Affected person traits
From 12 April 2018 to 14 Could 2021, a complete of 21 sufferers have been enrolled. Baseline affected person and tumor traits are summarized in Desk 1. The median age was 62 years (vary 46–76), and 19 of 21 (90%) sufferers have been male. On the idea of pretreatment staging by computed tomography (CT) and/or fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) scan mixed with endoscopic ultrasound, 17 of 21 (81%) sufferers had a cT3 or cT4a tumor and 16 of 21 (76%) had cN+ illness (Prolonged Knowledge Desk 1). Three sufferers had a mismatch restore poor (dMMR) tumor, and one affected person an Epstein–Barr virus (EBV)+ tumor. One affected person with a dMMR tumor died shortly after atezolizumab monotherapy due to exterior components unrelated to the examine therapy. Twenty sufferers underwent surgical procedure and have been evaluable within the per-protocol (PP) inhabitants for security and secondary efficacy endpoints in response to the examine protocol (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 2).
Security
Total, therapy was properly tolerated, and the examine met its main endpoint of security and feasibility. Immune-related opposed occasions (irAEs) of any grade occurred in 11 of 20 (55%) sufferers, and three grade 3 irAEs have been noticed in two (10%) sufferers, consisting of hepatitis, headache and diarrhea (Desk 2). There have been no grade 4 or 5 irAEs.
In a single affected person, grade 3 immune-related hepatitis and meningitis have been suspected on the idea of elevated liver enzymes and headache following monotherapy atezolizumab. Though liver biopsy and cerebrospinal fluid evaluation failed to substantiate these diagnoses, high-dose steroids and mycophenolate mofetil have been began, with full decision of each AEs. Atezolizumab was discontinued, and the affected person obtained all cycles of neoadjuvant chemotherapy. One affected person with grade 3 diarrhea had full decision of signs inside 1 week with supportive therapy. Lastly, one affected person who was excluded from the PP inhabitants skilled grade 3 fatigue after monotherapy atezolizumab, and steroid therapy was initiated. This AE couldn’t be adopted up due to examine unrelated loss of life.
Chemotherapy was administered to all 20 sufferers. Chemotherapy dose delays (>7 days) occurred in one in all 80 (1%) cycles in a single (5%) affected person, dose reductions have been required in eight of 80 (10%) cycles in 5 (25%) sufferers, and omission of chemotherapeutic medication occurred in three of 80 cycles (4%) in two (10%) sufferers (Prolonged Knowledge Desk 2). Grade 3 chemotherapy-related AEs have been noticed in 4 sufferers (20%, Prolonged Knowledge Desk 3) and consisted of febrile neutropenia (15%) and diarrhea (5%).
Twenty sufferers underwent surgical procedure, all with out treatment-related delays. One affected person selected to postpone surgical procedure for private causes. The median interval between the final examine therapy and surgical procedure was 6 weeks (vary 5–13 weeks). 13 sufferers underwent transhiatal esophagectomy with gastric tube reconstruction and cervical anastomosis, six sufferers a complete gastrectomy with Roux-and-Y reconstruction and one affected person subtotal gastrectomy with Billroth II reconstruction. Surgical resection margins have been tumor-free (R0) in 19 of 20 (95%) sufferers. One affected person present process whole gastrectomy for linitis plastica with a tumor-positive distal resection margin underwent adjuvant chemoradiotherapy.
No surprising surgical problems have been noticed, and there have been no intraoperative problems or surgery-related deaths. Surgical procedure-related AEs of any grade have been noticed in 11 of 20 sufferers (55%), and grade 3 or 4 AEs have been noticed in 10 sufferers (50%) (Prolonged Knowledge Desk 4). Anastomotic leakage occurred in three of 20 (15%) sufferers; all three sufferers underwent esophagectomy with cervical anastomosis, and leakage was handled with stents (n = 2) or conservatively (n = 1).
Neoadjuvant ICB plus chemo results in excessive pathologic response charges
Fourteen of 20 (70%, 95% confidence interval (CI) 46–88%) sufferers had a pathologic response, all consisting of an MPR with ≤10% RVT (Mandard tumor regression grading (TRG)1 or 2), together with 9 of 20 (45%, 95% CI 23–68%) pathologic full responses (Mandard TRG1). Amongst 18 sufferers with a mismatch restore proficient (pMMR) tumor, an MPR was noticed in 12 (67%, 95% CI 41–87%) sufferers, together with seven (39%, 95% CI 17–64%) pCRs (Prolonged Knowledge Desk 5). Each sufferers with a dMMR tumor who underwent surgical procedure had a pCR. The 2 sufferers with HER2+ tumors had a pCR and an MPR with 1% RVT. One affected person with a pCR of the first tumor however <1% RVT in lymph nodes was categorised as having an MPR (Fig. 1a). Remarkably, pCR was not restricted to sufferers with pretreatment American Joint Committee on Most cancers stage I and IIA tumors however was additionally noticed in sufferers with stage IIB, IIIA and even IIIB tumors (Prolonged Knowledge Desk 1).
a, Proportion of pathologic regression proven per tumor. The black horizontal line depicts the demarcation for MPRs akin to 90% tumor regression. The dashed line demarcates PR (50% tumor regression). Colours of the bars signify totally different Lauren subtypes, the asterisks beneath bars point out dMMR tumors, and the hash (#) signifies the affected person with a pCR within the main tumor however <1% RVT in lymph nodes. b, Kaplan–Meier plot of DFS for pathologic responders (purple) versus nonresponders (blue) in sufferers evaluable for response within the PANDA trial. c, Posttreatment resection specimen from a affected person with a pMMR GEJ tumor (cT3N1) who had a pCR. H&E stain exhibiting regular mucosa (M) and full regression of the adenocarcinoma, which was characterised by mucin lakes (star) and tertiary lymphoid constructions (arrowheads). d, Posttreatment H&E stains of a resected lymph node from a affected person with pretreatment scientific N3 stage. Left, some preexistent lymphoid tissue (arrowheads) and full tumor regression characterised by ldl cholesterol clefts (circle). Proper, multinucleated big cells (arrowheads).
Tumor regression was characterised histologically by fibrosis, neuronal hyperplasia, inflow of immune cells, acellular mucin swimming pools and regional necrosis (Fig. 1c). Notably, resection specimens from a number of sufferers contained lymph nodes with proof of histologic regression, together with a affected person with pretreatment scientific N3 stage whose resection specimen contained eight tumor-regressed lymph nodes with out viable tumor cells (Fig. 1d). Pathologically assessed downstaging was evident in 13 of 20 sufferers. Moreover, all six nonresponders (Mandard TRG3–5) displayed some pathologic regression, with 60–70% RVT. This included the affected person with an EBV+ tumor, who had obtained just one cycle of atezolizumab.
When contemplating intestinal and diffuse/blended subtypes individually, an MPR was noticed in 12 of 15 (80%, 95% CI 52–96%) intestinal-type tumors, together with 9 of 15 (60%, 95% CI 32–84%) pCR. Within the 4 tumors with a diffuse/blended sort histology, an MPR was noticed in two (50%, 95% CI 7–93%) sufferers.
Response evaluation by CT and FDG-PET imaging
For the secondary endpoint of radiographic response, CT and/or FDG-PET imaging was carried out earlier than the final therapy cycle in 19 and 17 sufferers, respectively. Notably, amongst 19 sufferers with posttreatment CT scans, just one affected person had a measurable goal lesion in response to Response Analysis Standards in Stable Tumors (RECIST) v.1.1, as a result of main tumors in hole organs will not be thought of goal lesions in response to RECIST v.1.1, no matter measurement. Subsequently, response evaluation was largely descriptive. Of the 13 pathologic responders who underwent preoperative CT scans, 11 sufferers have been described as having a lower in tumor measurement, but not one of the 9 sufferers with a pCR have been radiographically assessed as full responders.
Within the 17 sufferers who underwent preoperative FDG-PET scans, the posttreatment most standardized uptake worth (SUVmax) was considerably totally different (P = 0.05) between responders (median 4.2, vary 2.3–6.5) and nonresponders (median 5.7, vary 4.5–5.8). Though ten of 12 pathologic responders have been evaluated as (near-)full responders, the remaining two responders (each pCR within the main tumor) have been assessed as partial responder and secure illness. Within the 5 pathologic nonresponders who underwent FDG-PET, 4 sufferers have been evaluated as responders on FDG-PET.
Metabolic response was additionally assessed by calculating the distinction in whole lesion glycolysis (ΔTLG) between baseline and posttreatment FDG-PET, which was proven to precisely predict pathologic response to neoadjuvant ICB in head and neck cancers28. Nevertheless, amongst 17 FDG-PET evaluable sufferers in our cohort, 13 had a ΔTLG of −100%, together with pathologic nonresponders, indicating the inaccuracy of this methodology in our cohort. Within the remaining 4 sufferers, ΔTLG couldn’t be calculated as a result of the lack to precisely delineate the tumor impeded metabolic tumor quantity (MTV) calculation (Supplementary Desk 1).
These information are in step with the beforehand described underestimation of response to (neoadjuvant) immunotherapy by radiographic evaluation throughout tumor sorts, highlighting the necessity for extra correct strategies of response analysis17,29,30,31.
Affiliation of pathologic response with consequence
Scientific consequence confirmed a robust relationship with pathologic response, each secondary endpoints, after neoadjuvant remedy, as demonstrated by a considerably larger DFS (P = 0.0001, Fig. 1b) and OS (P = 0.0006, Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 3) in responders in comparison with nonresponders. On the time of knowledge cutoff on 24 April 2023, the median follow-up was 47 months (vary 11–59), and 13 of 14 (93%) sufferers with a pCR or MPR have been alive and disease-free. In distinction, solely one in all six nonresponders (16%) remained disease-free, and 5 of six (83%) sufferers developed illness recurrence (Fig. 1b).
Median DFS was not reached (95% CI 38—not reached), and DFS at 3 years was 73% (95% CI 55–97%). Illness recurrences in nonresponders occurred after a median follow-up of 10 months (vary 5–29) after surgical procedure, and nonresponding sufferers with illness recurrence died with a median survival after recurrence of 10 months (vary 2–14).
The nonresponder who remained disease-free had an EBV+ tumor. One responder with a cT3N3 tumor at baseline who had a pCR developed recurrent illness within the mind at 38 months after surgical procedure. A solitary mind lesion was resected and confirmed clonal relatedness to the first tumor. The affected person died 4 months after analysis of metastatic illness on account of quickly progressive mind metastases.
Circulating tumor DNA is related to response and DFS
At baseline, circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) might be detected in 85% (17 of 20) of sufferers throughout all levels, with 94.4% (17 of 18) of sufferers with tumors of stage II or larger (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 4). CtDNA standing was additionally analyzed after monotherapy atezolizumab, earlier than surgical procedure, postsurgery (molecular residual illness) and through follow-up, with ctDNA positivity charges of 75% (15 of 20), 15% (3 of 20), 10.5% (2 of 19) and 15% (3 of 20), respectively.
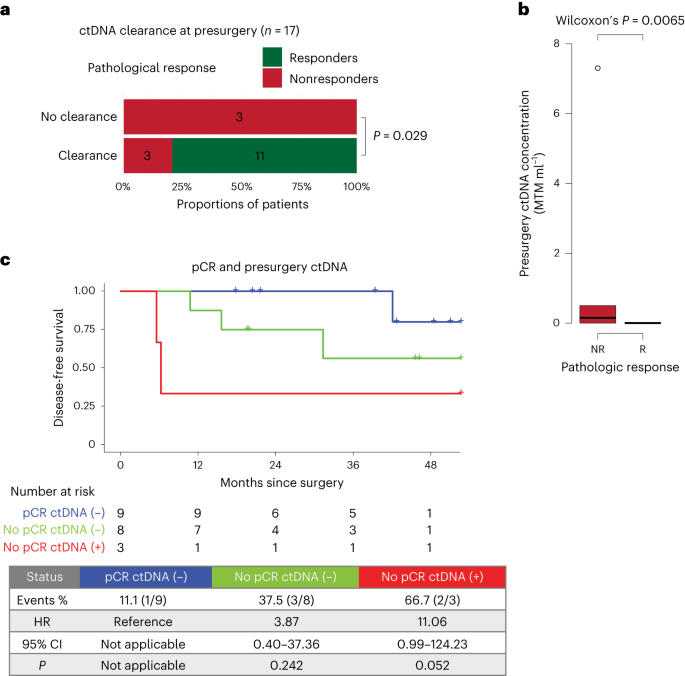
In spite of everything neoadjuvant therapy cycles and earlier than surgical procedure, ctDNA was cleared in 11 of 11 responders, whereas three of six nonresponders remained constructive (P = 0.029, Fig. 2a and Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 5c). As well as, ctDNA ranges have been considerably larger in nonresponders than in responders (P = 0.0065, Fig. 2b). These information point out an affiliation between ctDNA and pathologic response to neoadjuvant therapy. Though ctDNA positivity and nonclearance on the presurgery time level have been related to an inferior DFS, this was not important, most likely due to the small pattern measurement (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 5a,b). When contemplating pathologic response and presurgery ctDNA standing concurrently, ctDNA-positive nonresponders had a better danger of recurrence than ctDNA-negative sufferers with a pCR (Fig. 2c). Moreover, ctDNA positivity on the molecular residual illness and follow-up time factors was related to a 100% recurrence fee (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 5d,e).
a, Affiliation between pathologic response and ctDNA clearance in any case neoadjuvant therapy cycles and earlier than surgical procedure (n = 17). Significance was examined utilizing a one-sided Fisher’s actual check. b, Common ctDNA focus, in imply tumor molecules per milliliter of plasma (MTM per ml), throughout nonresponders (purple, n = 6) and responders (inexperienced, n = 14). Field plots signify the median, twenty fifth and seventy fifth percentiles; the whiskers prolong from the hinge to the most important worth no farther than 1.5 × interquartile vary (IQR) from the hinge. For comparability between nonresponders (purple) and responders (inexperienced), significance was examined utilizing a two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum check. c, Kaplan–Meier plot of DFS stratified by mixture of pathologic response (responders/nonresponders) and presurgery ctDNA standing. Hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% CIs have been calculated utilizing the Cox proportional hazard mannequin. P values have been calculated utilizing the two-sided log-rank check.
Biomarkers predictive of response to neoadjuvant ICB
With the exploratory purpose of figuring out potential biomarkers predictive of response, immunohistochemistry (IHC), RNA sequencing and whole-exome sequencing (WES) have been carried out on tumor biopsies to discover variations between responders (≤10% RVT, n = 14) and nonresponders (>10% RVT, n = 5). One affected person who discontinued atezolizumab after the primary cycle was excluded from exploratory translational analyses as a result of this TME was not thought of consultant for a response to the examine therapy. An summary of samples used for translational analyses is supplied in Supplementary Fig. 1.
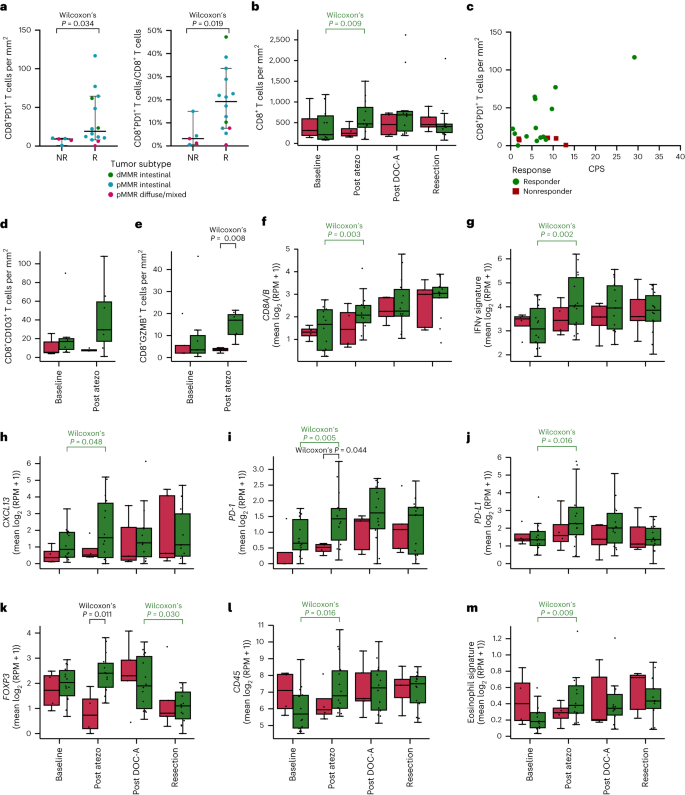
Expression of PD-1 on CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes has beforehand been proven to precisely establish clonally expanded tumor-reactive T cells, indicating its potential as a predictive biomarker of antitumor responses induced by ICB32, and up to date findings have supplied additional help for the predictive worth of CD8+PD-1+ TCI17,33,34. In our examine, CD8+PD-1+ TCI utilizing IHC (Strategies) demonstrated a considerably larger worth at baseline in responders than in nonresponders (P = 0.034, Fig. 3a). Moreover, the proportion of CD8+PD-1+ T cells amongst whole CD8+ T cell numbers was considerably larger in responders than nonresponders (P = 0.019, Fig. 3a). Furthermore, imaging mass cytometry (IMC) confirmed a better baseline abundance of CD103+ CD8+ T cells in responders than nonresponders (Fig. 3d). Each PD-1 and CD103 are thought of surrogates of presumed tumor-reactive T cells34,35. In distinction, no distinction was noticed in whole CD8+ TCI between responders and nonresponders (Fig. 3b), including to the proof that the useful standing of CD8+ T cells kinds a crucial parameter. Along with CD8+PD-1+ TCI predicting ICB responsiveness, research in anti-PD-1-treated non-small cell lung most cancers (NSCLC) sufferers discovered a robust correlation between excessive CD8+PD-1+ TCI and sturdy therapy response in addition to OS33,34. Alongside these traces, we additionally noticed an affiliation between the proportion of CD8+PD-1+ TCI and DFS, albeit not important (P = 0.060), and OS (P = 0.099).
a, Pretreatment CD8+PD-1+ T cells utilizing IHC per mm2 (left) and as proportion of all CD8+ cells (proper) in nonresponders (NR, n = 5) versus responders (R, n = 14). Dots signify particular person sufferers. The horizontal line represents the median; whiskers present the 95% CIs. The distinction between R and NR was examined utilizing a two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum check. b, Dynamics of CD8+ T cells per mm2 in R (inexperienced) versus NR (purple) at baseline (R, n = 13; NR, n = 5) after monotherapy atezolizumab (submit atezo; R, n = 13; NR, n = 4), after DOC plus atezolizumab (submit DOC-A; R, n = 10; NR, n = 4) and at resection (R, n = 14; NR, n = 5). c, Scatter plot exhibiting the relation between pretreatment PD-L1 CPS and CD8+PD-1+ T cells per mm2 in R (n = 14) versus NR (n = 5). Dots signify particular person sufferers. d,e, Dynamics of CD8+CD103+ T cells per mm2 (d) and CD8+GZMB+ T cells per mm2 (e) analyzed by IMC in pMMR-complete responders (inexperienced) versus pMMR nonresponders (purple) at baseline (R, n = 7; NR, n = 5) and after monotherapy atezolizumab (submit atezo; R, n = 7; NR, n = 4). f–m, Dynamics of gene expression of CD8 (=CD8A + CD8B) (f). IFNγ signature (g). CXCL13 (h). PD-1 (i). PD-L1 (j). FOXP3 (okay). CD45 (l). Eosinophil signature (m). f–m, Dynamics of gene expression in R (inexperienced) and NR (purple) at baseline (R, n = 14; NR, n = 4) after monotherapy atezolizumab (submit atezo; R, n = 14; NR, n = 4), after DOC plus atezolizumab (submit DOC-A; R, n = 14; NR, n = 5) and at resection (R, n = 14; NR, n = 5). b,d–m, Field plots signify the median, twenty fifth and seventy fifth percentiles; whiskers prolong from the hinge to the most important worth beneath 1.5 × IQR from the hinge. Variations between R and NR have been examined utilizing a two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum check. Variations between time factors in R and NR individually have been examined utilizing a two-sided Wilcoxon signed-rank check. Solely important P values are proven; colours point out a major enhance or lower in responders (inexperienced) or a major distinction between responders and nonresponders (black). RPM, reads per million.
Importantly, and in distinction to findings in metastatic illness, the place efficacy of immunotherapy is primarily noticed in PD-L1 CPS-positive tumors, CPS was not predictive of response at cut-offs of 1, 5 or 10 (Supplementary Desk 2). Furthermore, 4 of 14 responders confirmed a CPS ≤ 5, whereas two of 5 nonresponders confirmed a CPS ≥ 10. Curiously, tumors from nonresponders with a excessive CPS displayed comparatively low CD8+PD-1+ TCI (Fig. 3c), once more indicating the significance of the baseline presence of tumor-reactive T cells.
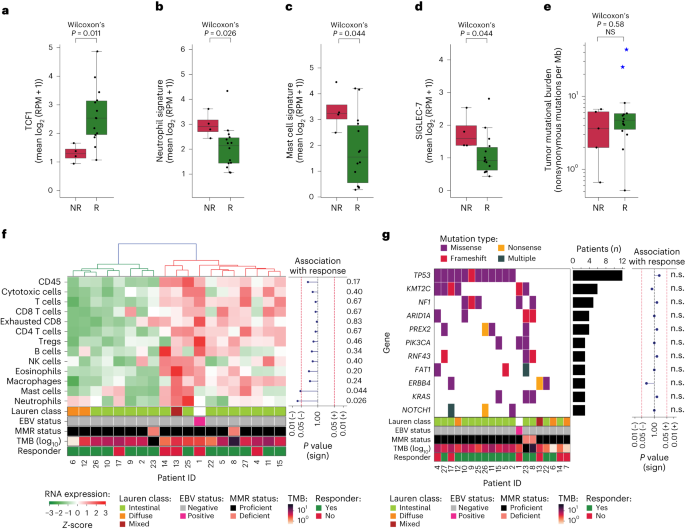
As well as, we carried out transcriptional evaluation of beforehand proposed biomarkers of response to ICB, together with IFNγ signature36, CD8A/B, CD274 (encoding PD-L1), FOXP3 and CXCL13, encoding a chemokine that’s related to follicular helper T cells and concerned within the formation of tertiary lymphoid constructions37. These analyses didn’t present important baseline variations between responders and nonresponders (Fig. 3f–m). Given the rising proof for TCF1 (encoded by TCF7) as a possible predictive biomarker of ICB response38,39, we assessed and located considerably larger baseline TCF1 RNA expression in responders than nonresponders (P = 0.011, Fig. 4a). TCF1 performs a principal position in T cell growth, as it’s a essential part for differentiation of CD4+ T cells into T follicular helper cells in addition to an figuring out marker of stem-like CD8+ T cells with self-renewal capability39.
a–d, Pretreatment gene expression in nonresponders (NR, n = 5) versus responders (R, n = 14) of TCF1 (a), neutrophil signature (b), mast cell signature (c) and SIGLEC-7 (d). Boxplots signify the median, twenty fifth and seventy fifth percentiles; whiskers prolong from the hinge to the most important worth beneath 1.5 * IQR from the hinge. The distinction between NR and R was examined utilizing a two-sided Wilcoxon Rank-sum check. e, TMB (variety of nonsynonymous mutations per megabase of protein coding genome, y axis, log10scale) in nonresponders (NR, n = 5) versus responders (R, n = 14). Blue stars point out sufferers with dMMR tumors. Field plots signify the median, twenty fifth and seventy fifth percentiles; whiskers prolong from the hinge to the most important worth beneath 1.5 × IQR from the hinge. The distinction between NR and R was examined utilizing a two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum check. f, Heatmap of baseline RNA expression (Z-scores) of TME-specific signatures for leukocytes (CD45), cytotoxic cells, T cells, CD8 T cells, exhausted CD8 T cells, CD4 T cells, Treg cells, B cells, NK cells, eosinophils, macrophages, mast cells and neutrophils. Sufferers (x axis) have been ordered on the idea of hierarchical clustering (higher dendrogram). The squares beneath point out Lauren classification, EBV standing, MMR standing, TMB (log10scale) and pathologic response per affected person. The affiliation of signature expression with response is proven on the suitable as a lollipop plot of signed, two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test-based P values (unadjusted for a number of speculation testing; x axis on log10 scale). g, Mutational standing of all cancer-driver genes altered in ≥3 sufferers (colours denote the mutation sort), alteration frequency (bar plot) and affiliation with response (lollipop plot of signed, two-sided Fisher’s actual test-based P values (unadjusted for a number of speculation testing; xaxis on log10 scale). The squares beneath point out Lauren classification, EBV standing, MMR standing, TMB (log10 scale) and responder standing per affected person. n.s., not important.
To higher perceive attainable underlying components of nonresponse, we explored the presence of immunosuppressive options within the TME and located that baseline neutrophil signature was considerably larger in nonresponders than responders (P = 0.026, Fig. 4b). Contemplating that neutrophils, but in addition tumor-associated macrophages and myeloid-derived suppressor cells, could also be recruited by mast cells40, we assessed and correspondingly discovered a considerably larger mast cell signature in nonresponders than responders (P = 0.044, Fig. 4c). Deconvolution of RNA sequencing information indicated no different important associations between pathologic response and relative cell sort compositions (Fig. 4f). As well as, expression of SIGLEC-7, an inhibitory checkpoint discovered on pure killer (NK) cells, T cells and dendritic cells and proven to advertise immune suppression when certain to sialic acids on most cancers cells, was considerably larger in nonresponders than responders (P = 0.044, Fig. 4d).
Genomic analyses confirmed that the genetic make-up of our cohort was consultant of this affected person inhabitants (Fig. 4g)41, rising the chance that our findings will translate to the overall affected person inhabitants. Moreover, these analyses didn’t present any important associations between pathologic response and alterations of driver genes (Fig. 4g) or mutational signatures (Supplementary Fig. 2). Notably, pathologic responses have been noticed regardless of a low pretreatment tumor mutational burden (TMB), and TMB was not considerably totally different between responders and nonresponders, with a median of 4.71 (vary 0.51–43.62) and three.63 (vary 0.66–6.66) mutations per megabase, respectively (P = 0.58, Fig. 4e).
A submit hoc translational evaluation excluding sufferers with dMMR tumors was carried out, exhibiting that baseline variations noticed by transcriptomics and CD8+PD-1+ IHC have been additionally current when contemplating solely pMMR responders versus nonresponders (Supplementary Fig. 3).
Atezolizumab results in immune activation within the TME
A problem in scientific immune-oncology research that consider mixture therapies has been to assign treatment-induced alterations of the TME to particular person medication or their mixture. To know whether or not therapy-induced TME alterations induced by the atezolizumab-chemotherapy mixture are considerably totally different from the consequences of atezolizumab monotherapy, we in contrast adjustments within the TME after the preliminary cycle of atezolizumab monotherapy to these noticed on subsequent mixture remedy.
Utilizing IHC, a major enhance in CD8+ TCI in responding sufferers was noticed after atezolizumab monotherapy (P = 0.009), whereas CD8+ TCI was secure in nonresponders (P = 1.0, Fig. 3b). Notably, the next mixture of atezolizumab with chemotherapy didn’t end in an extra substantial enhance within the CD8+ TCI in responders. Consistent with these information, evaluation of transcriptomic information confirmed considerably elevated CD8A/B expression after atezolizumab monotherapy solely in responders (P = 0.003), and not using a additional important change following the primary mixture cycle (Fig. 3f). IMC was carried out to additional characterize tumor-infiltrating immune cells in a subset of pMMR tumors, together with nonresponders and responders with a pCR (Supplementary Fig. 4a). On monotherapy atezolizumab, a considerable enhance within the expression of granzyme B in CD8+ T cells, indicating activation of this inhabitants, was noticed particularly in responding sufferers (Fig. 3e). As a result of there may be rising proof that the spatial proximity of immune cells to tumor cells could also be predictive for response to ICB42, IMC information have been additionally used to discover the spatial distribution of cells within the TME. A neighborhood evaluation confirmed an enrichment of interactions between CD8+ T cells and most cancers cells following monotherapy atezolizumab in responders (Supplementary Fig. 4b). Elevated immune infiltration was additionally evident from transcriptomic information, exhibiting will increase in CD45 and eosinophil signature expression (Fig. 3l,m). Moreover, elevated T cell exercise on atezolizumab monotherapy was indicated by upregulation of an IFNγ signature36 and PD-1, PD-L1 and CXCL13 expression (Fig. 3g–j), whereas no additional enhance was noticed after mixture remedy. Notably, IMC demonstrated a better proportion of HLA-DR+ most cancers cells in responders than nonresponders after monotherapy atezolizumab (Supplementary Fig. 4c), which is in step with the elevated IFNγ signaling in responders43. Consistent with this noticed immune activation, CD4 expression in addition to expression of varied inhibitory immune checkpoints, together with LAG3, SIGLEC-7 and SIGLEC-9, elevated considerably in responders on atezolizumab monotherapy (Supplementary Fig. 5). After exclusion of dMMR tumors, the noticed larger immune activation in responders after monotherapy atezolizumab typically held true, though to a barely lesser extent (Supplementary Fig. 6).
Lastly, constructing on current information exhibiting an essential position for eosinophils within the response to ICB in NSCLC, breast and colon most cancers44, on prime of histopathologic findings of eosinophil infiltration after therapy within the present examine, transcriptomic evaluation confirmed a major enhance in eosinophil signatures in responders after atezolizumab monotherapy (P = 0.009), whereas a pattern in the direction of lower was noticed in nonresponders (P = 0.273, Fig. 3m). By evaluation of delta (Δ) expression values to match the adjustments between time factors (Strategies) in responders and nonresponders, we discovered the adjustments in CD45, eosinophils and LAG3 after atezolizumab monotherapy to be considerably totally different between responders and nonresponders (Supplementary Fig. 7), implying that the noticed variations will not be pushed solely by the comparatively small variety of nonresponders.
With the supply of biopsies at totally different time factors per affected person, we have been additionally in a position to assess the dynamics of immune cell subsets after the next addition of chemotherapy to atezolizumab. We discovered a considerable enhance in CD45+ cells, CD4+ T cells and FOXP3+ regulatory T (Treg) cells in nonresponders, whereas these subsets decreased in responders (Fig. 3k,l and Supplementary Fig. 5), leading to a major distinction between responders and nonresponders by comparability of Δ values (Supplementary Fig. 7).
As a management, transcriptomic evaluation of samples at surgical procedure confirmed that expression ranges of above-mentioned immune-related genes remained comparatively secure, with no important adjustments relative to the samples obtained after the primary mixture cycle in both responders or nonresponders (Fig. 3 and Supplementary Fig. 5), emphasizing that the particular adjustments noticed after atezolizumab have been treatment-related.
Total, these findings show, additionally on the idea of study of the TME, that the addition of atezolizumab has a significant impression on the impact of chemotherapy in G/GEJ cancers.