AML-stroma proteome unveils a protein community primarily related to metabolic operate
BMSCs assist leukemogenesis and permit leukemic cells to evade chemotherapy-induced cell dying; nonetheless, the protein-signaling community resulting in leukemic progress and cell survival stays unknown. To unravel early (pre-apoptotic) adjustments in protein abundance regulated by leukemia-stroma interactions, we cultured main AML (n = 14) within the absence (AML Mono) or presence of HS-5 stroma cells (AML Cocu) and measured an untargeted international proteomic profile utilizing LC-MS/MS (Fig. 1A, Supplementary Desk 1, and Supplementary Dataset 1). A abstract of affected person scientific data reminiscent of gender, age, cytogenetics, and mutation standing is offered in Supplementary Desk 1. General, the typical protein counts in every pattern AML Mono (2359 ± 430) and AML Cocu (2540 ± 333) had been equally represented. A complete of 2231 distinctive proteins had been recognized and quantified. We decided the differentially expressed proteins with a fold change of >1.5 (FDR 0.05 cutoff) between AML Cocu and AML Mono (Fig. 1B) of which 114 proteins had been considerably differentially regulated. Compared to HS-5 monoculture, a minimal overlap of proteins was distinctive to stroma. To gauge molecular responses triggered by AML-stroma interplay, gene set evaluation exhibits an upregulation of membrane and cell differentiation markers together with ICAM1, ITGB1, SPN, ANPEP, and CD44. The differentially regulated proteins had been additionally subjected to DAVID and ClueGo for enriched molecular pathways. Thirty-eight of 114 proteins are related to upregulation of metabolic processes and related to enrichment of nucleic acid metabolism, translation/protein biosynthesis, mitochondrial matrix, glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, fatty acid biosynthesis, and signaling receptor exercise (Fig. 1C). Charge limiting NAD biosynthesis issue NAMPT, associated to vitality metabolism, was essentially the most stroma-dependent upregulated protein throughout the 14 AML samples. Down regulated proteins (25/144) had been enriched for NADP, oxidoreductase, mitochondrion, and lipid metabolism. The first AML cells stimulated by stroma interplay reveal a proteomic community predominately representing a signature of enriched metabolic pathways together with an upregulation of early membrane signaling molecules.
A A schematic diagram depicts how AML protein extracts had been created from 14 main AML cultured in a single day within the presence and absence of HS-5 stroma cells, known as AML Mono and AML Cocu, respectively. Each AML Mono (n = 14) and AML Cocu (n = 14) had been collected and protein lysates had been processed for LC-MS/MS to detect proteins concerned in signaling pathways stimulated by stroma. B A volcano plot depicts the differential protein expression in AML Cocu with a ≥1.5 fold change relative to AML Mono. Upregulated, downregulated, and proteins beneath the cutoff of 1.5 fold change are displayed in purple, blue, and grey, respectively. C A bar plot depicts high organic pathways which might be activated in main leukemic cells in response to stroma interplay (Supplementary Dataset 1).
Stoma-dependent safety of leukemic cells was most evident with HDAC inhibitor remedy
Recurrent mutations of epigenetic modifiers that seem in pre-relapse and post-relapse AML circumstances point out the significance of understanding epigenetic modalities in drug resistance [34, 35]. AML-stroma interactions additionally result in elevated drug resistance that may be partially depending on deregulation of leukemic epigenetic pathways. Thus to additional perceive pro-survival/anti-apoptotic response in AML, we modulated epigenetic pathways to present perception into how leukemia turns into resistant via stroma interactions [36, 37]. To this finish, we carried out an epigenetic drug display focusing on a big selection of epigenetic modifiers (80-epigenetic compound library). First, proliferative progress was measured for every compound in 9 leukemia cell traces. The compound library was then clustered by drug goal operate, which included histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi), histone methyltransferases (HTMi), bromodomain (BETi), DNA methylase (DNMTi), and sirtuins (SIRTi). Inhibitors focusing on histone deacetylases considerably lowered cell progress throughout all 9 leukemia cell traces relative to untreated cells, indicating that focusing on histone acetylation could obtain the best impact on leukemic subtypes (Supplementary Fig. 1).
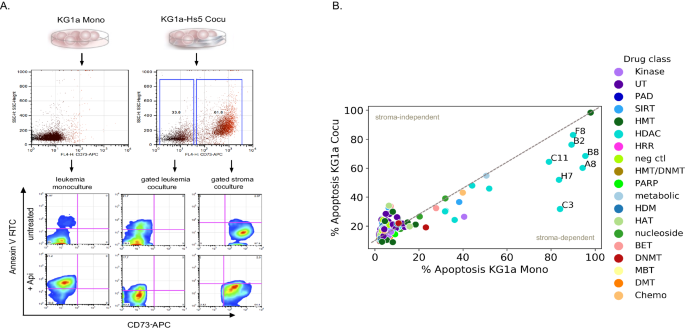
To mannequin leukemia-stroma interactions, we then decided the impact of apoptosis on leukemic KG1a cells in monoculture (KG1a Mono) versus KG1a coculture with stroma HS-5 cells (KG1a-HS-5 Cocu). We handled KG1a Mono and KG1a-HS-5 Cocu once more with the 80 epigenetic compound library for 48 h (Fig. 2A, B). Therapy with histone deacetylase inhibitors (10 μM), particularly Apicidin (C3), M344 (A8), CBHA (H7), SAHA (C11), and Oxamflatin (B8) considerably induced apoptosis in KG1a monocultures, whereas in coculture apoptosis was lowered by 10–50%. Of the 30 HDACi compounds surveyed, these 5 compounds primarily goal HDAC Class I. Stroma-induced safety of leukemia cells was most evident with Apicidin (Api) remedy, which successfully induced apoptosis in monocultured leukemia (84%) than in cocultured leukemic cells (31%, Fig. 2A, B). The protecting properties of stroma had been additional verified by coculture and remedy of 5 HDACi (A8, B8, C3, C11, and H7) in different leukemia cell traces and first AML (n = 10, Supplementary Fig. 2). In 6 of 10 AML main cocultures, a minimum of 40% apoptosis ranges had been reached in monoculture with HDACi remedy however exhibited considerably lowered apoptosis ranges in coculture. These outcomes point out that cocultured leukemic cells handled with HDACi could also be shielded from HDACi cytotoxicity in a stroma-dependent method.
A A schematic diagram is depicting the circulate cytometer gating strategy for monitoring apoptosis ranges in KG1a Mono and KG1a-HS-5 Cocu. CD71-APC was used to label stroma (HS-5 cells) thus CD71-APC destructive cells hint leukemia cells. Annexin V-FITC was used to find out the extent of apoptosis. An instance is given of stroma safety of leukemia cells handled for 48 h with HDACi, Api (10 µM). The apoptosis ranges of KG1a Mono (4%) and KG1a-HS-5 Cocu (21%) untreated are in contrast with KG1a Mono HDACi handled at 81% versus KG1a-HS-5 Cocu at 17.7%, respectively. B Abstract of apoptosis ranges in KG1a Mono and KG1a Cocu following remedy with an 80 epigenetic compound drug library. The x and y-axes characterize the % of apoptosis ranges in KG1a Cocu and KG1a Mono, respectively. The colours point out drug lessons and had been at a ten μM focus for every compound. The plot depicts the importance of a minimum of 3–6 replicate measurements of the info the place the labeled factors point out ≤0.05 P Worth decided by a paired t-test. The grey sprint distinguishes the slope of 1 the place lower than 1 signifies % apoptosis coculture is lower than monoculture (stroma-dependent safety pattern). Supplementary Dataset 2 lists the compound description used on this research.
Identification of phosphorylation occasions as stroma protecting results
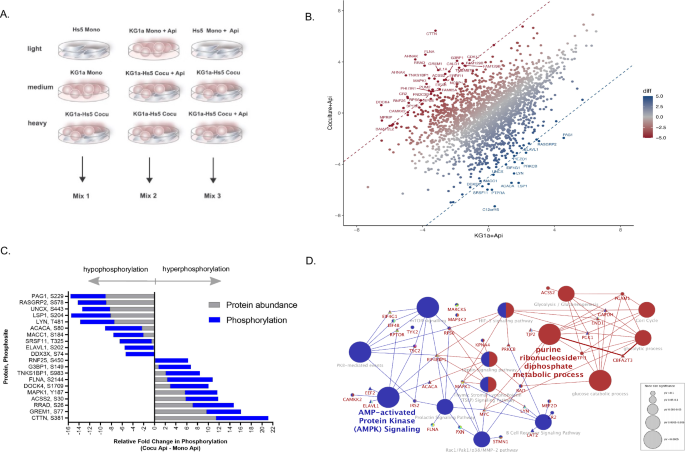
The marked variations between HDACi sensitivity in leukemia monocultures in comparison with cocultures led us to analyze signaling mechanisms related to mobile regulation via phosphorylation occasions. To this finish, we utilized mass spectrometry (MS)-based discovery phosphoproteomics to outline the earliest leukemia-stroma activated pathways below protecting coculture circumstances. We handled leukemia monoculture and leukemia-stroma coculture with HDACi for five h, a pre-apoptotic part with apicidin, (termed KG1a+Api and Coculture+Api, respectively), and used untreated monocultures and untreated coculture as reference alerts. Multiplex isotope labeled lysates coupled with LC-MS/MS evaluation was used to quantify PTMs of leukemia-stroma cocultures as compared with monoculture cells together with HDACi handled and untreated (Fig. 3A and Desk 1). Relative quantification was solely in contrast inside the mild, medium, and heavy alerts and cross-validated throughout three impartial labeling mixes (Combine 1, 2, or 3, isotope label scheme described in Desk 1). The multiplex isotope labeling strategy recognized 2381 distinctive phosphosites from 1319 proteins with 684 phosphosites exceeding a log2-fold change of ±2 (Fig. 3B and Desk 1). As a way to decide the differentially phosphorylated websites resulting in stroma-dependent safety of leukemic cells, relative quantification of phosphosite intensities of KG1a+Api (baseline) had been subtracted from Coculture+Api (Combine 2). To determine extremely related phosphosites we then surveyed the highest 1% differentially phosphorylated websites (log2-fold change larger than >5 or decrease than <5, Fig. 3C). Curiously, two extremely ranked phosphosites involving acetylation metabolism had been recognized: acyl-CoA synthetase 2 (ACSS2), which was up-regulated at phosphosite S30 (fold change: 6), and acetyl-CoA carboxylase alpha (ACACA), which was down-regulated at phosphosite S80 (fold change: −6.8) relative to KG1a+Api. Cross-validation in Combine 1 of ACSS2 (S30) indicated a >2-fold enhance in depth in contrast with Cocu+Api and Cocu relative to HS-5 Mono. Protein blot utilizing phospho-ACACA (S80) antibody helps in validating these leads to a lower ACACA (S80) expression in Cocu (±Api) relative to KG1a and KG1a+Api (Supplementary Fig. 3A, B). Enzymatically, ACSS2 mediates cytosolic acetyl-CoA manufacturing from acetate and coenzyme A and the phosphorylation of S30 impacts insulin signaling [38], whereas acetyl-CoA carboxylase alpha (ACACA) catalyzes the carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA in fatty acid synthesis [39] and its operate is suppressed by phosphorylation of S80 in mice [40].
A Discovery phosphoproteomic instruments had been used to determine and decide relative quantities of phosphorylated phosphosites in KG1a Mono, HS-5 Mono, and KG1a-HS-5 Cocu. Briefly, following a 24h-culturing interval, cells had been handled with HDACi Api at 1 μM for five h, a sub-apoptotic time level, after which harvested to create protein lysates. Protein extraction of every lysate, digestion, and isotope labeling was carried out on every experimental situation. To check phosphosite peptide intensities between culturing circumstances, a multiplex labeling scheme of sunshine, medium, and heavy-labeled lysates had been used. Mild, medium, heavy labeled lysates had been pooled right into a single combine termed Combine 1, 2, or 3. Every combine was then enriched for phosphopeptides utilizing TiO2. LC-MS/MS resolved the enriched phosphopeptides. This strategy permits for direct comparability of phosphopeptide intensities inside a mixture consisting of sunshine, medium, heavy isotope tags. B Phosphopeptide intensities between Coculture+Api as compared with KG1a+Api had been in comparison with depict upregulated phosphopeptides in rising purple hues and downregulated phosphopeptides in rising blue hues. A scatter plot depicts log2-transformed values of phosphopeptides (n = 2381). Phosphosites having a lacking worth (no expression or undetected) got a minimal depth worth for figuring out differential phosphorylation (log2-transformed LFQ values). C The proteome of KG1a Mono, HS-5 Mono, and KG1a-HS-5 Cocu label-free was decided in parallel to cross-validate enriched phosphopeptides. The highest 1% phosphopeptide fold change (Coculture+Api minus KG1a+Api) is depicted by gene identify and phosphopeptide fold change (blue). The corresponding protein abundance is plotted with the phosphopeptide within the stacked bars (grey). The fold adjustments are relative to KG1a+Api. D Differentially phosphorylated phosphosites with a minimum of log2-transformed distinction of three (309 phosphosites) in contrast with monoculture KG1a+Api had been uploaded to ClueGo to find out enriched functionally grouped organic networks, P ≤ 0.05. The node measurement of the organic theme correlates with rising significance. Functionally associated teams overlap with colour. For readability, a subset pathway is depicted with gene identify (circle signifies hyperphosorylation and triangle signifies hypophosphoryation) demonstrating the attainable sign transduction of glycolysis proteins (purple nodes) linking with AMPK signaling (blue nodes) in response to stroma-dependent safety of leukemia. This community highlights regulated genes mapped to the considerably enriched phosphosites, together with ACSS2 (S30) and ACACA (S80). The whole organic pathways (≤0.05 P Worth) of enriched phosphopeptides impacted by stroma-dependent safety of leukemia are depicted in Desk 2.
To evaluate how the phosphorylation profiles had been related to protein abundance, we measured and in contrast protein abundance in KG1a monoculture, HS-5 monoculture, and KG1a-HS-5 coculture. Relative quantification of protein abundance was decided by subtracting KG1a protein abundance intensities (baseline) from KG1a-Hs5. Thus, we uncovered 5.8-fold larger ACSS2 protein ranges in coculture relative to KG1a monoculture having no detection worth and had been certainly in settlement with phosphorylation ranges (Fig. 3C). Due to this fact, it’s possible that up-regulation of ACSS2 (S30) in coculture stems from inside the stroma mobile compartment. In the same vein, ACACA protein ranges had been 2.3-fold decrease in coculture in comparison with KG1a monoculture, mirroring the lower in phosphorylation ranges (Fig. 3C).
To realize a broader understanding of organic processes and pathways, we carried out enrichment analyses of 3-fold differentially up- and down-regulated phosphoproteins utilizing ClueGo with KEGG, Reactome, and gene ontology (GO) classes as useful resource databases. Essentially the most affected networks and pathways had been PKB-dependent occasions, PI3K, mTOR signaling, glycolysis, EGF/EGFR, and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling (P ≤ 0.03, Desk 2 and Fig. 3D, highlighted AMPK/mTOR signaling). Key phosphoproteins in AMPK/PI3K/mTOR signaling had been stimulated by stroma-dependent safety with HDACi remedy of leukemia for which its protein community kinase actions have been beforehand proven to guard leukemia cells by suppressing oxidative stress within the bone marrow microenvironment [41]. Taken collectively, phosphorylation occasions resulting in induce stroma-dependent safety of leukemia had been recognized by modulation with HDACi remedy.
CRISPR-edited ACSS2 knockout in stroma modulates leukemia in an ACSS2-dependent method
The phosphoproteome display indicated that the acetyl-CoA processing enzymes ACSS2 and ACACA may be metabolically supporting leukemia via stroma interactions. Because of the up-regulation of the ACSS2 (S30) sign from cocultured stroma cells, we wished to handle the ACSS2 purposeful function of in a stroma-dependent method. An antibody to observe ACSS2 (S30) phosphorylation was not commercially out there subsequently one other strategy was taken, single-guide RNAs (sgRNAs) with CRISPR/Cas9 gene enhancing had been designed to focus on the phosphosite S30 of ACSS2 which impacted ACSS2 expression in HS-5 stroma cells (termed HS-5 ACSS2-KO, Supplementary Fig. 4A). Surprisingly, HS-5 ACSS2-KO cells had a higher proliferative potential relative to wild sort cells implicating a lack of ACSS2 may change proliferative charges in non-cancer cells (Supplementary Fig. 4B).
To check whether or not the lack of ACSS2 in stroma cells (HS-5 ACSS2-KO) impacted the viability of leukemic cells, we first examined apoptosis ranges by treating leukemia cocultures with histone deacetylase inhibitors (Api, CBHA, and SAHA), with solely API and SAHA remedy leading to partial restoration of apoptosis in KG1a cocultured with HS-5 ACSS2-WT (Supplementary Fig. 4C). This consequence indicated that compensating metabolic pathways in HS-5 ACSS2-KO cells contributing to this path of proliferative progress and resistance could also be concerned [42].
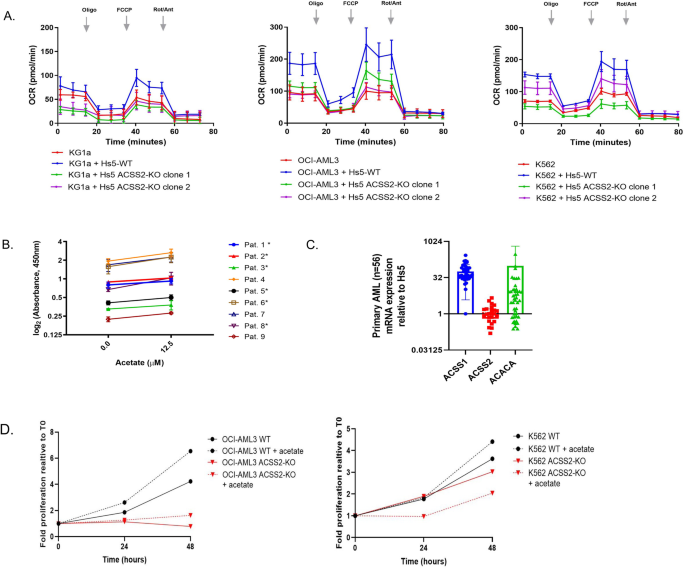
ACSS2 is thought to be vital for tumor metabolism in hypoxic environments [43,44,45]. Likewise, on this research, AML-stroma proteomic evaluation indicated upregulation of key metabolic pathways. We then wished to look at the potential achieve of metabolic operate of leukemic cells gained from stroma contact together with the function of ACCS2. As a way to measure metabolic potential, OCR of leukemic cells was measured stay in real-time. Leukemic cells had been pre-exposed to HS-5 ACSS2-WT or to HS-5 ACSS2-KO in a single day to permit cell-cell contacts then leukemic cells had been gently eliminated, re-seeded in RPMI assay media for recalibration. Any contaminating stroma cells re-adhered to plastic after which solely suspended leukemic cells had been transferred to an assay plate at equal cell densities and subjected to hypoxia for 45 min for downstream mitochondrial respiration measurements. Leukemic monocultures had been cultured in parallel as a management. The saturation oxygen ranges (maximal OCR) had been in comparison with the basal OCR to tell apart variations in mitochondrial respiration in leukemic cultures. Obvious regular fee will increase of OCR in KG1a (2-fold), OCI-AML3 (1.5-fold) and K562 (1.5-fold) pre-exposed to HS-5 ACSS2-WT relative to monocultures had been noticed (Fig. 4A). In distinction, KG1a, OCI-AML3 and K562 pre-exposed to HS-5 ACSS2-KO had a markedly diminished OCR (2.7-fold, 1.7-fold, and 1.5-fold, respectively, Supplementary Fig. 4D) in comparison with leukemia cells pre-cultured with HS-5 ACSS2-WT. The outcomes from these analyses point out that leukemic cells pre-exposed to wild-type stroma achieve metabolic respiratory capability in a hypoxic setting depending on ACSS2.
A Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress assay was used for assessing mitochondrial respiration of leukemia cells cultured in a single day with stroma cells that had been CRISPR-edited for ACSS2 (HS-5 ACSS2-KO) and in contrast with HS-5 WT. Leukemia cells (KG1a, OCI-AML3, or K562), monocultures, and cocultures had been gently eliminated, equilibrated with modified Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress RPMI buffer in a non-CO2 chamber at 37 °C, and re-platted into the supplied producer’s microwell plate to measure mitochondrial respiration OCAR output with Seahorse XFe96 instrument. Leukemia monoculture (purple), leukemia pre-cultured with HS-5 (blue), and leukemia pre-cultured with HS-5 ACSS2-KO (clone 1, inexperienced or clone 2, purple) OCR is displayed at 5 min time factors (imply ± SEM). Key parameters of oxidative respiration (mitochondrial respiration) are displayed as adjustments in fee mode at basal respiration, ATP-linked manufacturing, maximal respiration, and spare respiratory capability by sequential injections of Oligo, FCCP, Rot/Ant. B Exogenous acetate remedy improved viability in main AML blast specimens considerably in 6 of 9 specimens (paired t-test, P ≤ 0.05, indicated by an asterisk). C mRNA expression of ACSS1, ACSS2, and ACACA was measured in AML blasts (n = 46, stable circles). Measured in triplicate by normal SYBR Inexperienced quantitative RT PCR, plotted values show the relative mRNA expression measured relative to GAPDH and HS-5 (optimistic management). D Proliferative progress of OCI-AML3 WT and OCI-AML3 ACSS2-KO monocultures handled with acetate at 12.5 μM and measured at 0, 24, and 48 h (left plot). K562 WT and K562 ACSS2-KO had been handled as OCI-AML3 (proper plot). A stable black line depicts the proliferative progress of untreated WT cells whereas the black dashed line depicts the proliferative progress with acetate remedy. The blue traces depict the proliferative progress of OCI-AML3 ACSS2-KO cells untreated (stable line) and acetate handled (dashed). The purple traces depict the proliferative progress of K562 ACSS2-KO cells untreated (stable line) and acetate handled (dashed).
The ACSS2 substrate acetate will increase cell viability in leukemia
Extracellular acetate, a precursor of acetyl-CoA, has additionally been proven to contribute considerably to the rise in acetyl-CoA concentrations below hypoxic circumstances via ACSS2 exercise [45,46,47,48]. Due to this fact, we subjected cultured leukemic cell traces (KG1a, OCI-AML3, and K562) to an rising focus of acetate (0.5–5 μM) for 48 h to find out if leukemic proliferative progress was affected. The impression of acetate remedy on proliferative progress was 1.2- to 1.6-fold higher than on untreated leukemic cells (Supplementary Fig. 4E). To additional validate this discovering, we cultured main AML blasts (n = 9) with exogenous acetate (12.5 µM; 48 h), which additionally resulted in a proliferative progress benefit of 1.2–1.4-fold compared to untreated AML blasts (Fig. 4B).
From the proteomic display, we uncovered that KG1a ACSS2 protein abundance was undetected (confirmed by RT PCR), though acetate remedy enhanced proliferative progress in monocultures. We reasoned that ACSS1, an vital paralog of ACSS2, would operate as an alternate gene in processing acetate into acetyl-CoA within the absence of ACSS2 [44, 49]. Due to this fact, we probed ACSS1 mRNA expression in main AML and, certainly, discovered that 32 of the 56 specimens expressed ACSS1 at a staggering ~log2 fold change of 32 larger than ACSS2 which was expressed in 8 of 56 specimens (Fig. 4C). Half of the cohort expressed elevated ranges of ACACA relative to HS-5. Thus, surveying main AML ACSS1 and ACSS2 expression profiles and the results of exogenous acetate enhancement on proliferative progress yields the likelihood that leukemic cells could uptake acetate from exogenous sources such because the microenvironment and course of the metabolite via ACSS1or ACSS2.
On condition that HDAC inhibitors had been used to mannequin drug resistance of AML, we examined acetylation profile of KG1a cells with histone mark H3K9, a post-translation modification related to energetic transcription, to ask whether or not HDACi or acetate remedy transmits epigenetic modulation. By circulate cytometry, we handled KG1a with HDACi (Api, 1 µM) for 48 h and measured intracellular ranges of histone protein H3 and acetyl-modified histone residue, H3K9. We discovered that HDACi-treated KG1a cells resulted in elevated expression of H3 and H3K9ac relative to unstained cells (Supplementary Fig. 5A, B). KG1a cells had been additionally handled with acetate (48 h, 10 µM) resulted in the same sample of elevated H3 and H3K9ac implicating that leukemic cell publicity to HDACi or exogenous acetate could play a significant function within the general histone acetylation panorama of leukemic cells as beforehand proven in different most cancers sorts [50, 51].
Leukemic proliferative progress stimulated by exogenous acetate depends upon ACSS2
To check whether or not acetate uptake in leukemic cells was depending on ACSS2 expression, ACSS2 single-guide RNAs (sgRNAs) had been once more utilized to knockout ACSS2 expression in two leukemia cell traces expressing ACSS2, OCI-AML3, and K562. Monocultures of leukemic wild-type (WT) cells handled with exogenous acetate elicited a proliferative progress benefit in comparison with untreated cells, nonetheless proliferation was considerably diminished in ACCS2-KO leukemic cells (Fig. 4D). Our knowledge assist the view ACSS2 expression in leukemia is geared toward processing exogenous acetate to assist proliferative progress.
Excessive expression of ACSS1/ACSS2 predicts poor general survival in AML
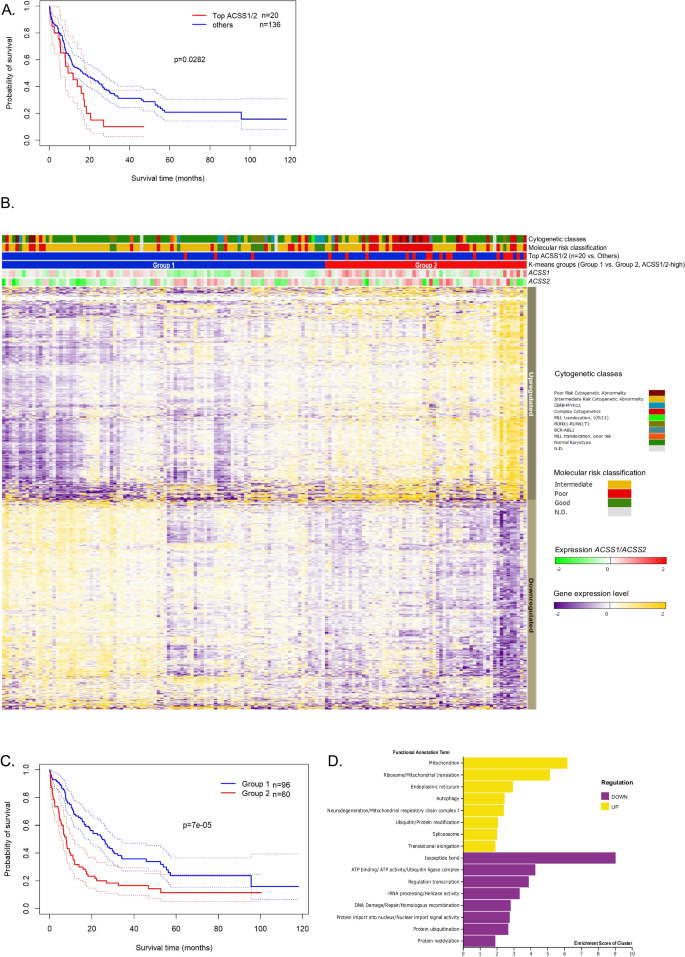
We additional explored the scientific impression of ACSS1, ACSS2, and ACACA expression in AML when it comes to general survival. We reasoned that the expression of ACSS1 and ACSS2 would carry scientific relevance based mostly on biochemical operate. Due to this fact, we examined the mRNA expression of ACSS1 and ACSS2 utilizing AML TCGA RNA-seq dataset [30] that included completely different cytogenetic AML subtypes (n = 156). We outlined two teams of AML samples utilizing sufferers with highest gene expression values of ACSS1 (n = 10) and highest gene expression values of ACSS2 (n = 10) denoted as high ACSS1/2 samples (n = 20). These circumstances displayed inferior consequence survival (OS) likelihood in comparison with the remaining samples (high ACSS1/2 median OS was 9.2 months versus Others with median 16.4 months; p = 0.028, Fig. 5A). We discovered 1225 genes differentially expressed between these two teams (Fig. 5B). Utilizing Ok-means clustering to statistically partition these expression patterns into two teams matching the expression sample of 1225 differentially expressed genes, we obtained a broader group of sufferers with ACSS1/2-high expression ranges (Group 2, n = 60) and with ACSS1/2-low expression ranges (Group 1, n = 96, Fig. 5B). Ok-means clustering remained statistically important in additional partitioning into 4 teams. Curiously, the two-group cluster additionally displayed completely different survival chances with an inferior consequence for sufferers in ACSS1/2-high (Group 2, median OS of seven.8 months versus Group 1 median OS of 24.8 months, p = 7E-05, Fig. 5C). The up-regulated genes embrace enrichment of 83 (14%) mitochondrial proteins (Fig. 5D and listed in Supplementary Dataset 5). ACSS1/2-high sufferers had been considerably older and encompassed virtually all of the molecular subtypes, and considerably harbored excessive molecular threat AML circumstances together with TP53 mutated AML. ACSS1/2-high was of prognostic significance in a uni- and multivariate evaluation (Supplementary Desk 2A, B) and stays important when together with solely intensively handled sufferers within the ACSS1/2-high group (p = 0.042).
A Kaplan-Meier estimation of the general survival exhibits the poor consequence of sufferers within the high ACSS1/2 expression (purple line, n = 20) in comparison with others (blue line, n = 136, log-rank take a look at). Dotted traces mark the 95% confidence bounds. B Heatmap illustration of differentially expressed genes within the TCGA AML dataset. Sufferers had been plotted within the columns with the differential expressed genes within the rows. Prime 20 ACSS1/ACSS2 expression samples (n = 20 sufferers) had been plotted within the horizontal rows above the warmth map. Teams 1 and a pair of present the division of the TCGA cohort into two teams utilizing unsupervised clustering of this gene expression matrix (Ok-means for two teams) leading to 1226 differentially expressed genes. Genes had been labeled as excessive or low in keeping with the typical expression of a gene in Group 2. C Kaplan-Meier estimation of the general survival exhibits the poor consequence of sufferers in Group 2 (purple line) in comparison with Group 1 (blue line, log-rank take a look at). Dotted traces mark the 95% confidence bounds. D Purposeful annotation and enrichment cluster rating from DAVID Bioinformatic Sources of genes up and downregulated with ACSS1/2 excessive expression are plotted.