Mechanical stress upregulates tumor EMT pathway and promotes tumor migration and invasion potential
We added Matrigel to the scratched LUAD cells seeded on 6-well plates to analyze the affect of mechanical stress to the migration and invasive potential of LUAD cells. The A549 and H1975 cells had enhanced migration potential after including matrix adhesive and had been considerably superior in 24-hour migration potential in comparison with their counterparts maintained with out Matrigel (Fig. 1a). When testing lung adenocarcinoma migration potential by means of the transwell experiments (Fig. 1b), we additionally discovered that the tumor cells with added Matrigel above achieved stronger migration potential and had statistical significance. Equally, when testing the invasive potential of lung adenocarcinoma cells by means of the Transwell experiment, we additionally discovered that the 2 varieties of tumor cells with added matrix glue achieved considerably stronger invasive potential than their counterparts maintained with out Matrigel. (Fig. 1b).
The migration and invasive potential of LUAD cells had been examined by scratch wound-healing assay (a) and transwell assays (b). c EMT marker expression in response to Matrigel addition was measured with Western blot. d Vimentin expression modifications had been visualized with an immunofluorescence assay. e Cell morphology and b-actin alterations had been visualized with Phalloidin Staining (Yellow arrow: tentacles).
The Western blot experiment confirmed that the EMT pathway of tumor cells was considerably upregulated when including the matrix gel, manifested because the upregulation of Vimentin and Snail and downregulation of beta-Catenin and E-cadherin (Fig. 1c). Moreover, the immunofluorescence experiments confirmed that the tumor cells with matrix glue added considerably upregulated Vimentin (Fig. 1d). The Phalloidin experiment demonstrated that the tumor cell cultured with matrix gel modified morphology considerably and had been not spherical and steady, with a major enhance in tentacles (Fig. 1e).
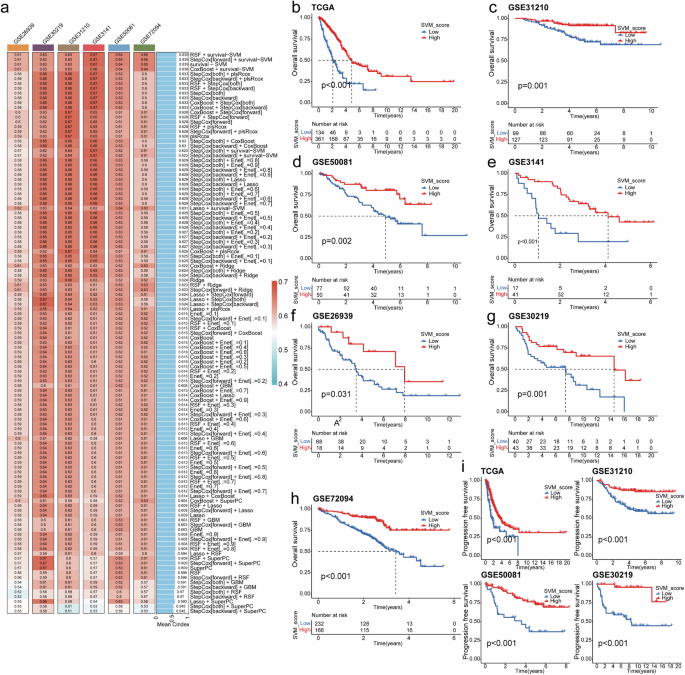
SVM_Score generated primarily based on machine studying successfully predicts the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma sufferers
A warmth map between regular and lung adenocarcinoma tissues of TCGA-LUAD is proven in Supplementary Fig. 1a. The upste plot then reveals 35 BM genes in all seven datasets we used (Supplementary Fig. 1b). The volcanic map shows the differential genes between regular and lung adenocarcinoma tissues of TCGA-LUAD (Supplementary Fig. 1c). On the similar time, we carried out unit correlation evaluation on these 35 BM genes and chosen 14 BM genes associated to the general survival of lung adenocarcinoma for subsequent modeling by intersecting with differential gene outcomes (Supplementary Fig. 1d). The oncoplt confirmed the mutations standing of those 14 genes in lung adenocarcinoma, with the FBN2 gene has the best mutation fee of 16%. (Supplementary Fig. 1e).
Our machine studying evaluation outcomes point out that SVM_score, constructed utilizing a Help Vector Machine (SVM), has the best Concordance Index(C-index), as proven in Fig. 2a. C-index is a statistical measure used to evaluate a mannequin’s discriminatory energy or predictive accuracy, significantly within the context of survival evaluation or time-to-event knowledge. The next C-index signifies a mannequin with good discrimination. Due to this fact, we chosen SVM_score for additional evaluation. Survival evaluation revealed that in TCGA-LUAD (Fig. 2b), GSE31210 (Fig. 2c), GSE50081 (Fig. second), GSE3141 (Fig. 2e), GSE26939 (Fig. 2f), GSE30219 (Fig. 2g), and GSE72094 datasets (Fig. 2h), decrease SVM_score values corresponded with a shorter general survival. Moreover, in TCGA-LUAD, GSE31210, GSE50081, and GSE30219 datasets, decrease SVM_score values had been related to shorter progression-free survival (Fig. 2i).
a Construct and display a prognosis prediction mannequin with machine studying algorithms primarily based on BM genes. b–i Kaplan–Meier survival evaluation for general survival primarily based on SVM_Scores in numerous datasets, together with TCGA-LUAD (b), GSE31210 (c), GSE50081 (d), GSE3141 (e), GSE26939 (f), GSE30219 (g), and GSE72094 (h). i Development-free survival evaluation primarily based on SVM_Scores in TCGA-LUAD, GSE31210, GSE50081, and GSE30219.
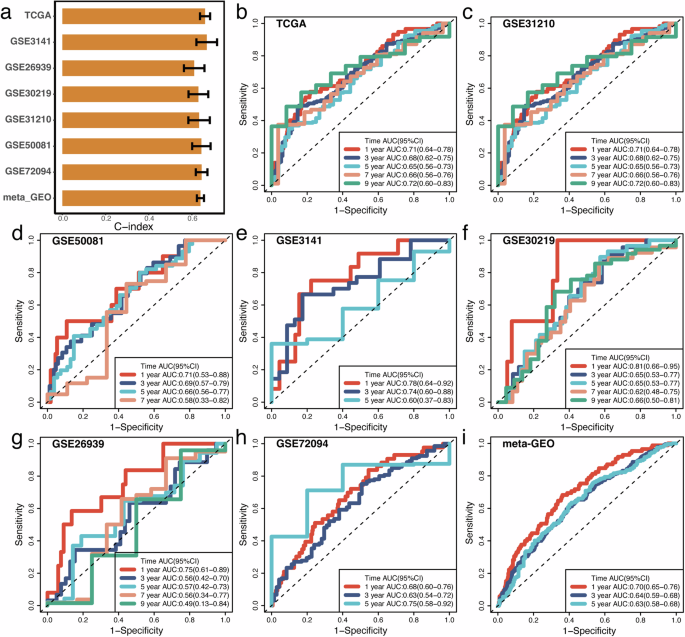
SVM_score demonstrated sturdy prognostic prediction capabilities in TCGA-LUAD, GSE31210, GSE50081, GSE3141, GSE26939, GSE30219, and GSE72094, with C-index values exceeding 0.6 throughout all seven datasets (Fig. 3a). Moreover, the world underneath the curve (AUC) values for one-year general survival, decided by ROC evaluation, exceeded 0.7 in TCGA-LUAD (Fig. 3b), GSE31210 (Fig. 3c), GSE50081 (Fig. 3d), GSE3141 (Fig. 3e), GSE26939 (Fig. 3f), and GSE30219 (Fig. 3g), with GSE30219(Fig. 3h) even surpassing 0.8. The one-year general survival AUC reached 0.7 when combining all GEO datasets (Fig. 3i).
(a) C-index Values: Comparability of C-index values for SVM_Score and different prognostic indicators, evaluating their effectiveness in predicting affected person outcomes. b–i AUC Evaluation with SVM_Score within the numerous datasets, together with TCGA-LUAD (b), GSE31210 (c), GSE50081 (d), GSE3141 (e), GSE30219 (f), GSE26939 (g), GSE72094 (h) and meta-GEO (i).
The c-index of SVM_score, in comparison with different generally used scientific components within the TCGA-LUAD dataset, is barely decrease than the Stage issue however larger than all different components (Supplementary Fig. 2a). Within the meta-GEO dataset, SVM_score outperforms all different components, together with Stage (Supplementary Fig. 2b). Equally, within the GSE31210 dataset, SVM_score surpasses all different components apart from Stage (Supplementary Fig. 2c). Within the GSE50081 dataset, SVM_score outperforms all different components (Supplementary Fig. second). Within the GSE26939 dataset, SVM_score exceeds all different indicators besides age (Supplementary Fig. 2e). Lastly, within the GSE30219 (Supplementary Fig. 2f) and GSE70294 (Supplementary Fig. 2g) datasets, SVM_score outperforms all different components.
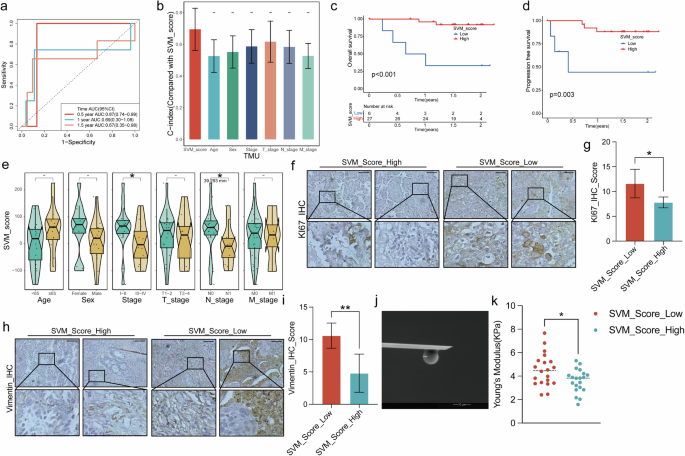
SVM_Score is related to tumor proliferation and EMT propensity in TMU LUAD sufferers
We additional examine the SVM_Score within the LUAD from our institute. Within the 33 circumstances of TMU LUAD sufferers, the one-year general survival AUC worth for SVM_score reached 0.87 (Fig. 4a). Though the C-index of SVM_score might not have achieved statistical significance in comparison with different scientific components, presumably as a result of restricted pattern measurement, it demonstrated a stronger development than all different scientific components (Fig. 4b). Survival evaluation outcomes revealed {that a} decrease SVM_score was related to a worse prognosis, each when it comes to general survival (Fig. 4c) and progression-free survival (Fig. 4d). We additionally assessed whether or not there have been variations in SVM_score amongst numerous scientific components, and the outcomes indicated an affiliation between SVM_score and the lymph node metastasis standing of lung adenocarcinoma (Fig. 4e).
a Utilizing SVM_Score within the carried out ROC evaluation on general survival fee for TMU LUAD sufferers. b Comparability of C-index values and SVM_Score and different scientific components with TMU LUAD sufferers. Survival evaluation illustrates decrease SVM_Score within the TMU LUAD sufferers related to poor general survival (c) and progression-free survival (d). e Verify SVM_Scores in TMU LUAD sufferers stratified by scientific components. Consultant photos of immunohistochemical ends in ten TMU LUAD sufferers with low/excessive SVM_Scores staining with Ki67 (f, g) and Vimentin (h, i). Sufferers with decrease SVM_Scores had considerably larger Ki67 (g) and Vimentin (i). j Electron microscopy scan picture of the probe of atomic pressure microscope. okay Comparability of tumor tissue Younger’s modulus worth between sufferers with excessive and low SVM_Scores.
Immunohistochemistry outcomes additional demonstrated that sufferers with decrease SVM_score had extra tumor cell expression Ki67, indicating a better diploma of malignancy constant and statistically important within the ten sufferers (Fig. 4f–g). Moreover, tumor tissues from sufferers with low SVM_score confirmed elevated expression of Vimentin, signifying larger EMT activation pathway and an elevated metastasis propensity(Fig. 4h). Once more, this development was constant and statistically important in all of the sufferers (Fig. 4i).
Atomic pressure microscopy was used to detect mechanical stress inside the tumor tissues. Tumor tissues from sufferers within the decrease SVM_score group had larger inside mechanical stress (Fig. 4j, okay).
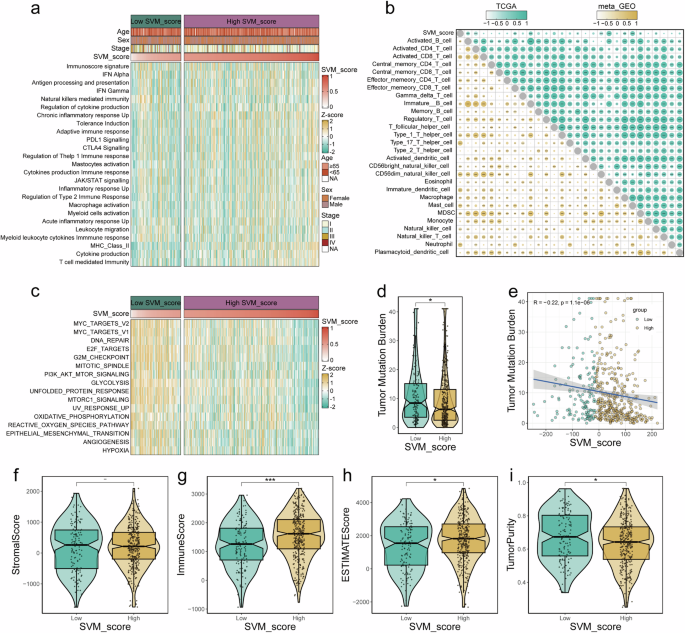
The decrease SVM_score is related to decrease immunogenicity
We employed GSVA to calculate scores for 25 immune-related pathways (Supplementary Appendix 1) in TCGA-LUAD and displayed a heatmap illustrating decrease SVM_Scores in tumor tissues related to lowered immunogenicity (Fig. 5a). For sufferers with low SVM_Scores, the diploma of activation of immune-related pathways is inversely correlated, indicating a decrease degree of immune pathway activation. We carried out separate analyses of the correlation between SVM_Scores and 27 immune cell varieties in TCGA and meta-GEO datasets. The outcomes revealed statistically important correlations between SVM scores and Activated B cell, effector reminiscence CD8+ T cell, immature B cell, CD56dim pure killer cell, immature dendritic cell, macrophage, mast cell, and MDSC in each datasets (Fig. 5b).
a Heatmap shows the correlation between SVM_Score and immunogenicity in TCGA-LUAD. b Correlation evaluation between SVM_Score and immune cell varieties in TCGA and meta-GEO datasets. c GSVA scores for HALLMARK cancer-related pathways, revealing variations in most cancers pathway exercise. d Evaluation of Tumor Mutation Burden (TMB) in relation to SVM_Score. e Adverse correlation between SVM_Score and TMB. The variations between the excessive and low SVM_Score teams when it comes to stromal rating (f), Immune rating (g), ESTIMATE rating (h), and Tumor purity (i).
Utilizing GSVA, we calculated scores for 50 HALLMARK cancer-related pathways (Supplementary Appendix 2). Our findings demonstrated that sufferers with decrease SVM scores exhibited elevated exercise in most cancers pathways, together with the EMT pathway (Fig. 5c). Moreover, sufferers with decrease SVM scores had larger Tumor Mutation Burden (TMB) (Fig. 5d), and SVM scores exhibited a unfavorable correlation with TMB (Fig. 5e).
We employed ESTIMATE to calculate tumor stromal, immune, estimate, and tumor purity scores. We noticed that SVM_Scores had been impartial of stromal scores (Fig. 5f). Sufferers with larger SVM_Scores exhibited larger immune scores (Fig. 5g) and estimate scores (Fig. 5h), in addition to decrease tumor purity (Fig. 5i).
The expression of COL5A1 of myofibroblasts influences the SVM_Score, whereas myofibroblasts are intricately related to the microenvironment
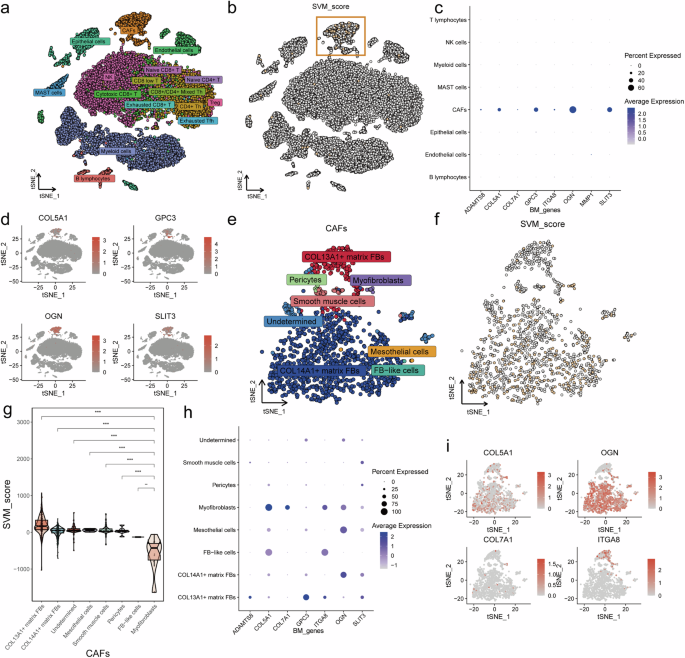
To additional examine SVM_Scores amongst totally different cell populations within the LUAD sufferers, we utilized the GSE131907 dataset, which incorporates single-cell sequencing knowledge from 11 LUAD samples, together with 25,369 cells. The t-SNE dimensionality discount plot shows the varieties of cells in single-cell sequencing knowledge. (Fig. 6a). We computed an SVM_Score for every cell inhabitants and visualized it on the t-SNE plot (Fig. 6b). The outcomes confirmed that the SVM_Score in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) considerably differed from different cell varieties (Fig. 6a, b). The genes contributing to the SVM_Score had been additionally predominantly expressed in CAFs (Fig. 6c). We offered the expression distribution of the highest 4 genes of SVM_Score, COL5A1, GPC3, OGN, and SLT3, on the general single-cell dimensionality discount plot, and so they had been primarily localized in CAFs (Fig. 6d). Due to this fact, we remoted CAFs and carried out a separate t-SNE dimensionality discount (Fig. 6e). When visualizing the distribution of SVM_Scores, the outcomes indicated that every one myofibroblasts have decrease SVM_Scores (Fig. 6f). Furthermore, myofibroblasts exhibited considerably decrease SVM_Scores than all different CAFs, apart from FB-like cells, which couldn’t be statistically analyzed resulting from their restricted numbers (Fig. 6g). Among the many genes contributing to SVM_Scores, COL5A1 confirmed the best expression in myofibroblasts (Fig. 6h). The expression distribution of COL5A1 in CAFs intently resembled the SVM_Score sample (Fig. 6i). In each the TCGA-LUAD cohort (Supplementary Fig. 3a) and the TMU sufferers (Supplementary Fig. 3b), COL5A1 is extremely expressed in tumor tissues. The findings above concerning COL5A1 counsel that COL5A1 might function a pivotal biomarker linking SVM_Scores and mechanical stress.
a, b t-SNE dimensionality discount plot and SVM_Score distribution highlighting cell clustering in numerous cell varieties. c Gene expression profile of SVM_Score-associated genes inside numerous cells. d Expression distribution of high genes (COL5A1, GPC3, OGN, and SLT3) throughout the single-cell dimensionality discount plot e, f Isolation and Distribution of SVM_Score for CAFs. g Comparability of SVM_Score values in myofibroblasts with different CAF subtypes. h Gene expression profile of SVM_Score-associated genes inside CAFs. i Expression distribution of high genes (COL5A1, COL7A1, ITGA8, and OGN) throughout the CAFs single-cell dimensionality discount plot.
Following that, we analyzed mobile interactions within the tumor microenvironment, which revealed that myofibroblasts had been probably the most interactive cell sort with different cells (Supplementary Fig. 4a). Moreover, myofibroblasts exhibited the best interplay depth with different cells (Supplementary Fig. 4b). We additionally recognized that myofibroblasts primarily work together by secreting Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Issue (MIF) and binding to CD74 on the cell floor of different cells, together with CXCR4 or CD44 (Supplementary Fig. 4c).
Notably, myofibroblasts predominantly interacted with different cells by means of the MIF signaling pathway (Supplementary Fig. 4d) and the MK signaling pathway (Supplementary Fig. 4e). Transferring ahead, our focus might be directed towards myofibroblasts and COL5A1.
COL5A1 from myofibroblasts will increase tumor invasiveness and upregulates the EMT pathway of tumor cells
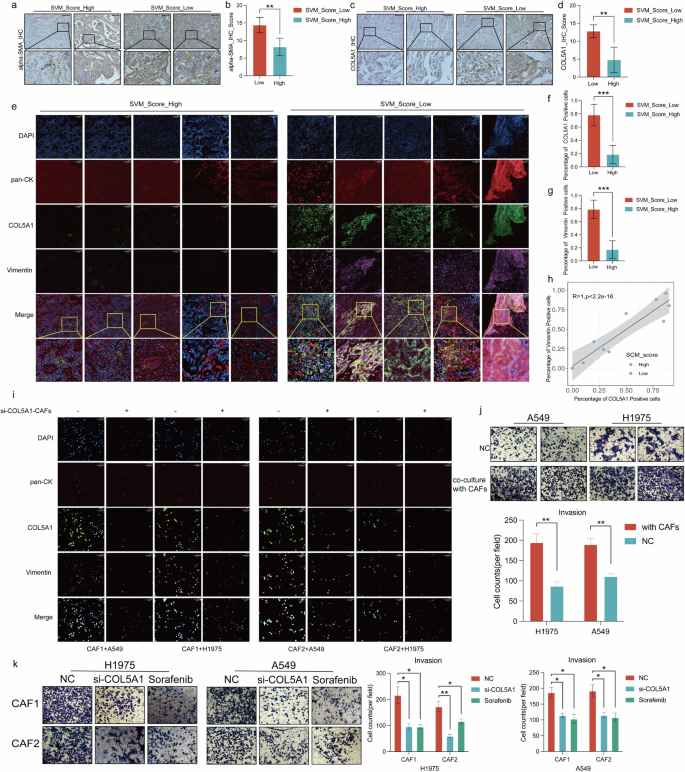
Moreover, immunohistochemistry was utilized to the ten FFPE samples of the aforementioned TMU LUAD sufferers. The outcomes indicated that sufferers with low SVM_Score exhibit larger expression of alpha-SMA (Fig. 7a), which is used as a marker for activated myofibroblasts, and this development is persistently noticed in all ten affected person tissues, with statistical significance (Fig. 7b). Equally, the low SVM_Score sufferers reveal elevated expression of COL5A1 (Fig. 7c), which is persistently important throughout all ten affected person tissues (Fig. 7d). Our examine signifies that elevated mechanical stress prompts the EMT pathway (Fig. 1c, d), concurrently highlighting the reported affiliation between the secretion of COL5A1 and tissue mechanical stress [32]. Due to this fact, multicolor immunofluorescence evaluation was employed to analyze the connection between COL5A1 and the tumor cell EMT pathway within the tissues of ten lung adenocarcinoma sufferers. The outcomes revealed that low SVM_score tissues exhibited larger COL5A1 expression, and close to the areas with elevated COL5A1 expression, Vimentin was additionally extremely expressed (Fig. 7e). This development is constant throughout all ten sufferers and is statistically important (Fig. 7f, g). Moreover, in-depth statistical evaluation of multicolor immunofluorescence reveals that the variety of COL5A1-positive cells is immediately proportional to the variety of vimentin-positive cells with a p-value lower than 0.0001 (Fig. 7h).
(a–d) The immunohistochemical outcomes confirmed that within the tumor tissue of the low SVM_Score group, the expression of alpha-SMA (a, b)was statistically larger than the excessive SVM_Score; and the expression of COL5A1was additionally statistically larger (c, d). e–g Multicolor immunofluorescence evaluation supplies perception into elevated COL5A1 and Vimentin expression in tissues from the decrease SVM_Score group (e). This development is persistently noticed in all ten sufferers and holds statistical significance (f, g). h Pearson correlation evaluation confirmed a robust correlation between the variety of COL5A1-positive and vimentin-positive cells. i Co-culturing si-COL5A1 downregulated CAF cell strains with two sorts of lung adenocarcinoma cells revealed modifications in floor markers COL5A1 and Vimentin expression. j The Transwell experiment detected modifications within the invasive potential of lung adenocarcinoma cells co-cultured with CAFs. okay The Transwell experiment detects the invasive potential of lung adenocarcinoma cells co-cultured with CAFs, particularly after flattening COL5A1 of CAFs or utilizing Sorafenib.
Concurrently, two myofibroblast strains, CAF1 and CAF2 (Supplementary Fig. 5a), had been extracted from the LUAD tumor tissues. Small RNA interference downregulates COL5A1 in these two myofibroblast strains(Supplementary Fig. 5b, c). When co-cultured with tumor cells, it was noticed that tumor cells situated close to CAFs with lowered COL5A1 expression additionally exhibited decreased Vimentin expression (Fig. 7i). We employed Transwell assays to analyze alterations within the invasive capability of lung adenocarcinoma cells co-cultured with cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs). The co-cultivation of lung adenocarcinoma cells with CAFs led to a rise within the invasive potential of lung adenocarcinoma cells (Fig. 7j). Nevertheless, once we knocked down COL5A1 in CAFs or handled them with Sorafenib, the invasive capability of lung adenocarcinoma cells co-cultured with CAFs decreased in contrast with scrambled transfected CAFs (Fig. 7k).
Sorafenib attenuates the tumor-promoting impact of COL5A1 from myofibroblast
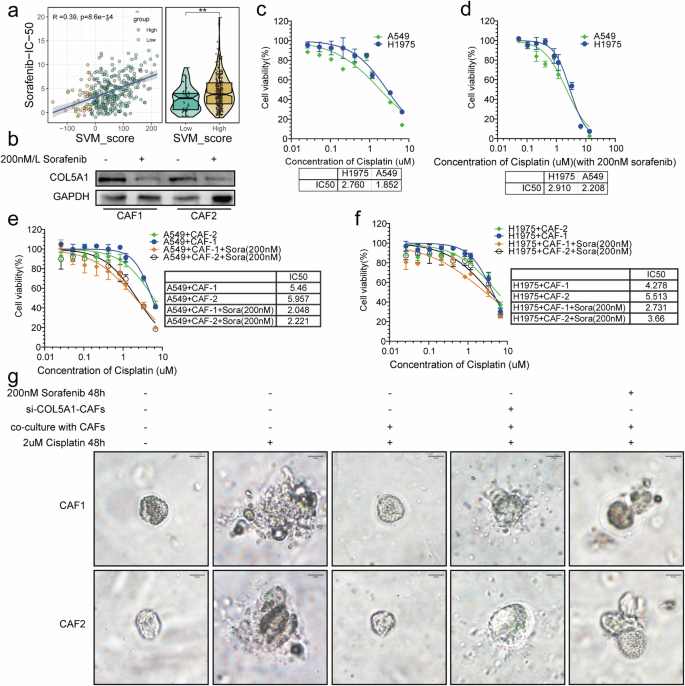
Earlier research have reported that Sorafenib decreases the expression of collagen and fibronectin genes, finally contributing to the discount of tumor-stroma stiffness and concurrently assuaging intertumoral stress [21, 33]. To analyze whether or not Sorafenib attenuates COL5A1 from myofibroblasts, we first analyzed drug sensitivity in TCGA-LUAD, indicating a direct proportionality between the IC-50 and SVM_Score for Sorafenib, suggesting its potential use in treating sufferers with a poorer prognosis characterised by low SVM scores (Fig. 8a). Subsequently, we handled two myofibroblast cell strains with Sorafenib, revealing its inhibitory impact on COL5A1 expression (Fig. 8b). The IC-50 values for Sorafenib in these two myofibroblast cell strains had been 4.133 µM/L and three.955 µM/L, respectively (Supplementary Fig. 5d). Due to this fact, we chosen a nonlethal focus of 200 nM/L of Sorafenib for additional remedy. CCK-8 experiments demonstrated that A549 and H1975 cells had IC-50 values of two.76 µM/L and 1.852 µM/L for cisplatin, respectively (Fig. 8c). Posttreatment with 200 nM/L Sorafenib, there was minimal change of their IC-50 values for cisplatin (Fig. 8d).
a Correlation between Sorafenib IC-50 values and SVM_Score in TCGA cohort. b Demonstration of the affect of Sorafenib on COL5A1 expression in each CAF cell strains by means of Western blot. Dedication of IC-50 values for cisplatin in A549 and H1975 cells (c), highlighting the affect of Sorafenib remedy on cisplatin IC-50 in H1975 cells (d). e, f IC-50 values for cisplatin after co-culture with CAF cell strains, with and with out Sorafenib remedy, demonstrating the affect of Sorafenib on drug sensitivity. g Evaluation of the response of organoids to cisplatin in co-culture with CAF cells and COL5A1-knockdown CAF cells, with and with out Sorafenib remedy, to evaluate modifications in drug sensitivity inside the tumor microenvironment.
Subsequent co-culturing of A549 and H1975 cells with the 2 CAF cell strains resulted in an almost twofold enhance of their IC-50 values for cisplatin (Fig. 8e, f). Nevertheless, after remedy with 200 nM/L Sorafenib, the IC-50 values reverted to their unique ranges (Fig. 8e, f).
Concurrently, we established organoid fashions utilizing patient-derived tissues from the identical sufferers as the 2 CAF cell strains. When co-cultured with CAF cells, the organoids resisted cisplatin at 2 μM/L (Fig. 8g). Conversely, co-culture with COL5A1-knockdown CAF cells rendered the organoids weak to 2 μM/L cisplatin (Fig. 8g). Equally, remedy with 200 nM/L Sorafenib didn’t restore resistance to cisplatin when co-cultured with CAF cells (Fig. 8g).