, R. Efficiency analysis of stool DNA methylation checks in colorectal most cancers screening: a scientific evaluation and meta-analysis. Shade Dis. (2021) 23:1030–42. doi: 10.1111/codi.15521
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
32. Nationwide Most cancers Middle, China
. Skilled Group of the Growth of China guideline for the screening, early detection and early remedy of colorectal Most cancers. [China guideline for the screening, early detection and early treatment of colorectal cancer (2020, Beijing)]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. (2021) 43:16–38. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20210105-00010
33. Pecere, S, Senore, C, Hassan, C, Riggi, E, Segnan, N, Pennazio, M, et al. Accuracy of colon capsule endoscopy for superior neoplasia. Gastrointest Endosc. (2020) 91:406–414.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2019.09.041
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
34. Hassan, C, Zullo, A, Winn, S, and Morini, S. Price-effectiveness of capsule endoscopy in screening for colorectal most cancers. Endoscopy. (2008) 40:414–21. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-995565
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
35. Zauber, AG, Lansdorp-Vogelaar, I, Knudsen, AB, Wilschut, J, van Ballegooijen, M, and Kuntz, KM. Evaluating take a look at methods for colorectal most cancers screening: a call evaluation for the U.S. preventive companies process power. Ann Intern Med. (2008) 149:659–69. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-149-9-200811040-00244
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
36. Wong, CK, Lam, CL, Wan, YF, and Fong, DY. Price-effectiveness simulation and evaluation of colorectal most cancers screening in Hong Kong Chinese language inhabitants: comparability amongst colonoscopy, guaiac and immunologic fecal occult blood testing. BMC Most cancers. (2015) 15:705. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1730-y
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
37. Wang, H, Ye, H, and Liu, L. Developing massive information prevention and management mannequin for public well being emergencies in China: a grounded idea research. Entrance Public Well being. (2023) 11:1112547. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1112547
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
38. Chiu, HM, Chen, SLS, Yen, AMF, Chiu, SYH, Fann, JCY, Lee, YC, et al. Effectiveness of fecal immunochemical testing in lowering colorectal most cancers mortality from the a million Taiwanese screening program. Most cancers. (2015) 121:3221–9. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29462
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
40. Hassan, C, Giorgi Rossi, P, Camilloni, L, Rex, DK, Jimenez-Cendales, B, Ferroni, E, et al. Meta-analysis: adherence to colorectal most cancers screening and the detection price for superior neoplasia, in response to the kind of screening take a look at. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. (2012) 36:929–40. doi: 10.1111/apt.12071
41. Lin, G, Feng, Z, Liu, H, Li, Y, Nie, Y, Liang, Y, et al. Mass screening for colorectal most cancers in a inhabitants of two million older adults in Guangzhou, China. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:10424. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46670-2
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
42. Miles, A, Rodrigues, V, and Sevdalis, N. The impact of details about false unfavourable and false optimistic charges on individuals’s attitudes in the direction of colorectal most cancers screening utilizing faecal occult blood testing (FOBt). Affected person Educ Couns. (2013) 93:342–9. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2013.06.010
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
43. Kaminski, MF, Robertson, DJ, Senore, C, and Rex, DK. Optimizing the standard of colorectal Most cancers screening worldwide. Gastroenterology. (2020) 158:404–17. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.026
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
44. Schreuders, EH, Grobbee, EJ, Nieuwenburg, SAV, Kapidzic, A, van Roon, AHC, van Vuuren, AJ, et al. A number of rounds of 1 pattern versus two pattern faecal immunochemical test-based colorectal most cancers screening: a population-based research. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2019) 4:622–31. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30176-1
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
45. Peng, L, Weigl, Okay, Boakye, D, and Brenner, H. Danger scores for predicting superior colorectal neoplasia within the average-risk inhabitants: a scientific evaluation and Meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. (2018) 113:1788–800. doi: 10.1038/s41395-018-0209-2
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
46. Williams, TG, Cubiella, J, Griffin, SJ, Walter, FM, and Usher-Smith, JA. Danger prediction fashions for colorectal most cancers in individuals with signs: a scientific evaluation. BMC Gastroenterol. (2016) 16:63. doi: 10.1186/s12876-016-0475-7
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
47. Li, J, Li, QL, Xue, F, Yu, LL, and Ma, WL. Software of Faecal occult blood testing and questionnaire danger evaluation in inhabitants screening for colorectal Most cancers. China Most cancers. (2015) 24:385–9. doi: 10.11735/j.issn.1004-0242.2015.05.A008
48. Spada, C, Hassan, C, Bellini, D, Burling, D, Cappello, G, Carretero, C, et al. Imaging alternate options to colonoscopy: CT colonography and colon capsule. European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) and European Society of Gastrointestinal and Belly Radiology (ESGAR) guideline – replace 2020. Eur Radiol. (2021) 31:2967–82. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07413-4