The World Well being Group estimates that 30% to 50% of all most cancers instances are preventable.
Sure, a lot of that may be attributed to wholesome way of life decisions, together with bodily exercise, higher diet, lack of smoking, and gentle to reasonable alcohol consumption, however data can be a strong most cancers prevention device. In response to the American Affiliation for Most cancers Analysis (AACR) Most cancers Progress Report 2023, the USA skilled a 33% decline in general most cancers mortality between 1991 and 2020 largely due to public well being campaigns and coverage initiatives applied to cut back smoking and improve early detection of cancers, based mostly on research findings in CA: A Most cancers Journal for Clinicians.
As they are saying (or no less than a sequence of public service bulletins did within the ’90s), “The Extra You Know.” And on this case, the extra you realize about your most cancers dangers might be lifesaving, and what you don’t know can have damaging penalties. A sequence of latest research have discovered that some individuals could lack a sure degree of readability and/or consciousness about some most cancers prevention methods akin to screening and vaccination. This will likely trigger gaps in guaranteeing profit from accessible strategies that may assist detect most cancers a lot earlier or outright stop it.
One of many a number of preliminary screening choices for colorectal most cancers (CRC) is a self-administered fecal immunochemical take a look at (FIT) by which a person offers a stool pattern to be examined for hidden blood. The FIT is both administered at a well being care workplace (typically with verbal directions) or by way of a mail-order program (with written and/or info-graphical directions). However 1 in 10 FITs couldn’t be processed because of unsatisfactory samples, in accordance with outcomes from a research revealed in Most cancers Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the AACR.
No less than a part of the problem is people don’t absolutely comprehend what’s required to offer a pattern that’s deemed passable for testing, in accordance with Rasmi Nair, MBBS, PhD, co-first creator of the paper and an assistant professor on the Peter O’Donnell Jr. Faculty of Public Well being of UT Southwestern Medical Heart. That was very true for the mail-order program, which was 2.66 occasions extra prone to produce unsatisfactory outcomes.
Nair and her colleagues examined digital well being file (EHR) information of 56,980 people aged 50 to 74 who underwent FIT screening between 2010 and 2019 inside the Dallas-based Parkland Well being system. Parkland, which is taken into account a safety-net hospital, offers care to multiple million low-income, uninsured Dallas County residents. Total, of the ten.2% FITs thought of unsatisfactory, 51% had been because of an insufficient specimen, 27% had been attributed to incomplete labeling, 13% of the stool specimens had been too previous, and eight% had a damaged or leaking container. Moreover, solely 40.7% of people with unsatisfactory assessments acquired follow-up FIT or colonoscopy screening inside 15 months of the failed take a look at.
Nair steered that minimizing language and well being literacy limitations may assist, and the research authors pointed to visible directions that confirmed constructive ends in bettering pattern assortment in different research. The authors additionally steered that testing services embody beforehand affixed affected person labels or barcodes to attenuate labeling errors in addition to coverage adjustments to permit utilizing the pattern ordering, mailing, or receiving date as the gathering date—if the date is lacking on the label itself and the pattern is shipped inside the two-week widow. Lastly, the authors additionally wish to see a greater system put in place to make sure correct follow-up.
“The truth that, in most situations, unsatisfactory FIT was not adopted by a well timed subsequent take a look at highlights the necessity for methods to have a greater, extra complete method to tagging and following up unsatisfactory FIT,” mentioned co-first creator Po-Hong Liu, MD, a gastroenterology fellow at UT Southwestern Medical Heart.
The Want for Extra HPV Vaccine Consciousness
The vaccine for human papillomavirus (HPV) has proven large ends in stopping cervical most cancers. Actually, a latest research analyzing cervical most cancers instances in Scotland discovered zero instances amongst girls born between 1988-1996 who had been absolutely vaccinated towards HPV between the ages of 12 and 13, in accordance with a paper revealed within the Journal of the Nationwide Most cancers Institute.
The HPV vaccine, nonetheless, can profit males and shield towards different cancers as effectively, together with anal, oral, and penile cancers. However this truth is probably not correctly introduced to Hispanic and Latino males who determine as sexual minorities, in accordance with outcomes introduced on the sixteenth AACR Convention on the Science of Most cancers Well being Disparities in Racial/Ethnic Minorities and the Medically Underserved.
Between August 2021 and August 2022, Shannon M. Christy, PhD, assistant member within the Division of Well being Outcomes and Conduct at Moffitt Most cancers Heart in Tampa, Florida, and her colleagues surveyed people between the ages of 18 and 26 who had been born male and had been dwelling in Florida and Puerto Rico, recognized as Hispanic or Latino, had intercourse with a person or had been drawn to males, and had been in a position to learn and perceive Spanish. Among the many 102 members who mentioned that they had not acquired the HPV vaccine, 56% responded incorrectly or “have no idea” to a query about whether or not most sexually lively people are in danger for being contaminated with HPV; 20% responded incorrectly or “have no idea” to a query assessing whether or not males might be contaminated with HPV; and greater than half responded incorrectly or “have no idea” to questions concerning the hyperlink between HPV and anal (54%), oral (61%), or penile (65%) cancers.
Fifty-six % did hear concerning the HPV vaccine, but solely 19% mentioned a supplier had beneficial it to them. At the moment, the Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention recommends HPV vaccination for adolescents round ages 11 or 12 and even encourages the vaccination of younger adults as much as age 26 if they didn’t obtain it after they had been youthful. The U.S. Meals and Drug Administration has authorized the HPV vaccine for individuals ages 9 to 45.
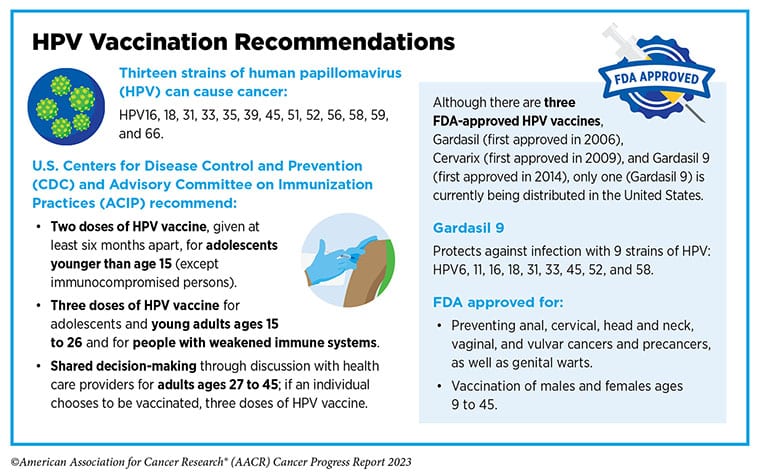
“Sexual minority males are a inhabitants group at increased threat for HPV infections and subsequent HPV-related well being issues, together with anal most cancers,” mentioned Christy. “Prior analysis has demonstrated suboptimal HPV vaccine uptake amongst younger adults, together with sexual minority males. Extra efforts are wanted to make sure that all age-eligible neighborhood members can profit from this efficient most cancers prevention methodology.”
One place to start out could be extra Spanish-language supplies about HPV vaccination for younger adults, as Christy and her collaborators discovered a scarcity of such training and no supplies culturally tailored for Hispanic and Latino sexual and gender minority neighborhood members. “To cut back HPV-related most cancers disparities, it’s important that data be related and actionable and accessible to age-eligible individuals of their most well-liked language,” mentioned Christy.
Your Genetics Know What You Might Not about Most cancers Prevention
Complete-exome sequencing can be utilized as a screening approach to determine if a person has any genes predisposed for hereditary ailments, together with some cancers. The Nationwide Complete Most cancers Community (NCCN) has established a set of pointers—together with ones for breast, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers and colorectal most cancers—to determine people who ought to bear genetic testing, however pointers like these won’t be catching everybody who ought to be screened, in accordance with N. Jewel Samadder, MD, a professor of medication on the Mayo Clinic School of Drugs and co-leader of the precision oncology program on the Mayo Clinic Complete Most cancers Heart.
“These standards had been created at a time when genetic testing was cost-prohibitive and thus aimed to determine these on the best likelihood of being a mutation provider within the absence of population-wide whole-exome sequencing,” Samadder mentioned. “Nevertheless, these circumstances are poorly recognized in present apply, and lots of sufferers usually are not conscious of their most cancers threat.”
Samadder introduced outcomes from the Tapestry medical trial on the AACR Annual Assembly 2023 that confirmed that 39.2% of people who consented to whole-exome sequencing and had been recognized as carriers of predisposition genes for hereditary breast and ovarian most cancers (HBOC) or Lynch syndrome wouldn’t have certified beneath present pointers. On the time of information cut-off, 44,306 sufferers from Mayo Clinic websites in Minnesota, Arizona, and Florida had offered a saliva pattern. For this a part of the trial, researchers used whole-exome sequencing to guage samples for BRCA1 and BRCA2, denoting HBOC, and MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2, and EPCAM, denoting Lynch syndrome.
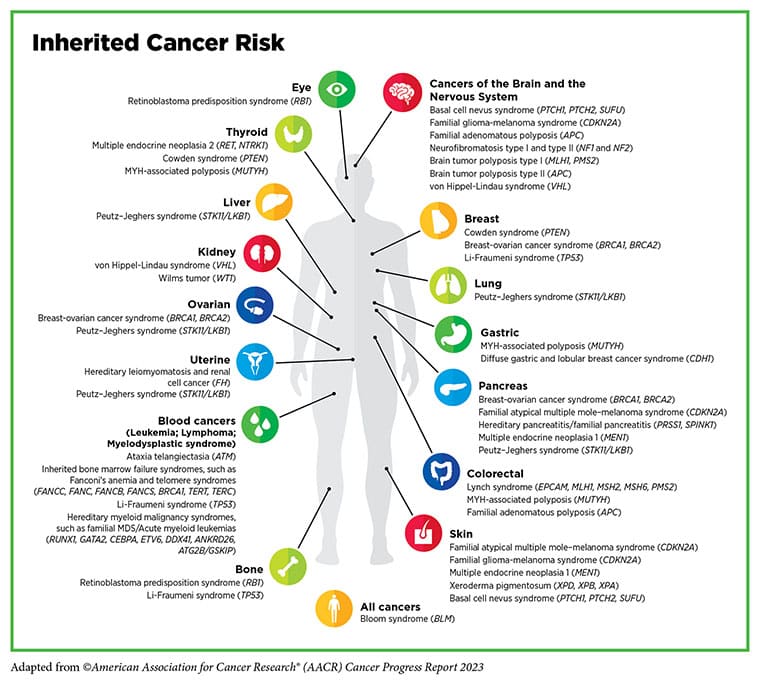
Of the 387 people with HBOC and 163 with Lynch syndrome recognized, 52.1% didn’t know previous to this research that they had a most cancers predisposition situation and 39.2% didn’t fulfill the prevailing NCCN standards for genetic testing. Among the many sufferers who had been newly recognized with HBOC or Lynch syndrome throughout this research, 60% had been ineligible for genetic testing per the present pointers. Samadder defined that sufferers with HBOC have as much as an 80% lifetime threat of creating breast most cancers and a markedly elevated threat, relative to the overall inhabitants, of creating ovarian most cancers, pancreatic most cancers, prostate most cancers, and melanoma. In the meantime, sufferers with Lynch syndrome have as much as an 80% lifetime threat of colorectal most cancers and as much as 60% lifetime threat of endometrial most cancers, plus elevated dangers of higher gastrointestinal, urinary tract, pores and skin, and different cancers.
Figuring out about their elevated genetic threat will help sufferers take acceptable subsequent steps, Samadder mentioned. For instance, sufferers with Lynch syndrome can bear common colonoscopies, blood and urine screening, and prophylactic hysterectomy, whereas sufferers with HBOC might be proactive via superior breast imaging and prophylactic mastectomy and/or oophorectomy.
“The data that comes from genetics,” Samadder mentioned, “can empower sufferers to take management of their illness threat and improve their chance of avoiding a lethal most cancers prognosis or catching it at an early stage when it’s extremely curable.”
Like they are saying, the extra you realize.
To see how a lot you realize about most cancers prevention, take the AACR’s Most cancers Prevention Quiz.

