Spherical and star-shaped gold nanoparticles (high) and colon most cancers cells after about 5 hours of publicity to them (backside, respectively). The photograph within the backside left nook reveals that, regardless of the small measurement of the spherical nanoparticles, the most cancers cells survived. False colours. [Image: IFJ PAN]
Researchers in Poland have found that the form, fairly than the scale, of gold nanoparticles issues most in relation to killing most cancers cells (Small, doi: 10.1002/smll.202400778). They carried out stay cell imaging with holotomography—a real-time, label-free laser method that measures the 3D refractive index of a pattern—discovering that star-shaped nanoparticles perforate cell membranes and set off cell dying.
The work provides to our understanding of the mechanical interplay between most cancers cells and gold nanoparticles, which can pave the way in which for the event of more practical, better-targeted therapies.
Benefits of holotomography
Reside cell imaging permits scientists to watch the inside workings of cells with out interfering with their pure physiology. Holotomography is a comparatively new stay cell imaging method, which measures the 3D refractive index distribution inside the cell in actual time, noninvasively and with out the addition of fluorophores, a fluorescent chemical compound utilized in microscopy to boost visuals.
The researchers wished to check whether or not the frequent assumption of “smaller kills sooner” rang true for various shapes of gold nanoparticles. With the Nanolive 3D CX-A holotomographic microscope, they had been in a position to visualize particular cell compartments and nanoparticle accumulation websites with little to no phototoxicity.
“Not like different high-resolution microscopy strategies, holotomography doesn’t require the preparation of samples or the introduction of any international substances into the cells,” stated research creator Joanna Depciuch-Czarny, Institute of Nuclear Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences, in a press launch accompanying the analysis. “The interactions of gold nanoparticles with most cancers cells might due to this fact be noticed instantly within the incubator, the place the latter had been cultured, in an undisturbed surroundings, what’s extra with nanometric decision, from all sides concurrently and virtually in actual time.”
Making a mannequin
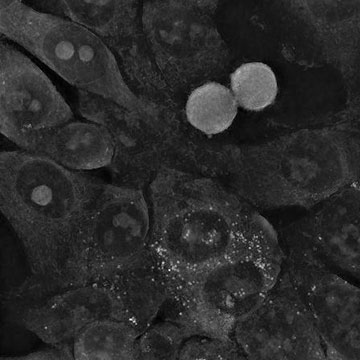
Interplay with small spherical gold nanoparticles didn’t change the morphology of colon most cancers cells, and the cells are nonetheless in a position to divide. [Image: IFJ PAN]
Depciuch-Czarny and her colleagues synthesized three forms of gold nanoparticles: sphere-like shapes with a mean measurement of 10 nm, star-like shapes with a mean measurement of 244 nm and rod-like shapes that measured roughly 45 nm × 10 nm. Experiments concerned culturing the nanoparticles with two totally different glioblastoma cell strains and one colon most cancers cell line with pictures taken after 10, 180 and 285 minutes.
Whereas the smaller spherical nanoparticles simply entered the most cancers cells, the cells had been in a position to get well and maintain dividing. The bigger star-shaped nanoparticles punctured membranes as they aggregated contained in the cell, inflicting irreparable injury and finally resulting in apoptosis. Primarily based on these knowledge, the researchers constructed a theoretical mannequin of the absorption dynamics of gold nanoparticles by cells.
“The ultimate result’s a differential equation into which suitably processed parameters will be substituted―in the meanwhile solely describing the form and measurement of nanoparticles―to shortly decide how the uptake of the analyzed particles by most cancers cells will proceed over a given time frame,” says research creator Pawel Jakubczyk on the College of Rzeszow. “Any scientist can already use our mannequin on the design stage of their very own analysis to immediately slim down the variety of nanoparticle variants requiring experimental verification.”

