by Kayt Sukel
Particular to Rice Information
Rice College researchers within the lab of chemist Han Xiao have recognized a promising new immunological pathway to deal with cussed bone tumors, certainly one of most prevalent types of metastases in breast most cancers sufferers.
“Greater than 70% of individuals with metastatic breast most cancers will see the most cancers cells transfer to bone, which may result in skeletal-related occasions like bone ache, fractures, and hypercalcemia,” mentioned Yixian Wang, a Rice graduate pupil within the Han lab who’s a lead creator on a research printed in Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences. “There are actually a number of immunotherapies that may doubtlessly profit breast most cancers sufferers with metastases, however they aren’t efficient in sufferers with bone tumors.”
Every year, greater than 240,000 new instances of breast most cancers are identified in america, in accordance with the Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention. Roughly one-quarter of these sufferers will expertise metastasis, the place most cancers cells unfold from the breast to different elements of the physique. New immunotherapies known as checkpoint inhibitors can uncloak cussed tumors, permitting the immune system to ship in highly effective immune cells to take care of the irregular cells. However whereas checkpoint inhibitors are efficient for a lot of sufferers, they don’t work for everybody ⎯ and medical trials have proven little to no response when used to deal with bone metastases.
Xiao, affiliate professor of chemistry, biosciences, and bioengineering at Rice, mentioned he and his crew wished to seek out one other pathway that is likely to be more practical in obliterating these cussed bone metastases.
“We thought there have to be one other novel checkpoint axis we might goal for the breast most cancers cells in bone,” Xiao mentioned. “And we found a novel glyco-immune checkpoint axis in bone metastases that includes a protein known as sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin (Siglec)-15. We discovered that it suppresses immune cells within the bone.”
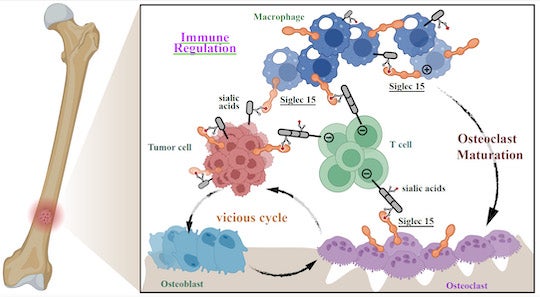
After noting that there was a major upregulation of Siglec-15 within the tumor microenvironment in bone tumor samples from breast most cancers sufferers, Xiao and colleagues demonstrated that this receptor performs an essential position in hiding bone tumors from the immune surveillance.
“Present FDA-approved checkpoint inhibitors are mediated by protein-protein interactions that suppress immune cells,” Xiao defined. “Siglec-15, nevertheless, is a glyco-immune checkpoint inhibitor. As an alternative of binding to a protein, Siglec-15 binds to the sugars you discover on the cell surfaces ⎯ and that’s the way it can suppress the immune system. That is a wholly new sort of immune checkpoint that provides nice promise for future remedy for bone cancers.”
Xiao’s crew performed a number of cell tradition experiments to check Siglec-15 interactions within the bone tumor microenvironment. They discovered it’s concerned in crosstalk between tumor cells and essential immune cells like T-cells and macrophages, in addition to bone-specific cells, osteoclasts.
“You’ll find these glycolipids and glycoproteins on all cells ⎯ and we all know they play an essential position in immune modulation,” added Xiao. “These findings supply us a chance to check these glyco-immune checkpoint inhibitors extra in depth and determine these that may assist bone tumors cease evading immune recognition.”

However merely modulating the habits of Siglec-15 could also be sufficient to deal with bone metastases. When the crew injected a monoclonal antibody that targets Siglec-15 into an animal mannequin of metastatic breast most cancers with bone tumors, they have been in a position to set off a strong immune response. In reality, the researchers noticed the tumors diminish after just one or two doses of the antibody remedy.
“It was actually a putting discovering,” mentioned Wang. “I’m very excited in regards to the potential therapeutic end result for a remedy like this. This could possibly be a really useful remedy for breast most cancers sufferers sooner or later.”
Xiao mentioned he and his crew plan to proceed learning the brand new and distinctive biology of glyco-immune checkpoint pathways within the tumor microenvironment. He added there may be nonetheless a lot to find out about these pathways and future research ought to present new organic insights with the ability to enhance each present and future immunotherapies. As well as, Xiao mentioned he wish to see if concentrating on Siglec-15 is likely to be useful in treating different kinds of cancers that have an effect on bone.
The analysis was supported by the Most cancers Prevention Analysis Institute of Texas (RR170014), the Nationwide Institutes of Well being (R01-CA277838, R35-GM133706, R21-CA255894, R01-AI165079) the U.S. Division of Protection (HT9425-23-1-0494, W81XWH-21-1-0789), the John S. Dunn Basis and Rice College.
- Peer-reviewed paper:
-
Siglec-15/Sialic Acid Axis as a Central Glyco-Immune Checkpoint in Breast Most cancers Bone Metastasis | Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences | DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2312929121
Authors: Yixian Wang, Zhan Xu, Kuan-Lin Wu, Liqun Yu, Chenhang Wang, Haoxue Ding, Yang Gao, Han Solar, Yi-Hsuan Wu, Meng Xia, Yuda Chen and Han Xiao
https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2312929121
- Picture downloads:
-
https://news-network.rice.edu/information/recordsdata/2024/01/240103_Han-Xiao-with-Yixian-Wang_Gustavo–af8f3518d906de73.jpg
CAPTION: Han Xiao (left) and Yixian Wang (Picture by Gustavo Raskosky/Rice College)https://news-network.rice.edu/information/recordsdata/2024/01/240103_Han-Xiao-with-Yixian-Wang_Gustavo-102207-4a7364784651b99c.jpg
CAPTION: Yixian Wang (left) and Han Xiao (Picture by Gustavo Raskosky/Rice College)https://news-network.rice.edu/information/recordsdata/2024/01/research-schematic-f7a95407b821945f.jpg
CAPTION: Siglec-15 is concerned within the crosstalk between metastatic bone tumors and immune cells, establishing a vicious cycle that permits immune cell suppression. (Picture courtesy of the Xiao lab/Rice College)
- Associated tales:
-
Rice U. chemist wins $3.2 million Nationwide Most cancers Institute grant:
https://information.rice.edu/information/2023/rice-chemist-wins-32m-national-cancer-institute-grantRice, Baylor growing ‘glyco-immune’ checkpoint inhibitor:
https://information.rice.edu/information/2023/rice-baylor-developing-glyco-immune-checkpoint-inhibitorAntibody with engineered peptide targets bone metastasis:
https://information.rice.edu/information/2022/antibody-engineered-peptide-targets-bone-metastasis - Hyperlinks:
-
The Xiao lab: https://xiao.rice.edu/Folks/hanxiao/hanxiao.html
Rice Division of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering: https://chbe.rice.edu/
Rice Division of Chemistry: https://chemistry.rice.edu/
Wiess College of Pure Sciences: https://naturalsciences.rice.edu/
George R. Brown College of Engineering: https://engineering.rice.edu
Bioscience Analysis Collaborative: https://brc.rice.edu/
- About Rice:
-
Situated on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice College is persistently ranked among the many nation’s high 20 universities by U.S. Information & World Report. Rice has extremely revered faculties of structure, enterprise, persevering with research, engineering, humanities, music, pure sciences and social sciences and is residence to the Baker Institute for Public Coverage. With 4,574 undergraduates and three,982 graduate college students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is slightly below 6-to-1. Its residential school system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, only one cause why Rice is ranked No. 1 for plenty of race/class interplay, No. 2 for best-run schools and No. 12 for high quality of life by the Princeton Assessment. Rice can also be rated as a greatest worth amongst non-public universities by Kiplinger’s Private Finance.

