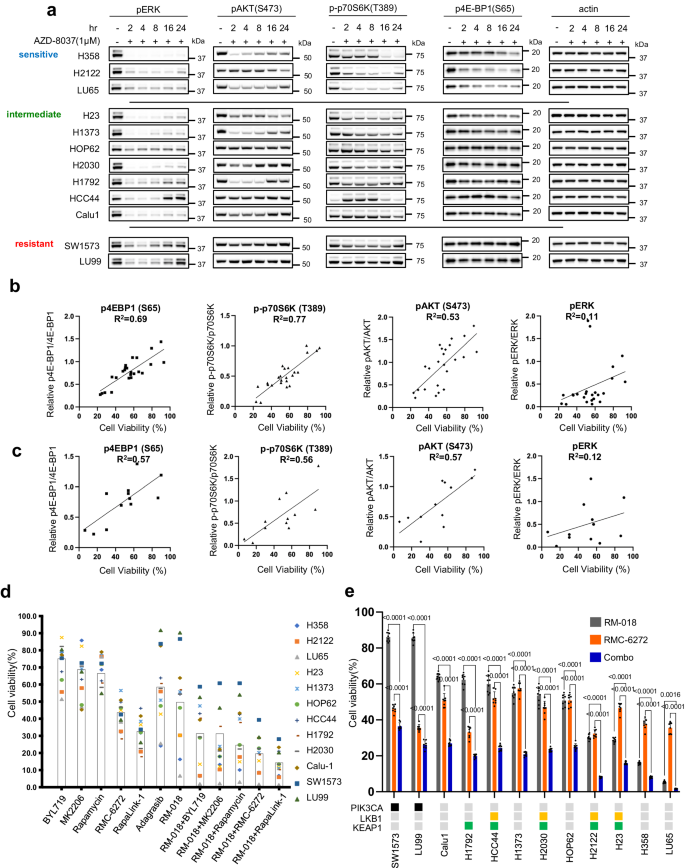
Lively-state KRASG12C inhibitors inhibit ERK pathway output extra potently and durably than inactive-state KRASG12C inhibitors
The consequences of pharmacologic inhibition of KRASG12C in NSCLC strains have been first studied with three inactive-state KRASG12C inhibitors, sotorasib16, adagrasib17, and AZD803718. After 4 h of incubation, AZD8037 inhibited ERK phosphorylation (pERK) at concentrations between 100 nM and 1000 nM within the KRASG12C NSCLC cell strains H358 and H23 however didn’t have an effect on pERK within the KRASG12S A549 lung most cancers cell line (Supplementary Fig. 1a). Cell viability was assessed after incubation of 12 KRASG12C NSCLC strains with various concentrations of sotorasib, adagrasib, or AZD8037 for 72 h (Fig. 1a). At 1 µM, sensitivity of cell strains to KRASG12C inhibition was variable, however every cell line responded equally to all three compounds.
Cell viability knowledge of KRASG12C mutant cell strains following therapy with (a) inactive-state KRASG12C inhibitors or (b) active-state KRASG12C inhibitors for 72 h. Knowledge are the imply ± SD of n = 8 experimental replicates. c LU65 and H23 cell strains have been handled with 100 nM Adagrasib or 100 nM RM-018 for the indicated instances and lysates have been analyzed by immunoblot. In parallel, the quantity of lively GTP-bound KRAS was decided by a RAS-GTP pulldown assay. d The mRNA expression of the indicated goal genes was decided by quantitative PCR in LU65 and H23 cell strains following 100 nM Adagrasib or 100 nM RM-018 therapy for the indicated instances. The info proven symbolize the means ± SD of n = 3 experimental replicates. P values are proven and have been calculated by two-sided t take a look at.
We requested whether or not these noticed variations in sensitivity mirror variations in efficiency or length of inhibition of RAS signaling. To this finish, we utilized a category of active-state RASG12C inhibitors which incorporates the preclinical device compounds RM-018 and RMC-4998, the latter being stronger and exhibiting oral bioavailability in vivo13,19. These preclinical device compounds are consultant of the investigational agent RMC-6291 which is presently in early-phase scientific trials. These compounds type a high-affinity tri-complex with cyclophilin A and GTP-bound KRASG12C, adopted by covalent bond formation, blocking the affiliation with downstream effectors. The speed of inhibition of KRASG12C by inactive-state KRASG12C inhibitors is set by the GTPase exercise of the mutant. Against this, RM-018 and RMC-4998 straight bind to GTP-bound KRASG12C which ends up in extra speedy and sustained inhibition19. RM-018 inhibited ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling within the KRASG12C cell strains LU65 and H23 in a concentration-dependent method and triggered a mobility shift in KRAS that indicated covalent binding (Supplementary Fig. 1b). Against this, RM-018 had little or no impact on ERK inhibition or the cell development of A549, a KRASG12S mutant NSCLC cell line or in PC-9, a NSCLC cell line with an EGFR mutation and KRASWT, in line with the specificity of this inhibitor for KRASG12C (Supplementary Fig. 1c, d).
The consequences of RM-018 and RMC-4998 have been additional evaluated within the panel of KRASG12C cell strains. H358, LU65, and H2122 cells have been probably the most delicate to RM-018, with IC50 values greater than 10-fold decrease than these of adagrasib (Fig. 1b). Nonetheless, these cell strains most proof against the inactive-state KRASG12C inhibitors akin to LU99A and SW1573 remained comparatively proof against RM-018. RMC-4998 had an identical sample of inhibition to RM-018 on this panel of cell strains however with IC50 values roughly 10-fold decrease reflecting its elevated efficiency (Fig. 1b). To straight examine the results of inactive-state and active-state KRASG12C inhibition, the influence of RM-018 on ERK signaling was in contrast with adagrasib within the LU65 and H23 cell strains. In line with the mechanisms of motion, 100 nM adagrasib maximally suppressed ERK signaling after 2–4 h of therapy, whereas RM-018 triggered disappearance of the pERK sign on immunoblot after simply 1 h of therapy (Fig. 1c). RM-018 additionally inhibited ERK signaling extra durably than adagrasib with much less reactivation of the pERK sign at 24 and 48 h of incubation (Fig. 1c).
To quantify output and pathway reactivation extra comprehensively, we assessed the results of those inhibitors on the transcriptional output of the ERK pathway20. ERK phosphorylation doesn’t range linearly with output as a result of the expression of the ERK phosphatases DUSP1, 4 and 6 is ERK dependent. We used PCR to find out the results of KRASG12C inhibitors on the expression of 9 ERK-regulated mRNAs as a operate of time (Fig. 1d). The mRNAs encode regulators of pathway activation and suggestions and transcription components regulated by ERK signaling. They have been chosen primarily based on the dynamic vary in expression after pathway inhibition and their comparatively brief half-life which might enable evaluation at 24 h.
Each forms of compounds considerably inhibited the expression of every of the mRNAs at 4 h, however, in each case, RM-018 was considerably stronger than adagrasib (Fig. 1d). Furthermore, whereas vital rebound in expression occurred by 24 h in 8/9 mRNAs in H23 cells handled with adagrasib, in these handled with RM-018, rebound occurred in solely 3/9 mRNAs and to ranges beneath these of adagrasib. In LU65, the preliminary impact of RM-018 was a lot higher than that of adagrasib and at 24 h, expression of seven mRNAs was lower than 10% of baseline, whereas this was the case for under 2 of the mRNAs in adagrasib handled cells. These outcomes are in line with these obtained by immunoblotting and clearly present that the active-state RASG12C inhibitor RM-018 is stronger and fewer prone to late rebound than the inactive-state KRASG12C inhibitors. Nonetheless, regardless of stronger and sturdy inhibition of the ERK pathway with RM-018, heterogeneity of response remains to be obvious throughout the panel of KRASG12C cell strains.
Sensitivity of NSCLC cell strains to KRASG12C inhibitors is very correlated with their inhibition of PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling
To analyze further variables that have an effect on sensitivity to RAS inhibition, the influence of the inactive-state KRASG12C inhibitor AZD8037 on effector pathways of RAS, RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling, was assessed within the panel of cell strains. To facilitate comparability, cell strains with lower than 50% viable cells in comparison with management at 1 µM AZD8037 have been categorized as delicate, whereas these for which greater than 75% have been viable have been categorized as resistant and people in between have been categorized as intermediate (Fig. 1a). After 2 h of therapy with AZD8037, pERK was markedly inhibited in all 12 examined cell strains (Fig. 2a). In most, inhibition endured for at the least 24 h, with no or solely slight rebound. In 5 cell strains (HOP62, H1792, HCC44, SW1573, LU99), vital rebound occurred at 24 h. Of those, two have been resistant and three have been intermediate, suggesting the persistence of ERK inhibition is said to sensitivity. Nonetheless, within the different cell strains with intermediate sensitivity (H23, H1373, H2030, Calu1), ERK was nonetheless potently inhibited at 24 h, suggesting that different variables play a job in figuring out sensitivity.
a Immunoblots of KRASG12C mutant cell strains handled with 1 µM AZD8037 for the indicated instances. Scattered plot of cell viability for the KRASG12C mutant cell strains following 72 h therapy plotted in opposition to quantified immunoblot intensities of the indicated phosphorylated protein normalized in opposition to the respective complete protein after 24 h therapy. The plots present 12 cell strains plotted twice every for impartial experiments with both 1 µM Sotorasib or 1 µM AZD8037. R2 calculated by linear regression. c Similar as (b) however with 12 cell strains plotted as soon as every after therapy with 100 nM RM-018. d Cell viability as proportion change from management of KRASG12C mutant cell strains handled for 72 h with BYL719 1 µM, MK2206 1 µM, Rapamycin 10 nM, RMC-6272 1 nM, RapaLink-1 10 nM, Adagrasib 100 nM, RM-018 100 nM, or mixture therapies as indicated. Every level represents the imply of n = 8 experimental replicates, and the bins symbolize the imply of the cell strains. e Cell viability as proportion change from management for KRASG12C mutant cell strains handled with both 100 nM RM-018, 1 nM RMC-6272 or the mix for 72 h. Knowledge are means ± SD for n = 8 experimental replicates. P values are proven and have been calculated by one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey’s take a look at. The standing of genetic co-alterations is proven.
We noticed that inhibition of PI3K/mTOR assorted considerably amongst cell strains after therapy with AZD8037 (Fig. 2a, Supplementary Fig. 2a). Within the delicate cell strains, we observe sustained inhibition of the mTORC1 substrates p-p70S6K T389 and p4EBP1 S65 at 24 h, whereas pAKT S473 is inhibited on the earlier time factors however with proof of rebound at 24 h. In distinction, the intermediate and resistant cell strains exhibit no suppression of p4EBP1 S65 and weak suppression of p-p70S6K T389, whereas pAKT S473 displays various kinetics with preliminary inhibition adopted by sturdy rebound in some cell strains. These knowledge counsel that inhibition of PI3K/mTOR signaling, and suppression of 4EBP1 phosphorylation particularly, is strongly associated to RAS inhibitor efficacy in these tumors. An analogous sample was noticed with the active-state RASG12C inhibitor RM-018 (Supplementary Fig. 2b).
To supply quantification of this commentary, we carried out correlative evaluation between inhibition of cell development and inhibition of ERK and PI3K/mTOR signaling. We discovered that inhibition of cell development by the inactive-state KRASG12C inhibitors sotorasib and AZD8037 is very correlated with the diploma of inhibition of pAKT S473, p-p70S6K T389, and p4E-BP1 S65 with R2 values starting from 0.53–0.77, whereas pERK inhibition was not considerably correlated with an R2 worth of 0.11 (Fig. 1a, Fig. 2b, Supplementary Fig. 2a). This evaluation was additionally carried out with RM-018, and an identical sample of correlation was noticed (Fig. 1b, Fig. 2c, Supplementary Fig. 2b). These outcomes counsel that suppression of ERK signaling by KRASG12C inhibitors is critical however not enough to sensitize the cells; further suppression of PI3K/mTOR signaling can be wanted. That is in line with earlier reviews and with our earlier discovering that anti-proliferative efficacy requires dephosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and its consequent inhibition of cap-dependent translation15. On the time, this was achieved by combining a MEK inhibitor with an AKT inhibitor, every of which inhibits signaling in each regular and tumor cells, nevertheless this mixture was discovered to be insupportable in vivo. Our present knowledge and the event of mutant allele-selective RAS inhibitors led us to revisit this concept.
The variability of inhibition of PI3K/mTOR signaling and its affiliation with sensitivity means that the connection could also be causal and that combining the RAS inhibitor with a stronger inhibitor of PI3K or mTOR exercise would possibly considerably improve antitumor exercise. We due to this fact examined the results of inhibitors of various parts of the PI3K pathway, alone and together with RAS inhibition (Fig. 2nd). We selected RM-018 for additional evaluation as a consultant and potent active-state RASG12C inhibitor. For PI3K/mTOR pathway inhibitors, we utilized BYL719, a PI3K alpha-specific inhibitor, MK2206, an allosteric pan-AKT inhibitor, rapamycin, an allosteric mTOR inhibitor that preferentially inhibits mTORC1 however is a weak inhibitor of 4E-BP1 phosphorylation, and two third-generation potent bi-steric inhibitors of mTOR: RapaLink-1 and RMC-6272 are each bi-steric inhibitors comprised of a rapamycin-like moiety covalently linked to an ATP-competitive inhibitor of mTOR kinase21,22,23. RMC-6272 is comparatively selective for mTORC1 whereas sparing mTORC2 over a big focus vary, as in comparison with Rapalink-1 (Supplementary Fig. 2c, d), whereas each successfully inhibit 4E-BP1 phosphorylation in KRASG12C NSCLC cells21. RMC-6272 is a preclinical device compound, consultant of the investigational agent RMC-5552. The selective bi-steric mTORC1 inhibitors retain antitumor exercise however don’t trigger hyperglycemia in preclinical fashions23.
We noticed that PI3K inhibition, AKT inhibition and rapamycin had modest results on proliferation of cells within the panel, with a median 20–40% discount in cell development in comparison with management at 72 h (Fig. 2nd). Nonetheless, the bi-steric mTOR inhibitors Rapalink-1 and RMC-6272 have been notably stronger with higher than 50% common discount. We then examined every of those inhibitors together with RM-018. PI3K or AKT inhibition had modest additive advantages together with RM-018. Nonetheless, combining RM-018 with the mTOR inhibitors had a extra marked synergistic impact, with the bi-steric mTOR inhibitors demonstrating a higher than 80% common development discount throughout the cell line fashions. The mix of RM-018 and RMC-6272 confirmed a big discount in cell viability in comparison with both compound alone in each mannequin examined, no matter co-mutation standing (Fig. 2e). These outcomes counsel that on this panel of KRASG12C mutant NSCLC cell strains, mTORC1 inhibition particularly is important within the context of mixture therapy with the KRASG12C inhibitor. We have been inspired to additional discover this therapeutic technique in vivo in related preclinical fashions.
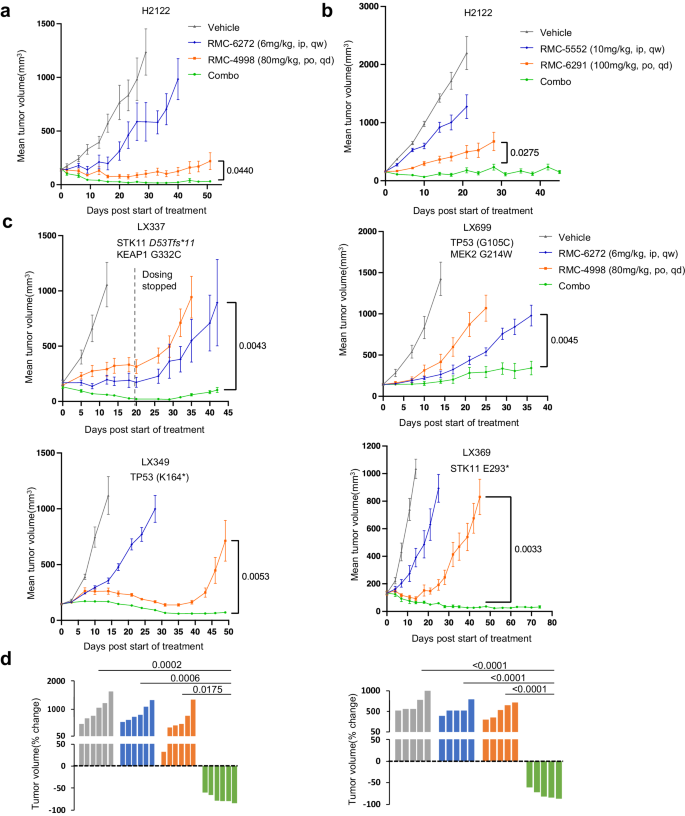
The mix of KRASG12C and mTORC1 selective inhibition causes sturdy tumor regressions in KRASG12C mutant NSCLC fashions in vivo
We first examined the orally bioavailable active-state KRASG12C inhibitor RMC-4998 and the mTORC1-selective bi-steric inhibitor RMC-6272 within the cell-line derived H2122 KRASG12C lung adenocarcinoma xenograft mannequin (CDX). RMC-6272 was administered as soon as weekly by intraperitoneal injection, and RMC-4998 was administered as soon as day by day by oral gavage. When administered as single brokers, the mTORC1 inhibitor triggered modest inhibition of tumor development, whereas the KRASG12C inhibitor prevented development for ~30–35 days after which tumors started to develop on therapy. In distinction, the mix of RMC-4998 with RMC-6272 triggered nearly full tumor regression starting quickly after administration and persisting all through the 50 days of therapy (Fig. 3a). The mix was nicely tolerated with out weight reduction and neither inhibitor monotherapy nor the mix triggered vital hyperglycemia over 4 weeks of therapy (Supplementary Fig. 3a, b). We additionally examined the investigational candidates RMC-6291 (active-state RASG12C inhibitor)19, and RMC-5552 (bi-steric mTORC1-selecive inhibitor)23 in each the H2122 and H2030 CDX fashions (Fig. 3b, Supplementary Fig. 3c). In H2122, the responses to RMC-6291 and RMC-5552, alone and together, have been similar to these seen with their preclinical device compounds, RMC-4998 and RMC-6272, respectively. In H2030, each single brokers triggered a modest slowing of tumor development however together tumor regressions elevated over time till there have been minimal residual tumors on day 70.
a H2122 xenografts have been handled with car, RMC-6272 6 mg/kg weekly, RMC-4998 80 mg/kg day by day, or the mix. Tumor volumes have been plotted from the beginning of therapy (imply ± SEM, n = 5 mice in every cohort). P values are proven and have been calculated by two-sided t-test. b H2122 xenografts have been handled 10 days post-implant with the car, RMC-6291 100 mg/kg day by day, RMC-5552 10 mg/kg weekly, or the mix. Tumor volumes have been plotted over time from the beginning of therapy (imply ± SEM, n = 8 mice in every cohort). P values are proven and have been calculated by two-sided t-test. c 4 completely different KRASG12C mutant lung PDX tumors have been implanted into NSG mice. PDXs have been handled with the car, RMC-6272 6 mg/kg weekly, RMC-4998 80 mg/kg day by day, or the mix. Tumor volumes have been plotted over time from the beginning of therapy (imply ± SEM, n = 5 mice in every cohort for LX349 and LX699, n = 6 mice in every cohort for LX369 and LX337). P values are proven and have been calculated by two-sided t take a look at. d Waterfall plot exhibiting the proportion change in tumor quantity (relative to preliminary quantity) for particular person LX349 (left) and LX369 (proper) tumors on the finish of therapy. P values are proven and have been calculated by one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey’s take a look at.
We then prolonged our examine of this mixture remedy strategy to a sequence of comparatively insensitive KRASG12C mutant lung most cancers PDX fashions with varied co-existent genetic lesions (mutant TP53, STK11/LKB1, KEAP1, MEK2) (Fig. 3c). The mix of RMC-4998 with RMC-6272 achieved dramatic tumor shrinkage in three of the 4 fashions with clear synergy in LX349, and LX369. These responses have been seen in all tumor-bearing mice harboring the LX349 and LX369 PDX fashions (Fig. 3d) and have been sturdy over a interval of seven weeks. In LX349, each the KRASG12C inhibitor and the mix have been efficient, however resistance to the KRASG12C inhibitor, and never the mix therapy group, developed on day 40. Against this, each the KRASG12C inhibitor and the mTORC1 inhibitor triggered solely a slight development delay in LX369, however the mixture triggered full tumor regression by day 40, with continued response at day 75. Curiously, LX699, the one mannequin that didn’t endure regression with the mix and grew slowly throughout the 36 days of therapy, harbored a MEK2 G214W mutation, which whereas beforehand uncharacterized, is presumably a mechanism of KRAS inhibitor resistance on this mannequin. Not one of the fashions developed resistance to the mix remedy whereas on therapy. No vital physique weight reduction was noticed in any of the mice throughout the therapy interval (Supplementary Fig. 3d).
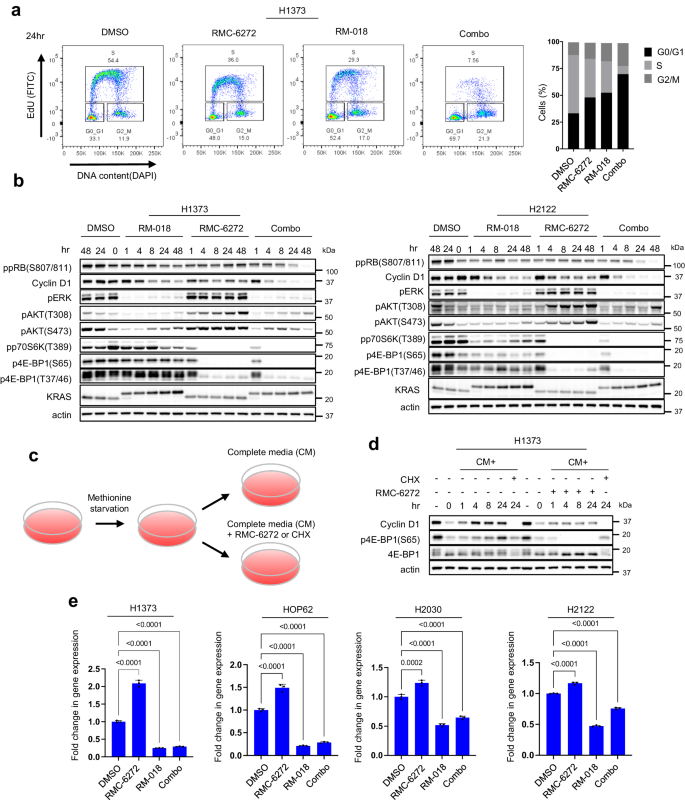
Mixed inhibition of KRASG12C and mTORC1 blocks Cyclin D1 expression on the transcriptional and translational ranges
We wished to additional discover the mechanistic foundation for the synergistic mixture exercise we noticed. We have now beforehand proven that the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and RAS/RAF/ERK pathways converge on key mobile processes, together with Cyclin D-Cdk4/6 activation and cap-dependent translation and that each pathways have to be inhibited to have an effect on tumor development or survival15,24. In H1373 and H2122, each RM-018 and RMC-6272 after 24 h therapy every resulted in a ~50% enhance in cells in G0/G1 with a concomitant lower in S section cells. Nonetheless, mixture therapy led to a way more profound impact with a 110% enhance in G0/G1 cells and concomitant lower in S section cells (Fig. 4a, Supplementary Fig. 4a). We investigated the underlying mechanism of this phenomenon within the H1373, H2122, HOP62, and H2030 cell strains. In these fashions, every inhibitor alone triggered a modest lower in Cyclin D1 protein ranges with out a vital lower in retinoblastoma (RB) phosphorylation (Fig. 4b, Supplementary Fig. 4b). Against this, the mix triggered marked decreases in each Cyclin D1 and phosphorylated RB protein ranges. To additional consider the useful significance of Cyclin D1, we carried out siRNA knockdown of Cyclin D1 in H1373 cells and noticed that that is enough to lower RB phosphorylation and inhibit cell proliferation to an identical diploma as the mix of RM-018 and RMC-6272 (Supplementary Fig. 4c, d). As well as, Cyclin D1 knockdown is enough to trigger cycle arrest with a 3-fold enhance in cells in G0/G1 and a concomitant 80% lower in S section cells (Supplementary Fig. 4e).
a H1373 cells have been handled with 1 nM RMC-6272, 100 nM RM-018, or the mix for twenty-four h. Cell cycle states have been detected with EdU-DAPI-based move cytometry. b H1373 and H2122 cells have been handled with both 100 nM RM-018, 1 nM RMC-6272, or the mix for the indicated instances, and lysates have been analyzed by immunoblot. c Schema of the move for the methionine hunger experiment in (d). d H1373 cells have been cultured in methionine starved medium for twenty-four h, adopted by including again full media (CM) alone, or with both 1 nM RMC-6272 or 50 µg/ml cycloheximide (CHX) for the indicated instances, and lysates have been analyzed by immunoblot. e Cyclin D1 mRNA ranges have been decided by quantitative PCR in H1373, HOP62, H2030, and H2122 cells following 1 nM RMC-6272, 100 nM RM-018, or the mix for twenty-four h. The info proven symbolize the means ± SD of n = 3 experimental replicates. P values are proven and have been calculated by one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey’s take a look at.
As Cyclin D1 translation is mTORC1 dependent25, we assessed whether or not it’s affected by RMC-6272. We starved cells for methionine for twenty-four h to inhibit initiation of translation, then refed cells 24 h later with full media with or with out RMC-6272 (Fig. 4c). The worldwide translation inhibitor cycloheximide was used as a optimistic management. Methionine deprivation decreased Cyclin D1 protein ranges whereas mRNA ranges weren’t considerably inhibited (Fig. 4d, Supplementary Fig. 4f). Cyclin D1 protein ranges instantly recovered as soon as full media was added again whereas RMC-6272 suppressed this enhance (Fig. 4d). These knowledge counsel that RMC-6272 inhibits induction of Cyclin D1 protein expression primarily by way of blocking its translation. Nonetheless, we famous that RMC-6272 alone doesn’t fully inhibit Cyclin D1 expression, and thus assessed whether or not RM-018, RMC-6272 or the mix affected the degrees of Cyclin D1 mRNA. Throughout 4 cell line fashions, Cyclin D1 mRNA ranges elevated by ~50–100% following RMC-6272 therapy, whereas it was suppressed with RM-018 therapy by ~50–75% (Fig. 4e). Mixture therapy additionally suppressed Cyclin D1 mRNA to roughly the identical degree as RM-018 alone, demonstrating that the impact of RM-018 dominates on this setting. In sum, these outcomes counsel that the results of RMC-6272 on Cyclin D1 translation are buffered by ERK-dependent induction of Cyclin D1 mRNA. The mix of RM-018 and RMC-6272 blocks each processes and synergistically reduces mobile Cyclin D1 protein ranges.
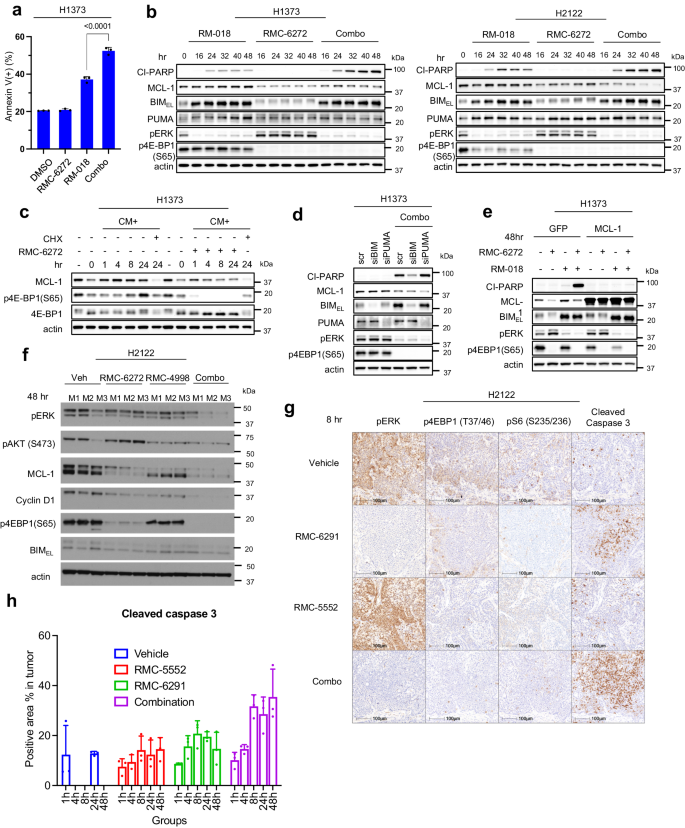
Mixed inhibition of KRASG12C and mTORC1 kinase synergize to induce apoptosis by inducing BIM and decreasing MCL-1 expression
The in vivo regression of KRASG12C NSCLC murine fashions means that the mix remedy induces cell demise. We requested whether or not mTORC1 inhibition enhances KRASG12C inhibitor-induced cytotoxicity. Induction of demise within the KRASG12C mutant H1373, H2122, and HOP62 cell strains was assessed with the annexin V-propidium iodide (PI) assay following 72 h of therapy with RM-018, RMC-6272, or the mix. In H1373, H2122, and HOP62, RM-018 alone roughly doubled the proportion of annexin V optimistic cells, whereas RMC-6272 solely triggered a minimal enhance (Fig. 5a, Supplementary Fig. 5a). Nonetheless, in comparison with RM-018 therapy alone, the mix with RMC-6272 considerably enhanced complete cell demise by three to four-fold as in comparison with controls. Induction of demise by the mix is suppressed by the pan-caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK (Z-VAD) in H1373 and H2122 cells to various levels, suggesting {that a} vital proportion of the demise is because of activation of the caspase cleavage cascade, however that different mechanisms could also be concerned as nicely (Supplementary Fig. 5b). In line with the outcomes of annexin V- PI assay, the inhibitor mixture induced a big time-dependent enhance in cleaved PARP in comparison with RM-018 alone (Fig. 5b). Notably, Cyclin D1 knockdown alone didn’t induce cleaved PARP or enhance the proportion of annexin V optimistic cells (Supplementary Fig. 5c).
a H1373 cells have been handled with 100 nM RM-018, 1 nM RMC-6272, or the mix for 72 h, and analyzed by FACS to quantify annexin V optimistic cells. Knowledge are means ± SD for n = 3 experimental replicates. P values are proven and have been calculated by one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey’s take a look at. b Immunoblot evaluation of lysates from H1373 and H2122 cells handled with 100 nM RM-018, 1 nM RMC-6272, or the mix for the indicated instances. c H1373 cells have been cultured in methionine-starved medium for twenty-four h, then changed with full media (CM) alone, or with both 1 nM RMC-6272 or 50 µg/ml cycloheximide (CHX) for the indicated instances, and lysates have been analyzed by immunoblot. d H1373 cells have been transfected with siRNAs concentrating on BIM, PUMA or scramble (scr) siRNA and incubated for twenty-four h. The cells have been then handled with the mix of 1 nM RMC-6272 and 100 nM RM-018 for 48 h and lysates have been analyzed by immunoblot. e H1373 cells contaminated with a GFP management or MCL-1 expressing lentiviral plasmid have been handled with 100 nM RM-018, 1 nM RMC-6272, or the mix for 48 h and lysates have been analyzed by immunoblot. f H2122-derived xenografts have been handled with car, RMC-6272 6 mg/kg as soon as, RMC-4998 80 mg/kg x 2 doses 24 h aside, or the mix. 48 h after begin of therapy, the tumors have been collected, lysed and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. M1, M2, M3 symbolize particular person mice from every therapy situation. g IHC evaluation of H2122-derived xenograft tumors collected 8 h after therapy with car, RMC-5552 (10 mg/kg, ip), RMC-6291 (100 mg/kg, po), or the mix. The magnification of all IHC slides are 40x, scale bars are 100 µm. h Quantification of Cleaved Caspase 3 IHC evaluation proven in (g). The info proven symbolize the means ± SD of n = 3 experimental replicates.
Binding of the BH3 domain-only proteins akin to BIM, PUMA, and BID to BCL2 relations like MCL-1 inhibits the anti-apoptotic results of the latter and induces apoptosis26. MCL-1 translation has beforehand been proven to be mTOR dependent27,28. Thus, we additional investigated if the impact of mTORC1 inhibition on MCL-1 translation was the idea for the improved cell demise together with the KRASG12C inhibitor. We discovered that RMC-6272 decreased MCL-1 protein ranges, in settlement with the earlier research, however alone doesn’t induce PARP cleavage (Fig. 5b). MCL-1 protein ranges have been decreased following methionine deprivation and recovered following addition of full media, whereas RMC-6272 blocked this restoration (Fig. 5c). In distinction, mRNA ranges of MCL-1 have been induced by methionine hunger, demonstrating that the discount in protein degree is because of the inhibition of MCL-1 translation (Supplementary Fig. 5d). Then again, RM-018 had little impact on MCL-1 protein ranges however strongly induced the pro-apoptotic BH3-only proteins BIM and PUMA (Fig. 5b). Inhibition of ERK-dependent phosphorylation of BIM stabilizes the latter and accounts for elevated expression of the protein29. In H2122, addition of RM-018 additional decreased MCL-1 protein ranges in comparison with RMC-6272 therapy alone. As a doable mechanism for this commentary, it has been beforehand reported that phosphorylated BIM binds to and stabilizes MCL-130.
From these knowledge, we hypothesized that induction of apoptosis by mixed inhibition of KRASG12C and mTORC1 is partially attributable to inhibition of MCL-1 translation by the latter and induction of BIM and/or PUMA protein expression by the previous. We due to this fact knocked down MCL-1 with siRNA (Supplementary Fig. 5e) and located that it was enough to cooperate with RM-018 inhibition to reinforce caspase3/7 exercise within the H1373, H2122, and HOP62 cell strains (Supplementary Fig. 5f). Furthermore, siRNA knockdown of BIM, however not PUMA, considerably decreased induction of PARP cleavage by the mixed inhibition of KRASG12C and mTORC1 in H1373 cells (Fig. 5d). This means that in these cells, BIM is critical for apoptosis induction, whereas PUMA is dispensable. MCL-1 overexpression additionally prevented the induction of PARP cleavage by the mix, suggesting that MCL-1 is enough in these cells to inhibit apoptosis (Fig. 5e). We demonstrated an identical impact in H2122 xenograft tumors in vivo 48 h after dosing with RMC-4998 and RMC-6272. The mix successfully suppresses Cyclin D1 and MCL-1 protein ranges, and 4E-BP1 phosphorylation (Fig. 5f). As predicted, immunohistochemistry evaluation exhibits that the mix of the scientific candidates RMC-6291 (active-state KRASG12C inhibitor) and RMC-5552 (bi-steric mTORC1-selective inhibitor) equally synergistically induces Caspase 3 cleavage (Fig. 5g, h, Supplementary Fig. 5g), extending our findings to the investigational brokers underneath scientific analysis.
Taken collectively, these knowledge show that BIM induction by KRASG12C inhibition and block of MCL-1 protein translation by mTORC1 inhibition collectively are necessary to induce the cell demise wanted for the antitumor exercise of the mix therapy.
KRASG12C inhibition and mTORC1 inhibition trigger synergistic discount in cap-dependent translation
We have now beforehand proven that AKT and MEK inhibition cooperate to inhibit 4E-BP1 phosphorylation and that dephosphorylation of 4E-BP1 is required for the anti-tumor exercise of the mix15. eIF4E acknowledges the mRNA m7GTP 5′ cap construction and assembles the eIF4F translation initiation advanced which additionally contains the proteins eIF4A and eIF4G31. Advanced meeting is inhibited by binding of 4E-BP1 to eIF4E, whereas phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 by mTORC1 releases eIF4E and permits cap-dependent translation to proceed32. Thus, RMC-6272 attenuates cap-dependent translation initiation by way of potent inhibition of the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 by mTORC1 (Fig. 4b, Supplementary Fig. 2c-d).
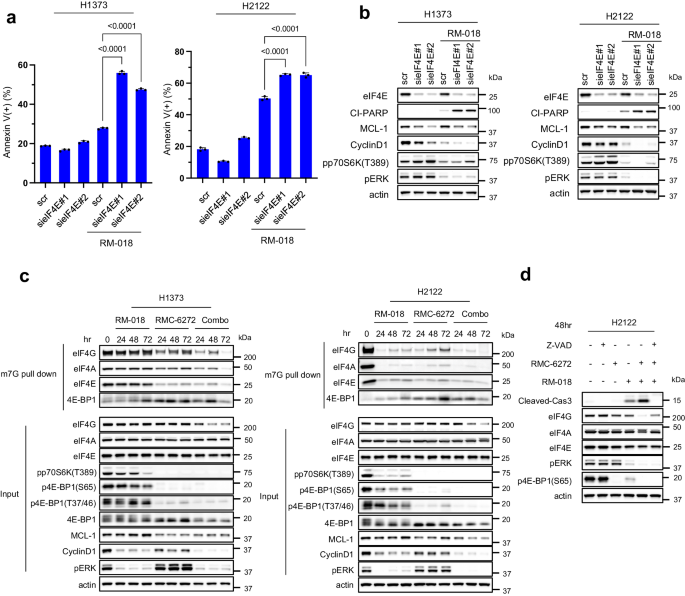
Beads conjugated to the 5’cap construction m7GTP have been in a position to pull down eIF4G, eIF4A, and eIF4E from lysates of the H1373 and H2122 cell strains. As anticipated, the eIF4E/eIF4G interplay was decreased by knockdown of eIF4E, thus suppressing formation of the interpretation initiation advanced (Supplementary Fig. 6a). Within the H1373 and H2122 fashions, eIF4E knockdown alone had a minimal impact on apoptosis, whereas treating these cells with RM-018 triggered an approximate two-fold enhance in Annexin V+ cells (Fig. 6a). These outcomes counsel that the impact of RMC-6272, by inhibition of 4E-BP1 phosphorylation, is just like that of flattening eIF4E, with each resulting in inhibition of eIF4F translation initiation advanced meeting. Alone neither causes apoptosis, nevertheless, both knockdown of eIF4E or RMC-6272 therapy cooperates with KRASG12C inhibition to induce vital cell demise. In line with this mechanism, knockdown of eIF4E inhibited MCL-1 and Cyclin D1 expression in H1373 cells, and to a lesser diploma, in H2122 cells (Fig. 6b). Combining RM-018 with eIF4E knockdown triggered higher inhibition of expression of each Cyclin D1 and MCL-1 than both alone. S6K phosphorylation was induced by knockdown of eIF4E whereas it was inhibited by RM-018. S6K impacts the helicase exercise of eIF4A by different translation regulators akin to eIF4B and PDCD433. Due to this fact, it’s doable that the twin inhibition of 4E-BP1 and S6K phosphorylation, as noticed with RMC-6272, might contribute to the inhibition of cap-dependent translation.
a H1373 and H2122 cells have been transfected with two completely different siRNAs concentrating on eIF4E or scramble (scr) siRNA and cultured for twenty-four h. Media was changed with or with out 100 nM RM-018 and cells have been handled for an extra 48 h and analyzed by FACS to quantify annexin optimistic cells. Knowledge are means ± SD for n = 3 experimental replicates. P values are proven and have been calculated by one-way ANOVA and post-hoc Tukey’s take a look at. b H1373 and H2122 cells have been transfected with two completely different siRNAs concentrating on eIF4E or scramble (scr) siRNA and cultured for twenty-four h. Media was changed with or with out 100 nM RM-018 and cells have been handled for an extra 48 h, and lysates have been analyzed by immunoblot. c H1373 and H2122 cells have been handled with 1 nM RMC-6272, 100 nM RM-018, or the mix for the indicated instances, adopted by incubation with m7GTP-conjugated beads, and lysates have been probed by immunoblot in parallel with entire cell extracts (enter). d H2122 cells have been handled with 100 µM Z-VAD-FMK, 1 nM RMC-6272, 100 nM RM-018, or indicated combos for 48 h, and lysates have been analyzed by immunoblot.
We assessed the results of the RM-018 and RMC-6272 mixture therapy on the formation of the cap-dependent translation initiation advanced within the H1373 and H2122 cell strains. As anticipated, the affiliation of 4E-BP1 with eIF4E was enhanced upon RMC-6272 therapy, leading to inhibition of eIF4F advanced meeting (Fig. 6c). eIF4F meeting was additional inhibited with the mix. We noticed the expression of complete eIF4G was decreased by the mix in H1373 whereas KRASG12C inhibition is enough in H2122. eIF4G has caspase websites and could be cleaved by caspase-3 throughout apoptosis34. Z-VAD prevented lack of eIF4G expression by the mix suggesting that activation of caspases together with caspase-3 by the mix therapy additionally induces cleavage of eIF4G (Fig. 6d). Thus, we conclude that induction of apoptosis by inhibiting translation and inducing BIM causes a feedforward loop inflicting additional inhibition of translation by eIF4G degradation. This will likely doubtless contribute to the antitumor results of KRASG12C inhibitors alone or together with mTORC1 inhibition.