Sufferers and therapy
From 18 March 2020 to 18 December 2021, 1,005 sufferers at 72 websites had been assessed for eligibility. Total, 738 had been randomized to therapy (intention-to-treat (ITT) inhabitants); 246 had been assigned to obtain benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC, 245 to obtain anlotinib plus EC, and 247 to obtain EC (Fig. 1). Baseline demographic and illness traits had been nicely balanced throughout therapy teams (Desk 1). Most sufferers had stage IV illness (660 of 738 (89.4%)), with a median age of 62 (vary 30–75) years at prognosis, and 73 sufferers (9.9%) had mind metastases at baseline.
Of the 738 enrolled sufferers, 736 sufferers obtained not less than one dose of protocol therapy (security inhabitants). After the completion of induction remedy, 214 sufferers within the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC group, 208 within the anlotinib plus EC group and 208 within the EC alone group obtained deliberate upkeep remedy. On the deliberate interim evaluation for OS (knowledge cutoff 14 Could 2022), 89 sufferers are nonetheless ongoing the assigned therapy. The first cause for therapy discontinuation was illness development (56.1%, 67.8% and 78.5%, respectively) or demise (3.3%, 3.3% and a couple of.8%, respectively). Among the many sufferers who withdrew from the examine, subsequent systemic remedy was administered to 42.7% of the sufferers within the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC group, 58.4% within the anlotinib plus EC group and 71.3% within the EC alone group (Prolonged Information Desk 1).
Efficacy
Main endpoint of OS
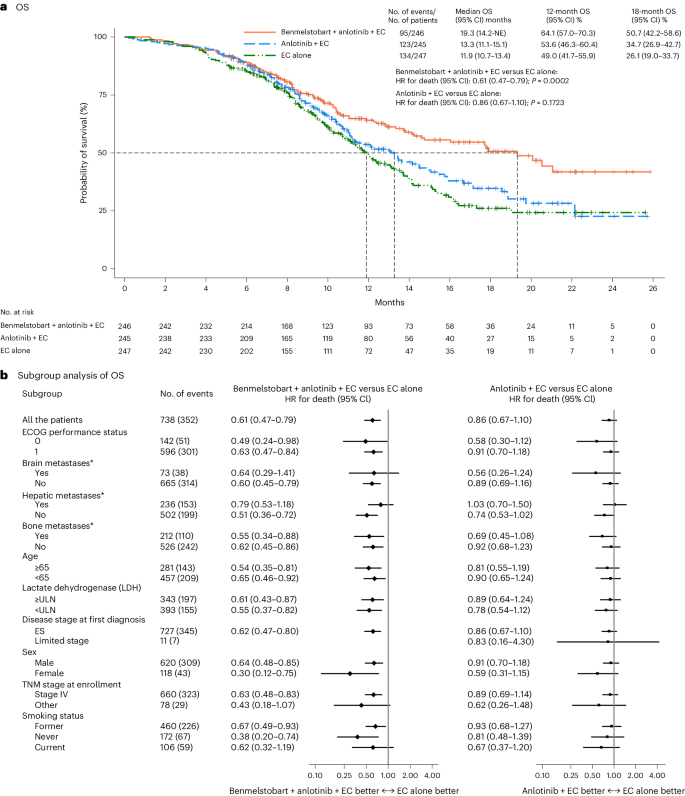
On the level of knowledge cutoff, the median follow-up for OS was 14.0 months (95% confidence interval (CI) 12.8–15.5) for the ITT inhabitants. On the prespecified interim evaluation for OS (at 352 deaths within the general inhabitants; knowledge cutoff 14 Could 2022), median OS was higher within the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC group in contrast with the EC alone group (19.3 months (95% CI 14.2 to not estimable) versus 11.9 months (95% CI 10.7–13.4); hazard ratio (HR), 0.61 (95% CI 0.47–0.79); P = 0.0002), assembly the prespecified standards for statistical significance (Fig. 2a). The anlotinib plus EC group had no important OS profit over the EC alone group (13.3 months (95% CI 11.1–15.1) versus 11.9 months (95% CI 10.7–13.4); HR, 0.86 (95% CI 0.67–1.10); P = 0.1723; Fig. 2a). The estimated OS price at 12 months was 64.1% (95% CI 57.0–70.3), 53.6% (95% CI 46.3–60.4) and 49.0% (95% CI 41.7–55.9) and at 18 months was 50.7% (95% CI 42.2–58.6), 34.7% (95% CI 26.9–42.7) and 26.1% (95% CI 19.0–33.7) within the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC, anlotinib plus EC, and EC alone teams, respectively. OS favored the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC group or anlotinib plus EC group over the EC alone group throughout a number of prespecified subgroups (Fig. 2b).
a, The Kaplan–Meier curves for OS in three therapy teams. The tick marks point out censored knowledge. Variations between the therapy teams had been evaluated with the stratified log-rank take a look at. P values are two-sided. b, The subgroup evaluation of OS. A stratified Cox regression mannequin was used to estimate the HR for demise and 95% CIs. The circles point out HR amongst subgroups of sufferers, the horizontal traces point out corresponding 95% CIs and the vertical dotted line signifies the HR for the general inhabitants. *Metastatic lesions had been categorized on the idea of their presence or absence. Any affected person with liver metastasis, no matter whether or not it was the only real metastatic website or coexisting with different metastases, was included within the liver metastasis group for evaluation. ULN, higher restrict of regular; TNM, tumor, node, metastasis.
Main endpoint of PFS
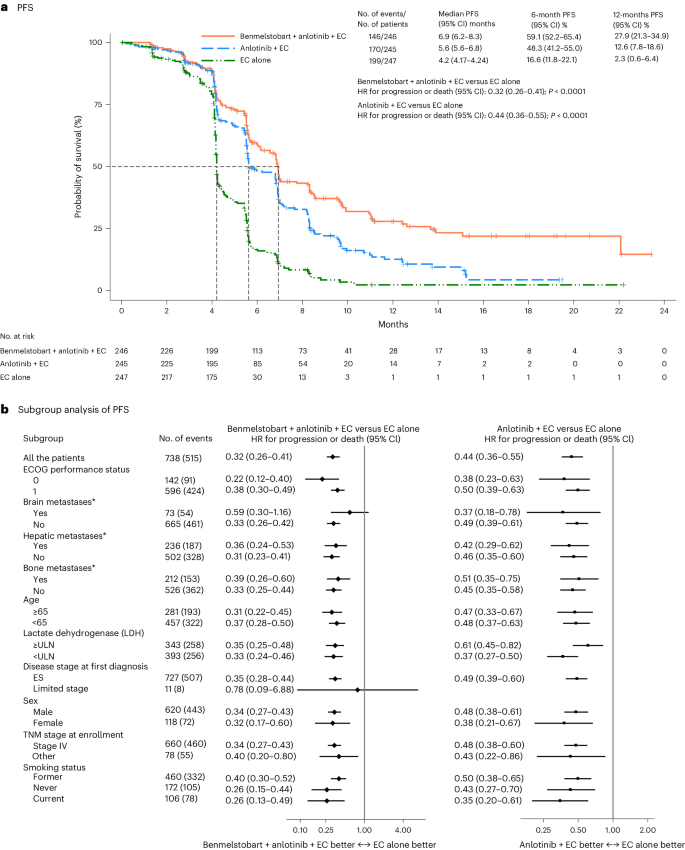
Development-free survival (PFS) was assessed by the Impartial Evaluate Committee (IRC). Right here, we report the outcomes of the prespecified last evaluation for PFS after prevalence of 347 PFS occasions. With 515 occasions of illness development or demise, median IRC-assessed PFS was considerably longer, in contrast with the EC alone group, in each the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC group (6.9 months (95% CI 6.2–8.3) versus 4.2 months (95% CI 4.17–4.24); HR 0.32 (95% CI 0.26–0.41); P < 0.0001) and within the anlotinib plus EC group (5.6 months (95% CI 5.6–6.8) versus 4.2 months (95% CI 4.17–4.24); HR 0.44 (95% CI 0.36–0.55); P < 0.0001) (Fig. 3a). The PFS price at 6 months was 59.1% (95% CI 52.2–65.4), 48.3% (95% CI 41.2–55.0) and 16.6% (95% CI 11.8–22.1) within the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC, anlotinib plus EC, and EC alone teams, respectively; at 12 months PFS price was 27.9% (95% CI 21.3–34.9), 12.6% (95% CI 7.8–18.6) and a couple of.3% (95% CI 0.6–6.4), respectively. The PFS good thing about the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC group or anlotinib plus EC group was noticed in all subgroups (Fig. 3b).
a, The Kaplan–Meier curves for PFS in three therapy teams. The tick marks point out censored knowledge. PFS was assessed in response to RECIST 1.1, by an unbiased assessment committee. Variations between the therapy teams had been evaluated with the stratified log-rank take a look at. P values are two-sided. b, The subgroup evaluation of PFS. A stratified Cox regression mannequin was used to estimate the HR for demise and 95% CIs. The circles point out HR amongst subgroups of sufferers, the horizontal traces point out corresponding 95% CIs and the vertical dotted line signifies the HR for the general inhabitants. *Metastatic lesions had been categorized on the idea of their presence or absence. Any affected person with liver metastasis, no matter whether or not it was the only real metastatic website or coexisting with different metastases, was included within the liver metastasis group for evaluation. ULN, higher restrict of regular; TNM, tumor, node, metastasis.
Secondary endpoints
The investigator evaluation reported that each the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC group and the anlotinib plus EC group improved PFS in contrast with the EC alone group per Response Analysis Standards in Stable Tumors model 1.1 (RECIST 1.1) (Supplementary Fig. 1a) or Immunotherapy Response Analysis Standards in Stable Tumours (iRECIST) (Supplementary Fig. 1b); this was in keeping with the IRC-assessed outcomes based mostly on RECIST 1.1. The share of sufferers with an IRC-assessed goal response was 81.3% (95% CI 75.9–86.0) within the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC group and 81.2% (95% CI 75.8–85.9) within the anlotinib plus EC group, which had been each considerably increased than within the EC alone group (66.8%; 95% CI 60.6–72.6; comparative P = 0.0001 and P = 0.0003, respectively) (Desk 2). Three (1.2%) sufferers within the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC group and one (0.4%) affected person within the anlotinib plus EC group attained a whole response (Desk 2). There was no important distinction in illness management price between the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC and EC alone teams (90.7% versus 87.0%; P = 0.2003); nevertheless, a major enchancment with anlotinib plus EC in contrast with EC alone was noticed (92.7% versus 87.0%; P = 0.0378). As assessed by IRC, the median period of response (DoR) for all responders was 5.8 months (95% CI 5.5–7.2) within the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC group, 5.5 months (95% CI 4.3–5.6) within the anlotinib plus EC group, and three.1 months (95% CI 2.9–4.1) within the EC alone group (Supplementary Fig. 2a). The outcomes had been in keeping with these assessed by the investigators per both RECIST 1.1 or iRECIST (Supplementary Fig. 2b and Supplementary Tables 1 and 2).
Security
Therapy-emergent antagonistic occasions (TEAEs) of any grade (100.0% in every group) and of grade 3 or increased had been related (94.3%, 95.9% and 89.0%) within the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC, anlotinib plus EC, and EC alone teams, respectively (Supplementary Desk 3), with the commonest toxicities together with thrombocytopenia, neutropenia and leukopenia (Prolonged Information Desk 2). Therapy-related antagonistic occasions (TRAEs) had been reported in 100.0%, 99.6% and 99.6% of sufferers within the three teams, respectively; of those, 93.1%, 94.3% and 87.0%, respectively, had been grade 3 or increased, with hematologic toxicities and hypertension being the commonest occasions (Desk 3). TRAEs resulting in benmelstobart/placebo interruption occurred equally between benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC (50.4%) and anlotinib plus EC (46.3%) teams, and had been extra widespread than within the EC alone (33.3%) group. The median time to first interruption of benmelstobart/placebo was 1.45 months (interquartile vary (IQR) 0.49–2.60) within the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC group, 1.12 months (IQR 0.49–2.14) within the anlotinib plus EC group, and 1.35 months (IQR 0.49–2.46) within the EC alone group. An analogous pattern of TRAEs resulting in anlotinib/placebo dose discount or interruption was noticed throughout three teams (61.4%, 61.1% and 37.0%, respectively), with a median time to first dose discount/interruption of 1.38 months (IQR 0.49–2.66), 1.25 months (IQR 0.49–2.17) and 1.51 months (IQR 0.49–2.56), respectively. TRAEs induced demise in 4.5%, 2.5% and 1.6% of sufferers within the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC, anlotinib plus EC, and EC alone teams, respectively. TRAEs resulting in demise are listed in Supplementary Desk 4 and embody pneumonitis (one, one and one affected person), hemoptysis (two, one and 0), dyspnea/respiratory failure (one, two and 0) and sepsis (one, zero and 0) within the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC, anlotinib plus EC, and EC alone teams, respectively. 5 sufferers had deadly TRAEs (attributable to pneumonitis, sepsis, empyema or acute coronary heart failure and one affected person with a mix of pulmonary an infection with suspected paraneoplastic syndrome, encephalopathies and meningeal metastasis) within the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC group, and every one affected person in different teams died because of EC-related AEs. Anlotinib-related AEs led to 2 deaths within the anlotinib plus EC group.
Critical antagonistic occasions (SAEs) had been reported in 135 (54.9%), 119 (48.8%) and 101 (41.1%) sufferers within the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC, anlotinib plus EC, and EC alone teams, respectively, with 115 (46.7%), 106 (43.4%) and 84 (34.1%), respectively, being grade 3 or increased. Of those, 83 (33.7%), 67 (27.5%) and 43 (17.5%), respectively, had been thought of to be benmelstobart/anlotinib-related SAEs. Immune-related antagonistic occasions (irAEs) assessed by investigators had been extra widespread within the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC group (42.7%) in contrast with the anlotinib plus EC group (27.5%) or the EC alone group (19.1%), with an analogous remark for grade 3 or increased irAEs (16.7%, 8.2% and 6.9%, respectively). Generally occurring irAEs within the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC group had been hypothyroidism (19.9%) and immune-related pneumonitis (4.5%). Deadly irAEs within the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC group had been immune-related pneumonitis, immune-mediated encephalopathies, acute coronary heart failure, acute coronary syndrome and infectious pneumonia, and the irAE-associated demise within the EC alone group was pneumonitis; no demise because of irAEs occurred within the anlotinib plus EC group. Extra AE particulars are supplied in Prolonged Information Desk 2 and Supplementary Tables 3 and 4.
Well being-related high quality of life (HRQoL)
There was an general enhance within the imply change from baseline over time in EuroQol visible analog scale (EQ-VAS) scores (indicating enhancements) by week 34 within the ITT inhabitants throughout all therapy teams. There have been no important variations in EQ-VAS scores between the examine teams (P > 0.05), which indicated that HRQoL was maintained throughout the therapy interval (Prolonged Information Fig. 1).